248x Filetype PDF File size 0.66 MB Source: wou.edu
1/7/2016
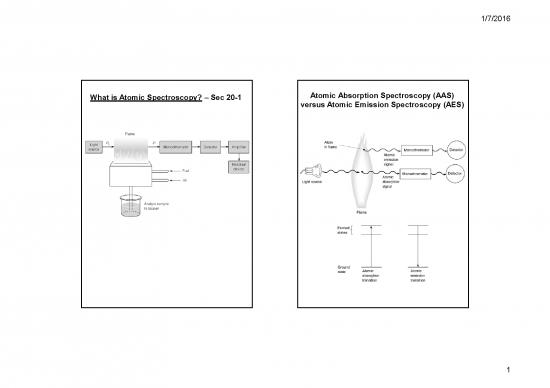
What is Atomic Spectroscopy? – Sec 20-1 Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (AAS)
versus Atomic Emission Spectroscopy (AES)
1
1/7/2016
Flame Atomization – Sec 20-2 Fuels and Flame Temperatures –Table 20-1
Atomization process = Fuel Oxidant Temperature
(K)
Complete atomization results in ____________________ acetylene air 2400 - 2700
acetylene Nitrous oxide 2900 - 3100
(N O)
2
acetylene oxygen 3300 - 3400
hydrogen air 2300 - 2400
hydrogen oxygen 2800 - 3000
Cyanogen oxygen 4800
2
1/7/2016
Instrumentation – Sec 20-4
The Linewidth Problem – absorbance is proportional to Line Broadening Mechanisms
concentration (i.e. Beer’s Law holds) when the linewidth of
the probing light is narrower than the absorption band
Both mechanisms result in more line broadening
as the temperature increases.
1. Doppler Effect – atom moving towards the
lamp samples EM wave more often = higher
frequency (shorter wavelength) absorbed
3
1/7/2016
2. Pressure Broadening – colliding atoms (and Hollow Cathode Lamps
molecules) absorb a broader range of frequencies
(wavelengths) Cathode composed of the same element as the analyte.
As long as line broadening within the cathode is less
than within the flame, the linewidth of the lamp is always
less than the linewidth of the absorbing atoms and Beer’s
Law is followed.
4
no reviews yet
Please Login to review.