266x Filetype PDF File size 0.31 MB Source: www.wscschools.org
Unit #1: Foundations of Economics Ch. #4: Production Possibilities Curve / Frontier
The PPC or PPF shows production with limited resources and its impacts.
Like all models there are several assumptions:
1. It is a simple model of a society’s ability to produce – the PPC or PPF uses two resources to
represent many resources.
2. Assume the means of production, the resources are fixed. In addition, the state of
technology is fixed as well.
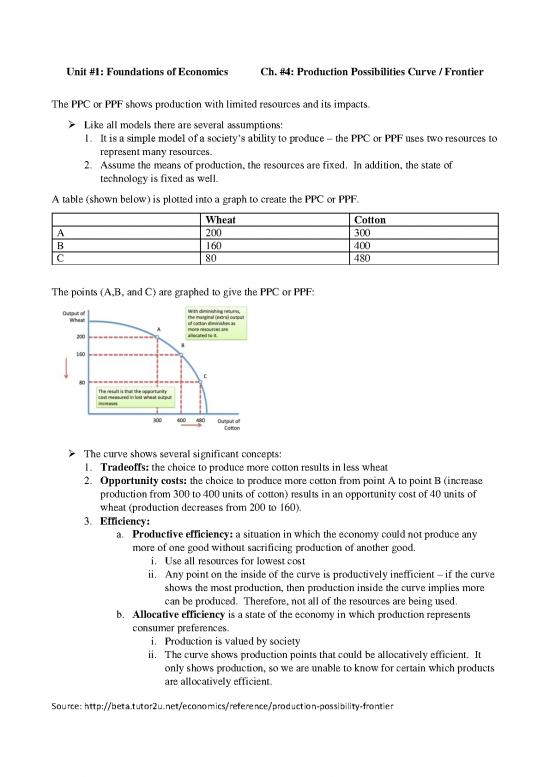
A table (shown below) is plotted into a graph to create the PPC or PPF.
Wheat Cotton
A 200 300
B 160 400
C 80 480
The points (A,B, and C) are graphed to give the PPC or PPF:
The curve shows several significant concepts:
1. Tradeoffs: the choice to produce more cotton results in less wheat
2. Opportunity costs: the choice to produce more cotton from point A to point B (increase
production from 300 to 400 units of cotton) results in an opportunity cost of 40 units of
wheat (production decreases from 200 to 160).
3. Efficiency:
a. Productive efficiency: a situation in which the economy could not produce any
more of one good without sacrificing production of another good.
i. Use all resources for lowest cost
ii. Any point on the inside of the curve is productively inefficient – if the curve
shows the most production, then production inside the curve implies more
can be produced. Therefore, not all of the resources are being used.
b. Allocative efficiency is a state of the economy in which production represents
consumer preferences.
i. Production is valued by society
ii. The curve shows production points that could be allocatively efficient. It
only shows production, so we are unable to know for certain which products
are allocatively efficient.
Source: http://beta.tutor2u.net/economics/reference/production-possibility-frontier
no reviews yet
Please Login to review.