216x Filetype XLSX File size 0.07 MB Source: www.oregon.gov
Sheet 1: IIA IPPF summary
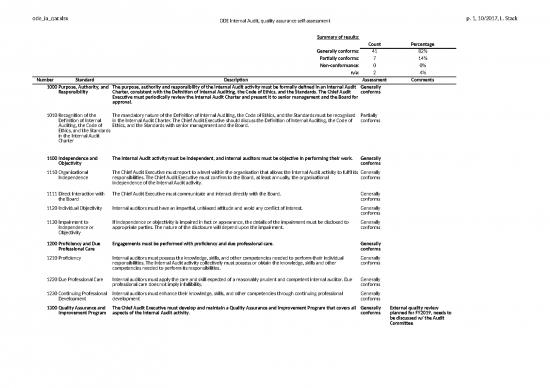
| Summary of results: | |||||
| Count | Percentage | ||||
| Generally conforms: | 41 | 82% | |||
| Partially conforms: | 7 | 14% | |||
| Non-conformance: | 0 | 0% | |||
| n/a: | 2 | 4% | |||
| Number | Standard | Description | Assessment | Comments | |
| 1000 | Purpose, Authority, and Responsibility | The purpose, authority and responsibility of the Internal Audit activity must be formally defined in an Internal Audit Charter, consistent with the Definition of Internal Auditing, the Code of Ethics, and the Standards. The Chief Audit Executive must periodically review the Internal Audit Charter and present it to senior management and the Board for approval. | Generally conforms | ||
| 1010 | Recognition of the Definition of Internal Auditing, the Code of Ethics, and the Standards in the Internal Audit Charter | The mandatory nature of the Definition of Internal Auditing, the Code of Ethics, and the Standards must be recognised in the Internal Audit Charter. The Chief Audit Executive should discuss the Definition of Internal Auditing, the Code of Ethics, and the Standards with senior management and the Board. | Partially conforms | ||
| 1100 | Independence and Objectivity | The Internal Audit activity must be independent, and internal auditors must be objective in performing their work. | Generally conforms | ||
| 1110 | Organisational Independence | The Chief Audit Executive must report to a level within the organisation that allows the Internal Audit activity to fulfil its responsibilities. The Chief Audit Executive must confirm to the Board, at least annually, the organisational independence of the Internal Audit activity. | Generally conforms | ||
| 1111 | Direct Interaction with the Board | The Chief Audit Executive must communicate and interact directly with the Board. | Generally conforms | ||
| 1120 | Individual Objectivity | Internal auditors must have an impartial, unbiased attitude and avoid any conflict of interest. | Generally conforms | ||
| 1130 | Impairment to Independence or Objectivity | If independence or objectivity is impaired in fact or appearance, the details of the impairment must be disclosed to appropriate parties. The nature of the disclosure will depend upon the impairment. | Generally conforms | ||
| 1200 | Proficiency and Due Professional Care | Engagements must be performed with proficiency and due professional care. | Generally conforms | ||
| 1210 | Proficiency | Internal auditors must possess the knowledge, skills, and other competencies needed to perform their individual responsibilities. The Internal Audit activity collectively must possess or obtain the knowledge, skills and other competencies needed to perform its responsibilities. | Generally conforms | ||
| 1220 | Due Professional Care | Internal auditors must apply the care and skill expected of a reasonably prudent and competent internal auditor. Due professional care does not imply infallibility. | Generally conforms | ||
| 1230 | Continuing Professional Development | Internal auditors must enhance their knowledge, skills, and other competencies through continuing professional development | Generally conforms | ||
| 1300 | Quality Assurance and Improvement Program | The Chief Audit Executive must develop and maintain a Quality Assurance and Improvement Program that covers all aspects of the Internal Audit activity. | Generally conforms | External quality review planned for FY2019, needs to be discussed w/ the Audit Committee | |
| 1310 | Requirements of the Quality Assurance and Improvement Program | The Quality Assurance and Improvement Program must include both internal and external assessments. | Generally conforms | ||
| 1311 | Internal Assessments | Internal assessments must include: • Ongoing monitoring of the performance of the Internal Audit activity; and • Periodic self–assessments or assessments by other persons within the organisation with sufficient knowledge of internal audit practices. |
Partially conforms | It would be good for a small team of ODE employees could do an assessment during the current fiscal year. | |
| 1312 | External Assessments | External assessments must be conducted at least once every five years by a qualified, independent assessor or assessment team from outside the organisation. The Chief Audit Executive must discuss with the Board: • The form and frequency of external assessment; and • The qualifications and independence of the external assessor or assessment team, including any potential conflict of interest. |
Generally conforms | I'm thinking it would be nice to have this done during FY2019. Would occur via reciprocity with at least two other agencies. There may be some budget impact for ODE, as I'd like to obtain formal training from the IIA. | |
| 1320 | Reporting on the Quality Assurance and Improvement Program | The Chief Audit Executive must communicate the results of the Quality Assurance and Improvement Program to senior management and the Board. | Generally conforms | This schedule accomplishes this. | |
| 1321 | Use of “Conforms with the International Standards for the Professional Practice of Internal Auditing” | The Chief Audit Executive may state that the Internal Audit activity conforms with the International Standards for the Professional Practice of Internal Auditing only if the results of the Quality Assurance and Improvement Program support this statement. | Partially conforms | I've been using this statement, with a qualification about the external QAR not having been performed. | |
| 1322 | Disclosure of Non-conformance | When non–conformance with the Definition of Internal Auditing, the Code of Ethics, or the Standards impacts the overall scope or operation of the Internal Audit activity, the Chief Audit Executive must disclose the non–conformance and the impact to senior management and the Board. | Generally conforms | ||
| 2000 | Managing the Internal Audit Activity | The Chief Audit Executive must effectively manage the Internal Audit activity to ensure it adds value to the organisation. | Generally conforms | ||
| 2010 | Planning | The Chief Audit Executive must establish a risk–based plan to determine the priorities of the Internal Audit activity, consistent with the organisation’s goals. | Generally conforms | ||
| 2020 | Commnications and Approval | The Chief Audit Executive must communicate the Internal Audit activity’s plans and resource requirements, including significant interim changes, to senior management and the Board for review and approval. The Chief Audit Executive must also communicate the impact of resource limitations. | Generally conforms | ||
| 2030 | Resource Management | The Chief Audit Executive must ensure that Internal Audit resources are appropriate, sufficient, and effectively deployed to achieve the approved plan. | Generally conforms | ||
| 2040 | Policies and Procedures | The Chief Audit Executive must establish policies and procedures to guide the Internal Audit activity. | Generally conforms | But no formal policy/procedure manual | |
| 2050 | Co-ordination | The Chief Audit Executive should share information and co–ordinate activities with other internal and external providers of assurance and consulting services to ensure proper coverage and minimise duplication of efforts. | Generally conforms | ||
