237x Filetype PPTX File size 0.10 MB Source: www.oasisacademysouthbank.org
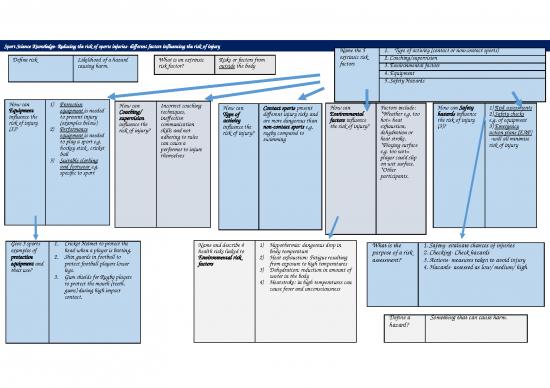
Sport Science Knowledge- Reducing the risk of sports injuries- different factors influencing the risk of injury
What is an intrinsic risk Risks or factors from 1. Physical Preparation
factor? within the body. Name the 5 intrinsic 2. Individual variables (age, gender, flexibility)
risk factors 3. Psychological factors
4. Posture and causes of poor posture
5. Sports injuries related to poor posture
How can 1) Training How can 1) Age: older age more injury prone How can Mental factors-can affect a How can 1) Poor stance/ gait e.g. How can Postural
Physical 2) Warm up Individual 2) Flexibility: more flexible= less Psychologi performer positively and Posture and hunched shoulders Sports misalignments
Preparation 3) Cool down variables chance of injury cal factors negatively e.g. causes of 2) Poor Sitting positions e.g. injuries can increase risk
influence the 4) Overuse- chronic influence the 3) Nutrition: poor nutrition can influence 1) Motivation. Over poor posture slouching related to of injury e.g.
risk of injury? injuries caused by risk of injury? cause fatigue and dehydration= lose the risk of motivation- performer can influence the 3) Physical defects e.g. poor posture -Pelvic tilt
repetitive focus/ concentration injury? become reckless risk of weakened muscles around an influence -Lordosis
movements which 4) Sleep: lack of sleep= poor decision 2) Aggression injury? injured area the risk of -Kyphosis
damage tendons making 3) Arousal/ Anxiety levels- 4) Lack of exercise e.g. being injury? -Round shoulder
and ligaments 5) Gender: what may be suitable for negative emotional state of overweight= strain on posture (shoulders
5) Muscle females may not be for males (+ vice worry causing performer to 5) Fatigue- tired muscles hunched
imbalance- one versa) become unfocussed. unable to support skeleton forwards)
muscle more 6) Previous/ recurring injuries: 6) Emotional factors -Scoliosis
powerful than the increased chance of injuring 7) Clothing/ footwear: e.g.
other themselves again high heels affect posture
Describe what lordosis is Excessive forward or inward curving of the lower
and the impact it can have back/ spine. Impact= back pain
The femur is Thigh bone
Describe what kyphosis is Excessive backward or outward curvature of the
What is the role of Attach muscles to bone and the impact it can have upper part of the spine Impact= back pain
tendons?
The pelvis is Large bone attached to
the backbone and What is the role of Attach bone to bone
forming the hip joint Describe what scoliosis is Condition where the spine is visibly curved to the
with the legs ligaments? and the impact it can have side, giving an ‘S’ or ‘C’ shape. Impact= back pain.
Sport Science Knowledge- Reducing the risk of sports injuries- how appropriate warm up and cool down routines can help to prevent injury.
