192x Filetype PDF File size 2.10 MB Source: www.ealingindependentcollege.com
Market Structures
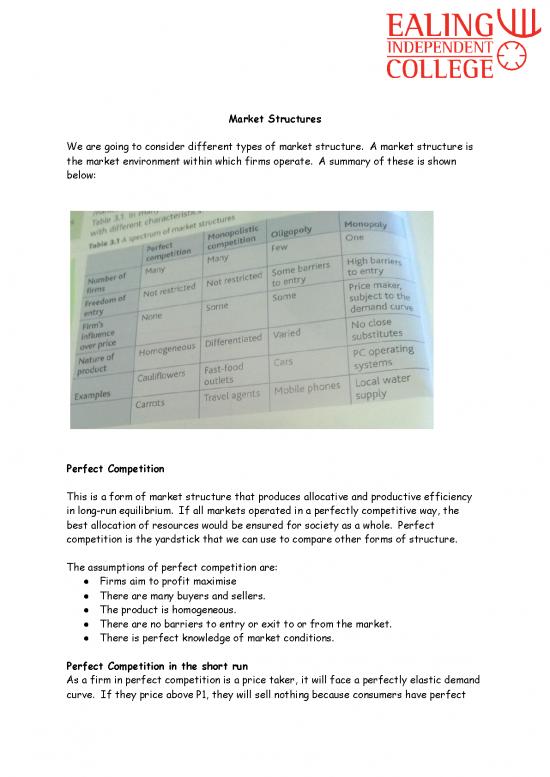
We are going to consider different types of market structure. A market structure is
the market environment within which firms operate. A summary of these is shown
below:
Perfect Competition
This is a form of market structure that produces allocative and productive efficiency
in long-run equilibrium. If all markets operated in a perfectly competitive way, the
best allocation of resources would be ensured for society as a whole. Perfect
competition is the yardstick that we can use to compare other forms of structure.
The assumptions of perfect competition are:
● Firms aim to profit maximise
● There are many buyers and sellers.
● The product is homogeneous.
● There are no barriers to entry or exit to or from the market.
● There is perfect knowledge of market conditions.
Perfect Competition in the short run
As a firm in perfect competition is a price taker, it will face a perfectly elastic demand
curve. If they price above P1, they will sell nothing because consumers have perfect
knowledge. As they can sell as much as they like at P1, there is no incentive to reduce
the price.
To maximise profits, the firm will set output where MR=MC.
The SMC cost curve represents the short-run supply curve for the firm, as it shows
the output that the firm would supply at any given price.
Industry equilibrium in the short run
In the industry as a whole, there is a downward-sloping demand curve, and this is
formed of the preferences of consumers in the market. If you add up all of the supply
curves for each firm, the result is the industry supply curve. The price is P1 and the
firms in the industry willl suppy Q1 output.
The figure below shows the firm in short-run equilibrium. To profit maximise, the
firm produces output q1, and accepts the market price of p1. As the AR is greater than
AC1, the firm is making supernormal profits of the shaded area. As there are no
barriers to entry, other firms will enter the market.
This will shift the industry supply curve to the right, and the market price will fall.
The firms will no longer mark supernormal profits. Some of them would choose to exit
the market, and the industry supply curve would shift to the left. The price would
stabilise so that the typical firm is only making supernormal profits.
Perfect Competition in long-run equilibrium
The diagram below shows the situation for a firm and for the industry as a whole once
long-run equilibrium has been reached and firms no longer have any incentive to enter
or exit the market. The market is in equilibrium, and the typical firm makes normal
profits.
In the diagram below, the intial market price is at p*. The typical firm is producing q*,
and the industry is producing Q*. Demand was initially at D0, but it has shifted to D1
as the product has become more popular. This makes the price rise, and the typical
firm then moves along its short-run supply curve. The combined supply of the firm then
increases to Q1.
no reviews yet
Please Login to review.