| 2060 | Reporting to the Board and Senior Management | The Chief Audit Executive must report periodically to senior management and the Board on the Internal Audit activity’s purpose, authority, responsibility, and performance relative to its plan. Reporting must also include significant risk exposures and control issues, including fraud risks, governance issues, and other matters needed or requested by senior management and the Board. | Partially conforms | Haven't made a formal report to senior management. | |
| 2070 | External Service Provider and Organisational Responsibility for Internal Auditing | When an external service provider serves as the Internal Audit activity, the provider must make the organisation aware that the organisation has the responsibility for maintaining an effective Internal Audit activity. | n/a | ||
| 2100 | Nature of Work | The Internal Audit activity must evaluate and contribute to the improvement of governance, risk management, and control processes using a systematic and disciplined approach. | Generally conforms | ||
| 2110 | Governance | The Internal Audit activity must assess and make appropriate recommendations for improving the governance process in its accomplishment of the following objectives: • Promoting appropriate ethics and values within the organisation; • Ensuring effective organisational performance management and accountability; • Communicating risk and control information to appropriate areas of the organisation; and • Co–ordinating the activities of and communicating information among the Board, external and internal auditors, and management. |
Partially conforms | Little explicit work on the first two bullet points | |
| 2120 | Risk Management | The Internal Audit activity must evaluate the effectiveness and contribute to the improvement of risk management processes | Partially conforms | ||
| 2130 | Control | The Internal Audit activity must assist the organisation in maintaining effective controls by evaluating their effectiveness and efficiency and by promoting continuous improvement. | Generally conforms | ||
| 2200 | Engagement Planning | Internal auditors must develop and document a plan for each engagement, including the engagement’s objectives, scope, timing and resource allocations. | Generally conforms | ||
| 2201 | Planning Considerations | In planning the engagement, internal auditors must consider: • The objectives of the activity being reviewed and the means by which the activity controls its performance; • The significant risks to the activity, its objectives, resources, and operations and the means by which the potential impact of risk is kept to an acceptable level; • The adequacy and effectiveness of the activity’s governance, risk management and control processes compared to a relevant control framework or model; and • The opportunities for making significant improvements to the activity’s governance, risk management and control processes. |
Generally conforms | ||
| 2210 | Engagement Objectives | Objectives must be established for each engagement. | Generally conforms | ||
| 2220 | Engagement Scope | The established scope must be sufficient to achieve the objectives of the engagement. | Generally conforms | ||
| 2230 | Engagement Resource Allocation | Internal auditors must determine appropriate and sufficient resources to achieve engagement objectives based on an evaluation of the nature and complexity of each engagement, time constraints, and available resources. | Generally conforms | ||
| 2240 | Engagement Work Program | Internal Auditors must develop and document work programs that achieve the engagement objectives. | Partially conforms | Need to be more disciplined about creating audit procedures. | |
| 2300 | Performing the Engagement | Internal Auditors must identify, analyse, evaluate, and document sufficient information to achieve the engagement’s objectives. | Generally conforms | ||
| 2310 | Identifying Information | Internal auditors must identify sufficient, reliable, relevant and useful information to achieve the engagement’s objectives. | Generally conforms | ||
| 2320 | Analyses and Evaluation | Internal auditors must base conclusions and engagement results on appropriate analyses and evaluations. | Generally conforms | ||
| 2330 | Documenting Information | Internal auditors must document relevant information to support the conclusions and engagement results. | Generally conforms | ||
| 2340 | Engagement Supervision | Engagements must be properly supervised to ensure objectives are achieved, quality is assured, and staff is developed. | n/a | ||
| 2400 | Communicating Results | Internal auditors must communicate the results of engagements. | Generally Conforms | ||
| 2410 | Criteria for Communicating | Communications must include the engagement’s objectives and scope as well as applicable conclusions, recommendations, and action plans. | Generally conforms | ||
| 2420 | Quality of Communications | Communications must be accurate, objective, clear, concise, constructive, complete, and timely. | Generally conforms | ||
| 2430 | Use of “Conducted in Conformance with the International Standards for the Professional Practice of Internal Auditing” | Internal auditors may report that their engagements are “conducted in conformance with the International Standards for the Professional Practice of Internal Auditing” only if the results of the Quality Assurance and Improvement Program support the statement. | Generally conforms | ||
| 2431 | Engagement Disclosure of Non– conformance | When non–conformance with the Definition of Internal Auditing, the Code of Ethics or the Standards impacts a specific engagement, communication of the results must disclose the: • Principle or rule of conduct of the Code of Ethics or Standard(s) with which full conformance was not achieved; • Reason(s) for non–conformance; and • Impact of non–conformance on the engagement and the communicated engagement results. |
Generally conforms | ||
| 2440 | Disseminating Results | The Chief Audit Executive must communicate results to the appropriate parties. | Generally conforms | ||
| 2450 | Overall Opinions | When an overall opinion is issued, it must take into account the expectations of senior management, the Board, and other stakeholders and must be supported by sufficient, reliable, relevant, and useful information. | Generally conforms | ||
| 2500 | Monitoring Progress | The Chief Audit Executive must establish and maintain a system to monitor the disposition of results communicated to management. | Generally conforms | ||
| 2600 | Communicating the Acceptance of Risks | When the Chief Audit Executive believes that senior management has accepted a level of residual risk that may be unacceptable to the organisation, the Chief Audit Executive must discuss the matter with senior management. If the Chief Audit Executive determines that the matter has not been resolved, the Chief Audit Executive must communicate the matter to the Board. | Generally conforms | ||
| Outcome of the Internal Assessment | |||||
| Outcome of the Internal Assessment: | (Reflect whether the Internal Audit activity is in conformance with the Standards Highlight strengths and weaknesses) Generally ODE's program of internal audit is in compliance with Audit Standards promulgated by the Institute of Internal Auditors (i.e. Red Book). Improvements should be made in drafting formal audit procedures ofr audit engagements, and in assessing and communicating agency-wide risk management. |