Warm up Cool down
Physical benefits of a warm up include:
- warming up muscles/preparing the body for physical activity Physical benefits of a cool down include:
- increase in body temperature - helps the body’s transition back to a resting state
- increase in flexibility of muscles and joints= decrease risk of injury - gradually lowers heart rate
- increase in pliability of ligaments and tendons - gradually lowers temperature
- increase in heart rate and/ or breathing rate= increase in O to working muscles
- increase speed of muscle contraction 2 - circulates blood and oxygen
- increase in blood flow and oxygen to muscles - reduces breathing rate
- Help delay muscle fatigue and build up of lactic acid - removes waste products e.g. lactic acid
- reduces the risk of muscle soreness and stiffness
- aids recovery by stretching muscles, i.e. lengthening and strengthening muscles for
4 Psychological benefits of a - heighten or control arousal levels -‘get in the zone’ or settle nerves. next work-out/use
warm up include: - improve concentration/focus e.g. not reckless
- increase motivation/ drive
- mental rehearsal/ preparation e.g. use correct technique
2 Key components of a 1) Pulse lowering, i.e. exercises which gradually lower
cool down: heart rate and reduce temperature (e.g. easy movements,
5 key components of a warm up: light running, stretching)
1) Pulse raising- exercises that slowly increase heart rate and body temperature (e.g. jogging, cycling, skipping) 2) Stretching, e.g. hamstring stretches, lunges, open and
2) Mobility- exercises that take the joints through their full range of movement (ROM) (e.g. arm swings, hip circles) close gates
3) Dynamic movements (e.g. change of speed and direction)
4) Stretching (e.g. developmental stretches, dynamic stretches linked to sport – ‘open and close the gate’ groin walk)
5) Skill rehearsal phase, i.e. using common movement patterns to be used in activity (e.g. dribbling drills for football,
passing drills for netball)
The specific needs which a - characteristics of the individual/group, i.e.
warm up and cool down must - Group size e.g. too big? May need more staff.
consider include… - age of participants
- experience of participants e.g. set at right level for ability of group
- individual fitness levels
- Individual medical conditions
- suitability for a particular activity/sport
- environmental factors (e.g. weather/temperature if outdoors, available facilities).
Sport Science Knowledge - Reducing the risk of sports injuries- How to respond to injuries within a sporting context. LO3
Injuries in sports are usually divided Acute injuries and Chronic injuries 10 Describe Soft tissue injuries: Damage to muscles, ligaments or tendons e.g. sprains, strains
1 into 2 types, they are:
11 State the difference between a Strain Strain: Injuries to muscles e.g, pulled muscle
2 Describe an acute injury: Happen quickly and caused by sudden trauma to the body e.g. injury and a Sprain injury: Sprain: Injuries to ligaments e.g. twisted ankle
hard rugby tackle, hit by ball 12 Describe a fracture: Partial or complete break in a bone. 2 main types: open and
closed
3 What do acute injuries usually result Immediate pain, usually swelling with a loss of function 13 Describe a Closed fracture: Broken bone with no break in the skin.
in?
4 Give examples of types of acute Soft tissue injuries (sprains/ Strains) 14 Describe an Open fracture? Broken bone in which the skin is also broken, exposing the
injuries: Fractures (open or closed) bone.
Concussion e.g. clash of heads in football 15 Describe a Concussion Injury in which the brain is shaken inside the skull e.g. head
Cuts- abrasions/ grazes collision to another person or object.
Contusions-bruises
Cramp 16 Give symptoms and treatments of Symptoms: dizziness, nausea, vomiting, memory loss, loss of
Blisters concussion balance, headaches
5 Describe a chronic injury. Aka Overuse injuries and are a result of continuous/ excessive Treatment: requires medical assistance. Temporary relief- cold
stress on an area. Tend to develop over time, Inflammation and compress applied to head.
painful 17 Describe Abrasion: Surface damage to the skin e.g. grazes (skin scraped away) and
6 Give examples of types of chronic e.g. hitting a tennis/ golf ball repeatedly= tennis elbow/ cuts
injuries: golfers elbow 18 Describe Contusion: A bruise to a part of the body.
Achilles tendonitis
Shin splints
Injuries related to children: Severs disease, Osgood Schlatter’s 19 Describe Blisters: Bubbles of fluid under the skin caused by friction.
disease
Injuries related to poor posture- round shoulders etc
7 Describe the overuse injury- Shin Pain in the shins or the front of the lower leg bone (tibia), 20 Describe Cramp: Painful sensations caused my involuntary muscle contraction.
splints: usually caused by exercise. Often caused by excessive exercise or poor hydration
Describe the overuse injury- Tennis Tendon injury due to repetitive actions such as tennis strokes. 21 Describe Sever’s disease (injury related Heel pain caused by an inflamed growth plate.
