221x Filetype PPT File size 0.10 MB Source: www2.seas.gwu.edu
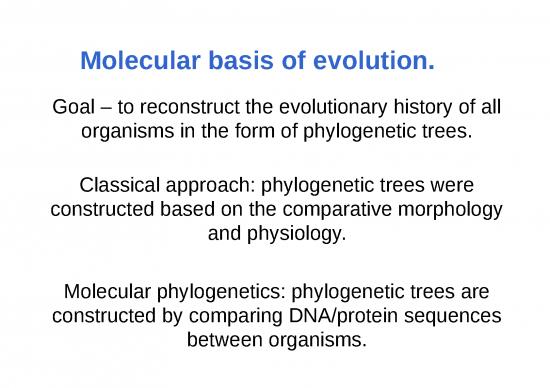
Evolution of mankind.
Analysis of mitochondrial DNA proposes that Homo sapiens
evolved from one group of Homo erectus in Africa (African
Eve) 100,000 – 200,000 years ago.
American indians I,
Europeans 25-35,000
40-50,000 American indians II,
7-9,000
Asians
55-75,000
Africans
100,000
Adam appeared 250,000 years ago, much earlier!
Mechanisms of evolution.
- Evolution is caused by mutations of genes.
- Mutations spread through the population via
genetic drift and/or natural selection.
- If mutant gene produces an advantage (new
morphological character), this feature will be
inherited by all descendant species.
Mutational changes of DNA sequences.
1. Substitution. 3. Insertion.
Thr Tyr Leu Leu Thr Tyr Leu Leu
ACC TAT TTG CTG ACC TAT TTG CTG
ACC TCT TTG CTG ACC TAC TTT GCT G—
Thr Tyr Leu Leu Thr Tyr Phe Ala
2. Deletion. 4. Inversion.
Thr Tyr Leu Leu Thr Tyr Leu Leu
ACC TAT TTG CTG ACC TAT TTG CTG
ACC TAT TGC TG- ACC TTT ATG CTG
Thr Tyr Cys Thr Phe Met Leu
Gene duplication and recombination.
New genes/proteins occur through the gene duplication and
recombination.
Ancestral globin Gene 1
duplication +
Gene 2
globin globin
hemoglobin myoglobin
New gene
Duplication Recombination
Codon usage.
Phe UUU Ser UCU Tyr UAU
UUC UCC UAC
Leu UUA UCA Cys UGU
UUG UCG UGC
Frequencies of different codons for the same amino acid are
different. Codon usage bias is caused:
- Translationary machinery tends to use abundant tRNA
(and codons corresponding to these tRNA). Codon usage
bias is the same for all highly expressed genes in the
same organism.
- Mutation pressure. Difference between mutation rates
between GC AT and AT GC. GC-content is different
in different organisms.
no reviews yet
Please Login to review.