||||
| Summary of partial conformances or non-conformances: | |||||
| Number | Standard | Description | Assessment | Action Plan | |
| 1010 | Recognition of the Definition of Internal Auditing, the Code of Ethics, and the Standards in the Internal Audit Charter | The mandatory nature of the Definition of Internal Auditing, the Code of Ethics, and the Standards must be recognised in the Internal Audit Charter. The Chief Audit Executive should discuss the Definition of Internal Auditing, the Code of Ethics, and the Standards with senior management and the Board. | Partially conforms | The IA Charter should be modified to reflect this standard. | |
| 1311 | Internal Assessments | Internal assessments must include: • Ongoing monitoring of the performance of the Internal Audit activity; and • Periodic self–assessments or assessments by other persons within the organisation with sufficient knowledge of internal audit practices. |
Partially conforms | It would be good for a small team of ODE employees could do an assessment during the current fiscal year. | |
| 1321 | Use of “Conforms with the International Standards for the Professional Practice of Internal Auditing” | The Chief Audit Executive may state that the Internal Audit activity conforms with the International Standards for the Professional Practice of Internal Auditing only if the results of the Quality Assurance and Improvement Program support this statement. | Partially conforms | I've been using this statement, with a qualification about the external QAR not having been performed. | |
| 2060 | Reporting to the Board and Senior Management | The Chief Audit Executive must report periodically to senior management and the Board on the Internal Audit activity’s purpose, authority, responsibility, and performance relative to its plan. Reporting must also include significant risk exposures and control issues, including fraud risks, governance issues, and other matters needed or requested by senior management and the Board. | Partially conforms | Haven't made a formal report to senior management. | |
| 2110 | Governance | The Internal Audit activity must assess and make appropriate recommendations for improving the governance process in its accomplishment of the following objectives: • Promoting appropriate ethics and values within the organisation; • Ensuring effective organisational performance management and accountability; • Communicating risk and control information to appropriate areas of the organisation; and • Co–ordinating the activities of and communicating information among the Board, external and internal auditors, and management. |
Partially conforms | Little explicit work on the first two bullet points | |
| 2120 | Risk Management | The Internal Audit activity must evaluate the effectiveness and contribute to the improvement of risk management processes | Partially conforms | ||
| 2240 | Engagement Work Program | Internal Auditors must develop and document work programs that achieve the engagement objectives. | Partially conforms | Need to be more disciplined about creating audit procedures. | |
| Definition of Assessment categories: | |||||
| Generally Conforms | Means the assessor has concluded that the relevant structures, policies, and procedures of the activity, as well as the processes by which they are applied, comply with the requirements of the individual Standard or element of the Code of Ethics in all material respects. For the sections and major categories, this means that there is general conformity to a majority of the individual Standards or elements of the Code of Ethics, and partial conformity to the others, within the section/category. There may be significant opportunities for improvement, but these should not represent situations where the activity has not implemented the Standards or the Code of Ethics, is not applying them effectively, or is not achieving their stated objectives. | ||||
| Partially Conforms | Means the assessor has concluded that the activity is making good–faith efforts to comply with the requirements of the individual Standard or element of the Code of Ethics, section and major category, but has fallen short of achieving some of the major objectives. This will usually represent some significant opportunities for improvement in effectively applying the Standards or Code of Ethics and/or achieving their objectives. Some of the deficiencies may be beyond the control of the activity and may result in recommendations to senior management or the Board of the organisation. | ||||
| Does Not Conform | Means the assessor has concluded that the activity is not aware of, is not making good–faith efforts to comply with, or is failing to achieve many/all of the objectives of the individual Standard or element of the Code of Ethics, section and major category. These deficiencies will usually have a significant negative effect on the activity’s effectiveness and its potential to add value to the organisation. They may also represent significant opportunities for improvement, including actions by senior management or the Board. |
| 16 | Number of Best Practices: | 118 | ||||||||||
| 27 | Number of Headings: | 36 | ||||||||||
| 1 | Percentage of Priority 1s: (58) | 49% | ||||||||||
| Percentage of Priority 2s: (44) | 37% | |||||||||||
| Percentage of Priority 3s: (13) | 11% | In Place? | Maturity level @ 12/31/17 | % | ||||||||
| Percentage n/a: (3) | 3% | 12/31/17 | 6/30/18 | 6/30/19 | 4 | 4% | ||||||
| Percentage in-place: (56) | 47% | 68% | 93% | 3 | 9% | |||||||
| Percentage not in-place: (59) | 50% | 29% | 3% | 2 | 25% | |||||||
| Percentage n/a: (3) | 3% | 3% | 3% | 1 | 57% | |||||||
| In Place (1/0)? | ||||||||||||
| Order | Standard | Headings | Best Practice | Priority? | 12/31/17 | 6/30/18 | 6/30/19 | Comments | Capability Maturity | |||
| 1 | Internal Audit Foundations | |||||||||||
| 2 | Standards 1000, 1010, 1100, 1110, 1111, 1120, 1130, 1300, 1310, 1320, 1321, 1322, 2000, 2040 | |||||||||||
| 3 | There is an Internal Audit Charter in place | |||||||||||
| 4 | Internal Audit Charter is in place | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | ||||||
| 5 | Internal Audit Charter follows the main characteristics of a suitable ‘model’ charter. In the public sector it may be a model provided by an Auditor–General, in the private sector it may be a version from the IIA | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 | ||||||
| 6 | Internal Audit Charter contains purpose, authority, responsibility, definition of internal auditing, reference to IIA Code of Ethics, reference to IIA Standards, independence, objectivity, organisational independence, direct interaction with the Audit Committee, reporting and communication arrangements, nature of work to be performed, records management, conflicts of interest, performance assessment, Quality Assurance and Improvement Program, requirement for annual review, approval by Audit Committee | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 3 | ||||||
| 7 | Organisation chart shows reporting arrangements for Internal Audit | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 | ||||||
