154x Filetype PDF File size 0.36 MB Source: mastermindsindia.com
No.1 for CA/CWA & MEC/CEC MASTER MINDS
15. MARGINAL COSTING
SOLUTIONS TO ASSIGNMENT PROBLEMS
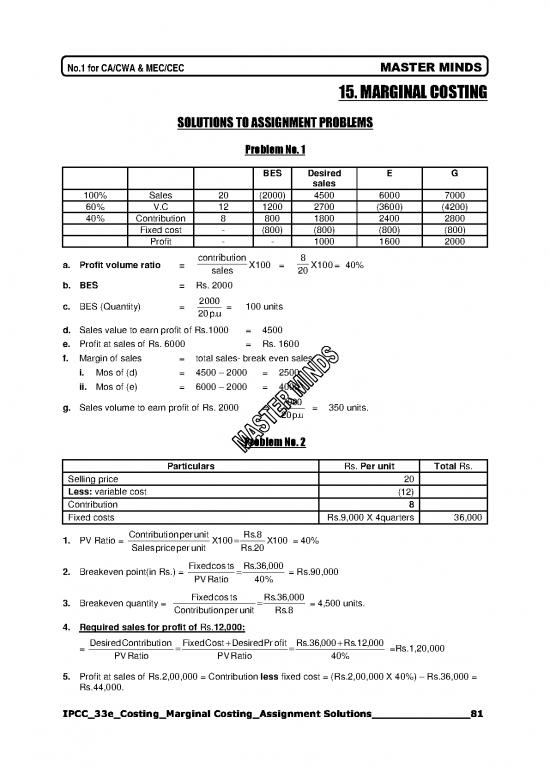
Problem No. 1
BES Desired E G
sales
100% Sales 20 (2000) 4500 6000 7000
60% V.C 12 1200 2700 (3600) (4200)
40% Contribution 8 800 1800 2400 2800
Fixed cost - (800) (800) (800) (800)
Profit - - 1000 1600 2000
a. Profit volume ratio = contribution X100 = 8 X100= 40%
sales 20
b. BES = Rs. 2000
2000
c. BES (Quantity) = = 100 units
20p.u
d. Sales value to earn profit of Rs.1000 = 4500
e. Profit at sales of Rs. 6000 = Rs. 1600
f. Margin of sales = total sales- break even sales
i. Mos of (d) = 4500 – 2000 = 2500
ii. Mos of (e) = 6000 – 2000 = 4000
g. Sales volume to earn profit of Rs. 2000 = 7000 = 350 units.
20p.u
Problem No. 2
Particulars Rs. Per unit Total Rs.
Selling price 20
Less: variable cost (12)
Contribution 8
Fixed costs Rs.9,000 X 4quarters 36,000
1. PV Ratio = Contributionperunit X100= Rs.8 X100 = 40%
Salespriceperunit Rs.20
2. Breakeven point(in Rs.) = Fixedcosts =Rs.36,000 = Rs.90,000
PVRatio 40%
3. Breakeven quantity = Fixedcosts =Rs.36,000 = 4,500 units.
Contributionperunit Rs.8
4. Required sales for profit of Rs.12,000:
= DesiredContribution =FixedCost+DesiredProfit =Rs.36,000+Rs.12,000 =Rs.1,20,000
PVRatio PVRatio 40%
5. Profit at sales of Rs.2,00,000 = Contribution less fixed cost = (Rs.2,00,000 X 40%) – Rs.36,000 =
Rs.44,000.
IPCC_33e_Costing_Marginal Costing_Assignment Solutions_______________81
Ph: 98851 25025/26 www.mastermindsindia.com
6. Margin of safety:
For (4) above, margin of safety = total sales - breakeven sales = 1,20,000 – 90,000 = Rs.30,000.
For (5) above, margin of safety = total sales – breakeven sales = 2,00,000 – 90,000 = Rs.1,10,000.
Problem No. 3
a. Calculation of profit:
BES % Calculation of Profit
Sales 160000 100% 2,00,000
V.C 1,20,000 75% 1,50,000
Contribution 40,000 25% 50,000
Fixed cost (40,000) (40,000)
Profit - 10,000
P/v ratio = 40,000 X 100 = 25%, Profit = Rs. 10,000
1,60,000
b. Calculation of sales:
BES Calculation of Sales
Sales 40,000 60,000 100%
V.C 20,000 30,000 50%
Contribution 20,000 30,000 50%
Fixed cost (20,000) (20,000)
Profit - 10,000
P/v ratio = 30,000 X 100 = 50%, Sales = Rs. 60,000
60,000
Problem No. 4
Note.1: Present selling price per unit = Rs.1,50,000 = Rs.10 per unit.
15,000
Note.2: present contribution per unit = selling price per unit – variable cost per unit = Rs.10 –Rs.6 =
Rs.4 per unit.
