244x Filetype PDF File size 0.19 MB Source: www.pxu.org
HS.E2.3 Use cost-benefit analysis and/or marginal analysis to evaluate an economic issue.
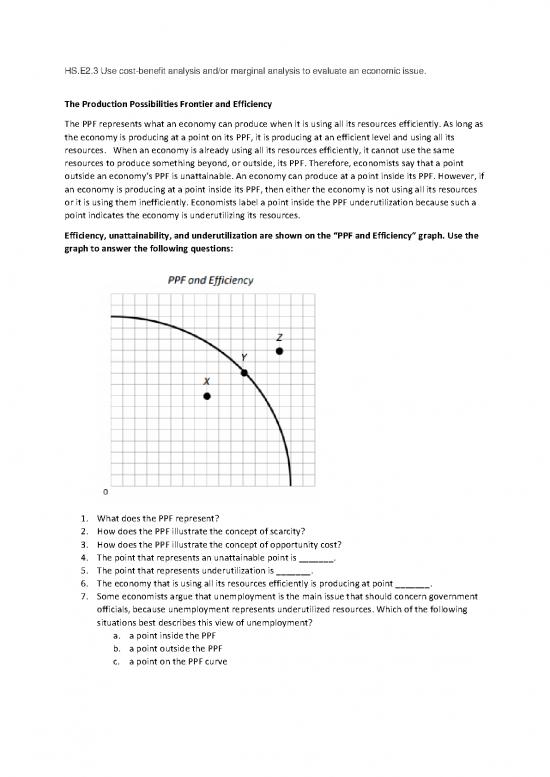
The Production Possibilities Frontier and Efficiency
The PPF represents what an economy can produce when it is using all its resources efficiently. As long as
the economy is producing at a point on its PPF, it is producing at an efficient level and using all its
resources. When an economy is already using all its resources efficiently, it cannot use the same
resources to produce something beyond, or outside, its PPF. Therefore, economists say that a point
outside an economy’s PPF is unattainable. An economy can produce at a point inside its PPF. However, if
an economy is producing at a point inside its PPF, then either the economy is not using all its resources
or it is using them inefficiently. Economists label a point inside the PPF underutilization because such a
point indicates the economy is underutilizing its resources.
Efficiency, unattainability, and underutilization are shown on the “PPF and Efficiency” graph. Use the
graph to answer the following questions:
1. What does the PPF represent?
2. How does the PPF illustrate the concept of scarcity?
3. How does the PPF illustrate the concept of opportunity cost?
4. The point that represents an unattainable point is _______.
5. The point that represents underutilization is _______.
6. The economy that is using all its resources efficiently is producing at point _______.
7. Some economists argue that unemployment is the main issue that should concern government
officials, because unemployment represents underutilized resources. Which of the following
situations best describes this view of unemployment?
a. a point inside the PPF
b. a point outside the PPF
c. a point on the PPF curve
HS.E2.3 Use cost-benefit analysis and/or marginal analysis to evaluate an economic issue.
Shifts in the Production Possibilities Frontier
The location of the PPF for an economy is determined mostly by the amount of resources available and
the level of technology in the society. If more resources become available or the level of technology
increases, more goods and services can be produced and the PPF will shift to the right (outward). If the
amount of resources diminishes, the economy can no longer produce at previous levels and the PPF will
shift to the left (inward).
Directions: Use the “Shifts in the PPF” graph to answer the following questions. Assume that the PPF
begins at the location labeled “C”. Read question the first and determine the direction (left or right) that
the PPF will move from the location C in response to the event described. Then write the letter of the
new location. Then read the next question and determine the direction the PPF will move from the
location you decided on in the first question. Then write the letter of the new location. Continue to
determine the direction and location for each subsequent event.
1. What two things would cause the PPF of an economy to shift to the right (outward)?
2. What would cause the PPF of an economy to shift to the left (inward)?
3. The invention of the light bulb allows laborers to work later hours and introduces the midnight
shift. Direction of Shift: ___________________ New Location of PPF: ______
4. A major drought makes much of America’s farmland unproductive. Direction of Shift:
___________________ New Location of PPF: ______
5. The baby boomer generation starts to retire, and millions leave the workforce. Direction of Shift:
___________________ New Location of PPF: ______
6. The invention of the Internet allows people to communicate and conduct business from
anywhere. Direction of Shift: ___________________ New Location of PPF: ______
7. The government loosens immigration policies, allowing millions of skilled workers to enter the
country. Direction of Shift: ___________________ New Location of PPF: ______
8. The invention of the cell phone allows people to communicate from remote
locations. Direction of Shift: ___________________ New Location of PPF: ______
HS.E2.3 Use cost-benefit analysis and/or marginal analysis to evaluate an economic issue.
Examples:
Student Budget
35
30
30 27
25 24
21
a20 18
Sod 15
15 12
10 9
6
5 3
0
0
0 5 10 15 20 25
Burritos
Scenario 1 - A student has a monthly budget of $120 to spend on either burritos, which cost $6 each, or
sodas, which cost $4 each. The Production Possibilities Graph above illustrates this budget constraint.
1. What is the largest number of burritos that the student could afford to purchase in one
month?
2. What is the largest number of sodas the student could afford to purchase in one month?
3. Which combinations of burritos and sodas are unaffordable--those to the left of the line
in the graph or those above the line in the graph? Why?
4. Which combinations would leave some budget unspent - those to the left of the line in
the above graph or those to the right of the line in the above graph?
5. What is the opportunity cost of a burrito?
6. What is the opportunity cost of a soda?
Scenario 2 - Guns versus Butter
During World War II the American auto industry reduced its production of consumer
automobiles so that more resources could be used for military production in the form of tanks
and airplanes.
Economists often speak of the way a society allocates its resources between military and
consumer production with the metaphor guns versus butter, where guns represents resources
allocated for military use and butter represents resources allocated for consumer use.
Economists often use the phrase “guns OR butter” because scarcity mandates that we choose
how to use the available resources.
HS.E2.3 Use cost-benefit analysis and/or marginal analysis to evaluate an economic issue.
In the example above, as more resources were used for government output (tanks, or “guns”),
fewer resources were allocated for consumer output (automobiles, or “butter”).
(The guns and butter phrase comes from 1916-17 during World War I, when nitrates were used
both in gunpowder and as the key ingredient of chemical fertilizer in farming. The National
Defense Act of 1916 directed “the Secretary of Agriculture to manufacture nitrates for
fertilizers in peace and munitions in war”.)
Use the production possibilities graph below to answer the following questions:
An Economy’s Production Possibilities Frontier for Guns and Butter
16 15
14
14
12 11
er10
tut8 7
B6
4
4
2
0
0
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14
Guns
1. Can this economy produce 6 units of guns and 12 units of butter? Explain.
2. Can this economy produce 11 units of guns and 11 units of butter? Explain.
3. If the economy is presently producing 0 units of guns and 15 units of butter, what is the
opportunity cost of increasing the production of guns from 0 units to 3 units?
4. If the economy is presently producing 12 units of guns and 4 units of butter, what is the
opportunity cost of increasing the production of butter from 4 units to 11 units?
no reviews yet
Please Login to review.