| 8 | The Internal Audit Charter is reviewed annually to assure it remains effective and in line with best practice | |||||||||||
| 9 | Annual review of Internal Audit Charter | 3 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 10 | Documentation to indicate the content and structure of the Internal Audit Charter has been reviewed and assessed against a best practice model | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 11 | The Internal Audit Charter complements the mandate of the Audit Committee and assurance is available that the Audit Committee has been structured to accord with contemporary best practice and statutory or regulatory requirements | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 12 | Changes to Internal Audit Charter approved by Audit Committee | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 | ||||||
| 13 | There are no conflicts of interest that will affect the individual objectivity of Internal Audit employees or service providers | |||||||||||
| 14 | Internal Audit employees have no conflicts of interest, for example conflict of interest declaration for internal audit engagements, annual conflict of interest attestation | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 | ||||||
| 15 | Conflicts of interest are reported to the Audit Committee | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 | ||||||
| 16 | ||||||||||||
| 17 | There is no impairment to Internal Audit independence or objectivity | |||||||||||
| 18 | Chief Audit Executive can demonstrate there is no impairment to independence or objectivity such as conflicts of interest, scope limitations, restrictions on access to records or personnel, funding or resource limitations | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | ||||||
| 19 | Chief Audit Executive makes impairment attestation to the Audit Committee annually | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 20 | The organisation structure and Internal Audit Charter arrangements should both illustrate the reporting lines for the Chief Audit Executive are appropriate and strengthen the independence and objectivity of Internal Audit. The Audit Committee should be required to be involved in hiring, firing, and remuneration decisions concerning the Chief Audit Executive; review and endorse the scope and budget of Internal Audit on the recommendation of the Chief Audit Executive; consider the outcomes of all internal audit engagements reported; meet periodically ‘in camera’ with the Chief Audit Executive | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 3 | ||||||
| 21 | There is a Quality Assurance and Improvement Program in place | |||||||||||
| 22 | There is a comprehensive documented Quality Assurance and Improvement Program in place | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | ||||||
| 23 | The Quality Assurance and Improvement Program is measured, monitored and reported | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 24 | There is effective management of Internal Audit so it adds value to the organisation | |||||||||||
| 25 | Stakeholder Relationship Program is in place, monitored, reviewed and up–to–date | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | ||||||
| 26 | A Balanced Scorecard Report approach is in place and reports are provided periodically to senior management and the Audit Committee | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 27 | Results of management feedback surveys after each internal audit engagement and annual feedback which flows into Balanced Scorecard Report | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 28 | Results of Internal Assessments | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 29 | Results of External Assessments | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | |||||||
| 30 | An Action Plan is available to address any issues arising from Internal Assessments and External Assessments, action is taken, and progress is reported periodically to senior management and the Audit Committee | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 31 | ||||||||||||
| 32 | There is an up–to–date Internal Audit Manual of policies and procedures | |||||||||||
| 33 | There is a documented and up–to–date Internal Audit Manual of policies and procedures | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 34 | The Internal Audit Manual has been approved by the Chief Audit Executive and the Audit Committee | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 35 | The content of the Internal Audit Manual is reasonable, complete and consistent with the IIA Standards | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 36 | Internal Audit employees and service providers consistently use the Internal Audit Manual | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 37 | Internal Audit employees and service providers have been inducted and trained in its use | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 38 | ||||||||||||
| 39 | Professional Development | |||||||||||
| 40 | Standards 1200, 1210, 1220, 1230 | |||||||||||
| 41 | Internal Audit employees and service providers are professionally qualified | |||||||||||
| 42 | Internal Audit employees have relevant professional qualifications | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | ||||||
| 43 | Internal Audit employees have relevant professional certifications | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | ||||||
| 44 | Internal Audit operates at a consistently high standard, with membership of the IIA recognised as the minimum requirement for practicing Internal Auditors | 2 | 1 | 1 | 3 | |||||||
| 45 | The Chief Audit Executive and anyone issuing internal audit reports should be required to be IIA–certified | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | ||||||
| 46 | An employees Profile is developed and reviewed annually, including the experience, qualifications, certifications, and years of auditing experience | 3 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 47 | The Staff Profile is reported to the Audit Committee as part of periodic performance reporting | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 48 | There is a performance management process for Internal Audit employees that includes a Professional Development Plan for each employee | |||||||||||
| 49 | An Internal Audit Capability Framework has been developed that drives recruitment planning, training and development activities, and job design. It should be consistent with the IIA Global Internal Audit Competency Framework | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 50 | There is a Job Description for each Internal Audit job consistent with the above mentioned job design approach | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 51 | There is a documented career development path for Internal Audit employees | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | ||||||
| 52 | There is a performance management process in place for Internal Audit employees that is linked to Job Descriptions and Internal Audit business objectives | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | ||||||
| 53 | There is a high–level Professional Development Plan in place covering Internal Audit | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | ||||||