Note.3: in the following calculations
PVR = Contributionperunit X100
Salespriceperunit
BEQ = FixedCosts
ContributionPerUnit
Computation of PVR, BEP, and MOS
BES = MOS(Qtty) = MOS (Rs.) =
Particulars PVR = see note BEQ = see note BEQ X SP p.u. Total Sales - MOS X SP p.u.
BEQ
Data given 106 =40% Rs.34,000 = 8,500 8,500 X 10 = 15,000 – 8,500 = 6,500 X 10 =
10 Rs.4 Rs.85,000 6,500 units Rs.65,000
units
10% decrease in 96 =33.33% Rs.34,000 = 11,333 X 9 = 15,000 – 11,333 = 3,667 X 9 =
selling price 9 Rs.3 Rs.1,01,997 3,667 units Rs.33,003
11,333 units
IPCC_33e_Costing_Marginal Costing_Assignment Solutions_______________82
No.1 for CA/CWA & MEC/CEC MASTER MINDS
10% increase in 106.6 =34% Rs.34,000 = 10,000 X 10 = 15,000 – 10,000 = 5,000 X 10 =
variable costs 10 Rs.3.4 Rs.1,00,000 5,000 units Rs.50,000
10,000 units
Sales Increase by 106 =40% Rs.34,000 = 8,500 8,500 X 10 = 17,000 – 8,500 = 8,500 X 10 =
2,000 units 10 Rs.4 Rs.85,000 8,500 units Rs.85,000
units
Rs.6,000 increase 106 =40% Rs.40,000 = 10,000 X 10 = 15,000 – 10,000 = 5,000 X 10 =
in fixed costs 10 Rs.4 Rs.1,00,000 5,000 units Rs.50,000
10,000 units
Problem No. 5
Selling price to earn same
Particulars Present Proposed Contribution
Sales (let) 100 80 20 = 40
160
80 = ?
Less: Variable cost (60) (60)* (120)
Contribution 40 20 40
Therefore if selling price is reduced by 20% selling price has to be increased by 60% i.e. from Rs. 100
to Rs. 160.
* Variable cost will not change for change in selling price.
Problem No. 6
a)
1. % of margin of safety = Margin of safety
Total sales
Total sales = Margin of safety
%ofMargin of safety
= 2,40,000
40%
= 6,00,000
Break even sales = Total sales – Margin of Safety sales
= 6,00,000 – 2,40,000
= 3,60,000
2. Profit = [Total sales – Break even sales] x P/V Ratio
= (9,00,000 – 3,60,000) x 30%
= 1,62,000
b) Fixed cost = Contribution – Profit
= 2,00,000 – 1,50,000
= 50,000 Rs.
P/V Ratio = Contribution = 2,00,000 = 25%
sales 8,00,000
BEP = Fixedcost = 50,000 = 2,00,000
P/VRatio 25%
Margin of safety = Total sales – BEP
= 8,00,000 – 2,00,000
= 6,00,000
IPCC_33e_Costing_Marginal Costing_Assignment Solutions_______________83
Ph: 98851 25025/26 www.mastermindsindia.com
Problem No. 7
P/V ratio = Contribution X100=1,50,000 X100=50%
Sales 3,00,000
i. If in the next period company suffered a loss of Rs. 30,000, then
Contribution = Fixed Cost - Profit
= Rs. 90,000 – Rs. 30,000 (as it is a loss)
= Rs. 60,000.
Then Sales = Contributionor 60,000 =Rs.1,20,000
P/VRatio 0.50
So, there will be loss of Rs. 30,000 at sales of Rs. 1,20,000.
ii. safety = Profit or 90,000 =Rs.1,80,000
PVratio 0.50
Problem No. 8
i. In the First half year:
Contribution = Fixed cost + Profit = 4,50,000 + 3,00,000 = Rs. 7,50,000
P/V ratio =ContributionX100 = 7,50,000 X 100 = 50%
sales 15,00,000
Fixed cost 4,50,000
Break-even point = P/V ratio = 50% = Rs. 9,00,000
Margin of safety = Actual sales – Break-even point = 15,00,000 – 9,00,000 = Rs. 6,00,000
ii. In the second half year:
Contribution = Fixed cost – Loss = 4,50,000 – 1,50,000 = Rs. 3,00,000
Expected sales volume = Fixed cost -loss = 3,00,000 = Rs. 6,00,000
P/V ratio 50%
iii. For the whole year:
B.E. point = Fixed cost = 4,50,000X2 = Rs.18,00,000
P/V ratio 50%
Margin of safety = PROFIT = 3,00,000 . 1,50,000 = Rs. 3,00,000.
P/V ratio 50%
Problem No. 9
1. Marginal cost sheet for the given data is prepared as under –
Particulars Rs.
Sales (given) 3,00,000
Less: variable cost (balancing figure) 1,20,000
Contribution (fixed cost + profit) 1,80,000
Less: fixed cost (given) 90,000
Profit (given) 90,000
IPCC_33e_Costing_Marginal Costing_Assignment Solutions_______________84
no reviews yet
Please Login to review.