8 elbow: to children):
21 Describe Osgood-Schlatter’s disease Knee pain caused by growth spurts.
9 Describe the overuse injury- Chronic injury to tendons e.g. Achilles tendonitis, tennis (injury related to children)
Tendonitis: elbow, etc
Sport Science Knowledge - Reducing the risk of sports injuries- How to respond to injuries within a sporting context. LO3
1 One way to respond to injuries See: did you see injury occur? Ice therapy can manage sports Reducing pain and swelling. Apply for 15-20 mins
is SALTAPS, describe this on- Ask: ask player what happened? 3 injuries by: every 2-3hours.
field assessment routine Look: at injury/ compare to other limbs
Touch: feel for tenderness 4 Heat treatment can manage Reducing pain and stiffness, increasing blood flow
Active: can player move injured area? sports injuries by: to the area which promotes healing.
Passive: coach to see if they can move injured area
Strength: can player hold their weight on it? What is an Emergency Action Written document identifying what action to take
5 Plan (EAP)? in the event of an emergency at a sporting event.
6 List the 3 main components of 1. Emergency personnel
2 The 2nd way to respond to Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation - treatment for acute soft tissue an emergency Action Plan 2. Emergency communication
injuries is R.I.C.E, describe injuries to reduce swelling, ease pain and prevent further damage for (EAP) 3. Emergency equipment
this process: acute but less serious injuries to soft tissues. 7 Define emergency personnel in People who are responsible in a emergency e.g. first
a EAP: responders, first aider, coach
8 Define emergency Details of whom to contact in an emergency e.g.
3 Stretching and massage - Increases blood flow to affected body part and increases flexibility communication in a EAP? telephone, emergency services 999 and location of
response to sports injury: - Relaxes muscles and relieve tension nearest phone.
- Manages pain and DOMS 9 Define emergency equipment in Equipment required in an emergency situation e.g.
a EAP? first aid kits, evacuation chair, defibrilator
4 What can be used to support Taping and strapping- reduce pain
weak or injured muscles and Bandaging- prevents swelling and decrease blood flow to the injured
joints? area. Can reduce pain keeps area immobilised
5 Describe a Splint as a Plastic or fibreglass support for acute limb fractures and sprains e.g.
treatment method fractured arm
6 Describe a Sling as a treatment Support, usually of folded cloth, to immobilise and rest the injured
method: limb (injured elbow)
Sport Science Knowledge- Reducing the risk of sports injuries- How to respond to common medical conditions. LO4
1 Describe the common medical condition- 8 The term used for a Hypoglycaemia
asthma: Lung condition that causes occasional breathing difficulties diabetic having low blood
2 Identify the 6 symptoms of asthma: 1. Breathlessness sugar is…
2. Wheezing / 9 Describe the common Condition causing abnormal brain activity leading to
3. Tightness in the chest medical condition- seizures.
4. Coughing epilepsy:
5. Pale / clammy (skin)
6. (Severe) grey / blue lips 10 Identify the 6 symptoms of 1. Fitting / seizures / shaking
3 How would you treat an asthma • Inhaler OR pump epilepsy 2. Rigidity / muscle stiffness
attack? • Reassure/ Stay calm 3. Tingling / pins and needles
• Sit them down OR sit upright 4. Eyes rolling to back of head
• Provide a caffeinated beverage (helps to open airways) 5. Loss of consciousness
• Move them away from the trigger (dust / smoke) 6. Foaming at mouth
• Emergency services (if needed) 11 How would you treat an Emergency/ Individual care plan in place
•
epileptic seizure? • Make the area safe
4 Describe the common medical condition- Condition in which blood sugar levels are unregulated by the body. • Remove harmful objects
diabetes: • Cushion head (with pillow)
• Let them fit
• Don’t restrain or hold them down
5 Compare the two types of diabetes: Type 1 Type 2 • Put them in the recovery position after the fit has
Insulin-dependent Insulin resistant diabetes finished
diabetes - managed through careful dietary • Anti- epileptic drugs (AEDs)
- requires insulin control.
injections. 12 How to respond to these • Ensure awareness of any participants’ medical
common medical conditions before starting physical activity
6 Identify the 4 symptoms of diabetes: 1. Increased thirst / hunger conditions:
2. Going to the toilet lots 12 When should someone refer Loss of consciousness or an obvious concussion
3. Weight loss / gain •
4. Extreme tiredness the performer to a • Potential or suspected fractures
7 How would you treat a diabetic Give them sugar e.g. fruit juice/ sweets / chocolate professional? • Recurring injury
• • Severe or considerable pain
episode? • Give insulin (for Type 1) • Struggling to breathe
• Lifestyle changes (for Type 2) / glucose (tablets) • Person in charge is unqualified
no reviews yet
Please Login to review.