| 54 | Internal Audit employees have an individual professional development plan linked to the high–level Professional Development Plan | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 55 | There are professional development opportunities for Internal Audit employees | |||||||||||
| 56 | Internal Audit employees have opportunities and funding for professional development | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | ||||||
| 57 | Internal Audit employees receive sufficient opportunities and funding to participate in appropriate professional development activities each year to maintain professional certifications | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | ||||||
| 58 | Internal Audit employees are encouraged to participate in the activities of relevant professional bodies | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | ||||||
| 59 | Internal Audit employees are trained so they can effectively perform their jobs | |||||||||||
| 60 | Internal Audit employees receive training in Internal Audit methodology and use of technology tools | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 61 | Induction training is provided on initial recruitment of Internal Audit employees and service providers, with periodic refresher training provided and completed | 3 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 62 | ||||||||||||
| 63 | Internal Audit Planning | |||||||||||
| 64 | Standards 2010, 2020, 2030, 2050, 2100, 2110, 2120, 2130 | |||||||||||
| 65 | The division of effort amongst Internal Audit, external audit, and other governance functions is minimised | |||||||||||
| 66 | Co–ordination and division of assurance effort between Internal Audit, external audit, and other internal governance and assurance functions | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 67 | Internal Audit has championed and / or documented a suitable ‘3 Lines of Defence’ model | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 68 | The nature of Internal Audit work is designed to evaluate and contribute to improvement of governance, risk management and control processes using a systematic and disciplined approach | |||||||||||
| 69 | Internal Audit Charter, Job Descriptions, methodology and Internal Audit Plan demonstrate Internal Audit contributes to management improvement of governance, risk management and control processes | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | ||||||
| 70 | Internal Audit has used a suitable model and structured approach within the last 2 to 3 years to assess the organisation governance arrangements | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | Candidate? | 1 | |||||
| 71 | Internal audit planning is linked to organisation strategic objectives and risks | |||||||||||
| 72 | Internal Audit conducts an annual Risk Assessment to support its risk–based planning, or leverages the Enterprise Risk Management resources and documentation where the organisation has reached an appropriate level of risk management maturity | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | ||||||
| 73 | There is an Assurance Map that is reviewed and updated at least annually | 2 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||
| 74 | There is a comprehensive risk–based Audit Universe that is reviewed and updated at least annually | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | ||||||
| 75 | The Internal Audit Plan links proposed internal audit engagements to the organisation strategic objectives, statutory objectives, risks and business drivers | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 76 | There is input from management to development of the Internal Audit Plan via interviews, workshops, questionnaires, and Enterprise Risk Management resources | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | ||||||
| 77 | The Internal Audit Plan is effectively structured | |||||||||||
| 78 | The Internal Audit Plan takes into account various audit types, Audit Committee input, provision for future management initiated requests, and follow–up of previous higher risk reports and recommendations | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | ||||||
| 79 | The Internal Audit Plan reconciles available resources with the resources required to complete the plan, and shows the limit of internal audit work that can be completed with the available resources. Higher risk areas which cannot be audited because resources are not available are highlighted to the Audit Committee | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | ||||||
| 80 | There is a well–defined process for assessing, actioning and approving management initiated requests | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 81 | Multi–Stage Audits are included, especially for programs and projects | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | e.g. A/P audits | 2 | |||||
| 82 | The Internal Audit Plan is approved by the Audit Committee, including changes to the Internal Audit Plan | |||||||||||
| 83 | The Internal Audit Plan and any changes are approved by the Audit Committee | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | ||||||
| 84 | A documented process is in place to flexibly interchange risk–based internal audit work as the level of risk changes or new higher level risks emerge | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | ||||||
| 85 | The interchange of internal audit work continues to reflect the limit of available resources | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | ||||||
| 86 | Internal Audit has adequate resources to be effective and to complete its Internal Audit Plan | |||||||||||
| 87 | Internal Audit has adequate resources that are appropriate, sufficient and effectively deployed to achieve the Internal Audit Plan | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 88 | The financial budget for Internal Audit is reviewed and endorsed by the Audit Committee | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 89 | There is scope in the Audit Committee Charter for the Audit Committee to engage with the Chief Executive Officer about the resources required to complete the Internal Audit Plan | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | ||||||
| 90 | ||||||||||||
| 91 | Internal Audit Engagements | |||||||||||
| 92 | Standards 2070, 2200, 2201, 2210, 2220, 2230, 2240, 2300, 2310, 2320, 2330, 2340 | |||||||||||
| 93 | There is a scheduling process and resource allocation for internal audit engagements | |||||||||||
| 94 | There is a documented and up–to–date Internal Audit Manual of policies and procedures | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 95 | There is an approved Internal Audit Plan that details Internal Audit work and estimated resource allocation | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | ||||||
| 96 | There is a schedule for internal audit work to be conducted over the period of the Internal Audit Plan | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | ||||||
| 97 | There is adequate planning for each internal audit engagement | |||||||||||
| 98 | There is adequate planning for each internal audit engagement including audit objectives, scope, timing, risks, resources, audit team, timeframes, stakeholder engagement, and audit work schedule and milestones | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 99 | There is a systematic and disciplined process followed for each internal audit engagement | |||||||||||
| 100 | There is a systematic and disciplined process that is planned, documented and followed for each internal audit engagement. This covers performing the engagement through identifying, analysing and evaluating information, then documenting the related observations and finding | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 101 | The work performed for each internal audit engagement aligns to the approved audit objectives, as does the audit report containing the overall audit opinion, observations, findings and recommendations | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 102 | There is adequate supervision and quality review of internal audit engagements to assure conformance with Internal Audit methodology and standards | |||||||||||
| 103 | There is a consistent methodology established and used for performing internal audit engagements and preparing the associated working papers | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | ||||||
| 104 | Internal Audit employees and service providers have been trained in use of the methodology | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | ||||||
| 105 | Each internal audit engagement is allocated to an Audit Manager to supervise completion of the audit and ensure quality of the audit | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | ||||||
| 106 | There is consideration for use of IT tools such as data extraction and computer aided analysis techniques and applications (CAATs) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | ||||||
| 107 | There is a formal quality review process performed for internal audit engagements | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | ||||||
| 108 | The Chief Audit Executive or a senior delegate attends the audit opening meeting and closing meeting for each internal audit engagement | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||
| 109 | Internal audit reports are reviewed and signed–off by the Chief Audit Executive | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | ||||||
| 110 | If the Chief Audit Executive is not IIA–certified, the report will be counter–signed by an IIA–certified senior Internal Audit employee | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | |||||
| 111 | Adequate confidentiality and security arrangements are in place, documented and maintained for all working papers including electronic data obtained during audits | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | ||||||
| 112 | There is regular, documented review of working papers during internal audit engagements | |||||||||||
| 113 | There is a consistent and documented methodology for conducting internal audit engagements and preparing working papers | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 114 | There is a formal quality process for internal audit engagements that includes sign–offs at key stages or milestones of each audit | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 115 | There is adequate control of service providers who perform internal audit engagements and other audit–related services | |||||||||||
| 116 | Requirements for internal audit engagements performed in–house also apply to service providers | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 117 | Service providers have performance measures that are monitored and periodically reported in conjunction with Internal Audit performance reporting | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | ||||||
| 118 | Internal Audit reviews and retains working papers prepared by service providers | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 119 | Adequate documented confidentiality and security arrangements are in place for all service provider engagements, with periodic assertions (at least annually) from the service provider that these arrangements are being maintained | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 120 | Service providers provide evidence of security clearances for their personnel relative to the security level required for each internal audit engagemen | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 121 | ||||||||||||
| 122 | Reporting | |||||||||||
| 123 | Standards 2070, 2200, 2201, 2210, 2220, 2230, 2240, 2300, 2310, 2320, 2330, 2340 | |||||||||||
| 124 | Internal audit engagement reports are distributed to management and the Audit Committee | |||||||||||
| 125 | Internal audit engagement reports are distributed to management and the Audit Committee in a timely way | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | ||||||
| 126 | An assessment has been completed to ensure the Audit Committee is satisfied with the style, structure, timing, reliability and content of internal audit reports | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 127 | High–level planning and reporting is conducted to identify reflect ‘audit themes’ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 128 | Internal Audit monitors and reports on progress and completion of higher risk audit findings and associated recommendations | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 129 | Periodic reports on Internal Audit operations are provided to the Audit Committee | |||||||||||
| 130 | Internal Audit operations and the Internal Audit Charter are reviewed annually | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 131 | Periodic reports on Internal Audit operations are distributed to the Audit Committee that include the Internal Audit purpose, authority, responsibility, performance, significant risk exposures and control issues that include fraud risks, governance, and other matters needed or requested by management and the Audit Committee | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 132 | A Balanced Scorecard Report is provided to the Audit Committee regularly | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 133 | An Internal Audit Annual Report on operations and performance is provided to the Audit Committee to demonstrate the Internal Audit contribution to the organisation | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | ||||||
| 134 | The Internal Audit Annual Report should be provided to the Chief Executive Officer through the Chair of the Audit Committee | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | ||||||
| 135 | Results of Internal Assessments are distributed to the Audit Committee | |||||||||||
| 136 | Internal Audit senior management sign–off an annual Quality Assurance assertion for each completed internal audit engagement, usually in the form of a post–engagement survey. The results are used in assessing and reporting on Internal Audit performance | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 137 | The Chief Audit Executive and Internal Audit senior management sign–off an annual Quality Assurance assertion that is reported to the Audit Committee and provides explicit assurance Internal Audit has conformed to standards, including how key elements were managed such as independence, restrictions on work, conflicts of interest, errors and omissions, and quality assurance and improvement | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | ||||||
| 138 | Timely distribution of Internal Assessments to the Audit Committee | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | ||||||
| 139 | Results of External Assessments are distributed to the Audit Committee | |||||||||||
| 140 | External Assessments are distributed to the Audit Committee in a timely way | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 141 | Results of Internal Audit performance measures are reported to the Audit Committee | |||||||||||
| 142 | Surveys are distributed and reviewed on return to assess the level of satisfaction key stakeholder groups have with Internal Audit. This includes the Audit Committee, senior management, audit clients after internal audit engagements, and Internal Audit employees | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 143 | Results of Internal Audit performance measures regularly reported to the Audit Committee | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 144 | Monitoring and Follow-up | |||||||||||
| 145 | Standard 2500 | |||||||||||
| 146 | There is a follow–up system in place for internal audit recommendations and action plans to assure they are implemented in a timely way, including external audit recommendations | |||||||||||
| 147 | A user–friendly audit recommendation follow–up system is in place that is regularly reviewed and updated with management comments and evidence of remedial action | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 148 | Progress on implementation of recommendations and action plans is regularly reported to the Audit Committee | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | ||||||
| 149 | There is risk–based follow–up of internal audit recommendations and action plans to evidence they have been effectively implemented | |||||||||||
| 150 | There is periodic follow–up assurance of implementation of internal audit recommendations and management action plans, with follow–up action reported to the Audit Committee | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 151 | Progress of management actions to remediate higher risk audit recommendations are reviewed by the Audit Committee to ensure it remains aware of the status of high risk and long–overdue recommendations | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 152 | ||||||||||||
| 153 | Performance and Process Improvement | |||||||||||
| 154 | Standard 1300 | |||||||||||
| 155 | There are performance measures in place for Internal Audit | |||||||||||
| 156 | Internal Audit performance measures are approved by the Audit Committee and included in the Internal Audit Charter | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 157 | Internal Audit performance is monitored and reviewed against target performance measures | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 158 | Periodically the Chief Audit Executive undertakes benchmarking of the Internal Audit, for example against leading practices such as the IIA–Australia Policy Agenda or an Internal Audit Maturity Assessment | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 159 | Benchmarking results are reported to the Audit Committee, together with action plans for improvement | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 160 | There is a management feedback survey distributed after each internal audit engagement | |||||||||||
| 161 | Internal Audit performance ratings are monitored and reviewed against target performance measures in the Internal Audit Charter | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 162 | Information received from management feedback surveys is used to improve services and performance of Internal Audit | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 163 | There is an annual management feedback survey distributed each year | |||||||||||
| 164 | Internal Audit performance ratings are monitored and reviewed against target performance measures in the Internal Audit Charter | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 165 | ||||||||||||
| 166 | Internal Assessments and External Assessments | |||||||||||
| 167 | Standards 1311, 1312 | |||||||||||
| 168 | There is an annual Internal Assessment performed through self–assessment or by other persons within the organisation with knowledge of internal audit practices and the Standards | |||||||||||
| 169 | An Internal Assessment against the Standards is conducted annually | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | Need to beef-up to the IPPF. | 1 | |||||
| 170 | An Internal Audit Action Plan is developed and implemented to address any partial conformances and non–conformances or opportunities for improvement, with progress periodically reported to the Audit Committee | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 171 | An External Assessment is scheduled at least once every 5 years by a qualified, independent assessor or assessment team from outside the organisation | |||||||||||
| 172 | An External Assessment against the Standards is conducted at least once every 5 years | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | ||||||
| 173 | The terms of reference for the External Assessment are approved by the Audit Committee, together with reporting arrangements | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 174 | An Internal Audit Action Plan is developed and implemented to address any partial conformances and non–conformances or opportunities for improvement, with progress periodically reported to the Audit Committee | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 175 | ||||||||||||
| 176 | Code of Ethics | |||||||||||
| 177 | Principles and Rules of Conduct | |||||||||||
| 178 | The IIA Code of Ethics is included in the induction for Internal Audit employees and service providers | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 179 | Compliance with the IIA Code Ethics is a requirement mandated in the Internal Audit Charter | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | ||||||
| 180 | Internal Audit employees and service providers are obliged to comply with the IIA Code of Ethics through an appropriate means that may include being IIA members and signing an appropriate acknowledgement annually | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | ||||||
| 0% | 74% | 74% | ||||||||||
| In Place (1/0)? | ||||||||||||
| Order | Standard | Headings | Best Practice | Priority? | 6/30/18 | 5/1/19 | 6/30/19 | Comments | Capability Maturity | |||
| 1 | Internal Audit Foundations | |||||||||||
| 2 | Standards 1000, 1010, 1100, 1110, 1111, 1120, 1130, 1300, 1310, 1320, 1321, 1322, 2000, 2040 | |||||||||||
| 3 | There is an Internal Audit Charter in place | |||||||||||
| 6 | Internal Audit Charter contains purpose, authority, responsibility, definition of internal auditing, reference to IIA Code of Ethics, reference to IIA Standards, independence, objectivity, organisational independence, direct interaction with the Audit Committee, reporting and communication arrangements, nature of work to be performed, records management, conflicts of interest, performance assessment, Quality Assurance and Improvement Program, requirement for annual review, approval by Audit Committee | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | done as of 1/22/19 Audit Committee meeting | 3 | |||||
| 8 | The Internal Audit Charter is reviewed annually to assure it remains effective and in line with best practice | |||||||||||
| 9 | Annual review of Internal Audit Charter | 3 | 0 | 1 | 1 | done as of 1/22/19 Audit Committee meeting | 3 | |||||
| 10 | Documentation to indicate the content and structure of the Internal Audit Charter has been reviewed and assessed against a best practice model | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | See Track Changes copy of the last IA charter upate, approved by the AC on 1/22/19 | 3 | |||||
| 17 | There is no impairment to Internal Audit independence or objectivity | |||||||||||
| 20 | The organisation structure and Internal Audit Charter arrangements should both illustrate the reporting lines for the Chief Audit Executive are appropriate and strengthen the independence and objectivity of Internal Audit. The Audit Committee should be required to be involved in hiring, firing, and remuneration decisions concerning the Chief Audit Executive; review and endorse the scope and budget of Internal Audit on the recommendation of the Chief Audit Executive; consider the outcomes of all internal audit engagements reported; meet periodically ‘in camera’ with the Chief Audit Executive | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | done as of 1/22/19 Audit Committee meeting | 3 | |||||
| 21 | There is a Quality Assurance and Improvement Program in place | |||||||||||
| 22 | There is a comprehensive documented Quality Assurance and Improvement Program in place | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | In place as of 5/7/19 | 1 | |||||
| 24 | There is effective management of Internal Audit so it adds value to the organisation | |||||||||||
| 25 | Stakeholder Relationship Program is in place, monitored, reviewed and up–to–date | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | in place as of 1/1/18 | 1 | |||||
| 32 | There is an up–to–date Internal Audit Manual of policies and procedures | |||||||||||
| 33 | There is a documented and up–to–date Internal Audit Manual of policies and procedures | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | In place as of 4/29/19 | 1 | |||||
| 35 | The content of the Internal Audit Manual is reasonable, complete and consistent with the IIA Standards | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | In place as of 4/29/19 | 1 | |||||
| 39 | Professional Development | |||||||||||
| 40 | Standards 1200, 1210, 1220, 1230 | |||||||||||
| 41 | Internal Audit employees and service providers are professionally qualified | |||||||||||
| 46 | An employees Profile is developed and reviewed annually, including the experience, qualifications, certifications, and years of auditing experience | 3 | n/a | 1 | ||||||||
| 47 | The Staff Profile is reported to the Audit Committee as part of periodic performance reporting | 2 | n/a | 1 | ||||||||
| 59 | Internal Audit employees are trained so they can effectively perform their jobs | |||||||||||
| 61 | Induction training is provided on initial recruitment of Internal Audit employees and service providers, with periodic refresher training provided and completed | 3 | n/a | 1 | ||||||||
| 63 | Internal Audit Planning | |||||||||||
| 64 | Standards 2010, 2020, 2030, 2050, 2100, 2110, 2120, 2130 | |||||||||||
| 67 | Internal Audit has championed and/or documented a suitable ‘3 Lines of Defence’ model | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | ||||||
| 70 | Internal Audit has used a suitable model and structured approach within the last 2 to 3 years to assess the organisation governance arrangements | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 71 | Internal audit planning is linked to organisation strategic objectives and risks | |||||||||||
| 75 | The Internal Audit Plan links proposed internal audit engagements to the organisation strategic objectives, statutory objectives, risks and business drivers | 1 | 0 | 1 | ||||||||
| 77 | The Internal Audit Plan is effectively structured | |||||||||||
| 80 | There is a well–defined process for assessing, actioning and approving management initiated requests | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | in place | 1 | |||||
| 86 | Internal Audit has adequate resources to be effective and to complete its Internal Audit Plan | |||||||||||
| 88 | The financial budget for Internal Audit is reviewed and endorsed by the Audit Committee | 2 | 0 | n/a for governmental organizations | 1 | |||||||
| 91 | Internal Audit Engagements | |||||||||||
| 92 | Standards 2070, 2200, 2201, 2210, 2220, 2230, 2240, 2300, 2310, 2320, 2330, 2340 | |||||||||||
| 93 | There is a scheduling process and resource allocation for internal audit engagements | |||||||||||
| 94 | There is a documented and up–to–date Internal Audit Manual of policies and procedures | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | In place as of 4/29/19 | 1 | |||||
| 112 | There is regular, documented review of working papers during internal audit engagements | |||||||||||
| 114 | There is a formal quality process for internal audit engagements that includes sign–offs at key stages or milestones of each audit | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | In place as of 4/29/19 | 1 | |||||
| 129 | Periodic reports on Internal Audit operations are provided to the Audit Committee | |||||||||||
| 130 | Internal Audit operations and the Internal Audit Charter are reviewed annually | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | in place | 1 | |||||
| 131 | Periodic reports on Internal Audit operations are distributed to the Audit Committee that include the Internal Audit purpose, authority, responsibility, performance, significant risk exposures and control issues that include fraud risks, governance, and other matters needed or requested by management and the Audit Committee | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | ||||||
| 135 | Results of Internal Assessments are distributed to the Audit Committee | |||||||||||
| 136 | Internal Audit senior management sign–off an annual Quality Assurance assertion for each completed internal audit engagement, usually in the form of a post–engagement survey. The results are used in assessing and reporting on Internal Audit performance | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | ||||||
| 137 | The Chief Audit Executive and Internal Audit senior management sign–off an annual Quality Assurance assertion that is reported to the Audit Committee and provides explicit assurance Internal Audit has conformed to standards, including how key elements were managed such as independence, restrictions on work, conflicts of interest, errors and omissions, and quality assurance and improvement | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | ||||||
| 144 | Monitoring and Follow-up | |||||||||||
| 145 | Standard 2500 | |||||||||||
| 149 | There is risk–based follow–up of internal audit recommendations and action plans to evidence they have been effectively implemented | |||||||||||
| 151 | Progress of management actions to remediate higher risk audit recommendations are reviewed by the Audit Committee to ensure it remains aware of the status of high risk and long–overdue recommendations | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | ||||||
| 176 | Code of Ethics | |||||||||||
| 177 | Principles and Rules of Conduct | |||||||||||
| 179 | Compliance with the IIA Code Ethics is a requirement mandated in the Internal Audit Charter | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | in place | 2 | |||||
no reviews yet
Please Login to review.