206x Filetype PPTX File size 1.48 MB Source: ocw.snu.ac.kr
Pure Substance
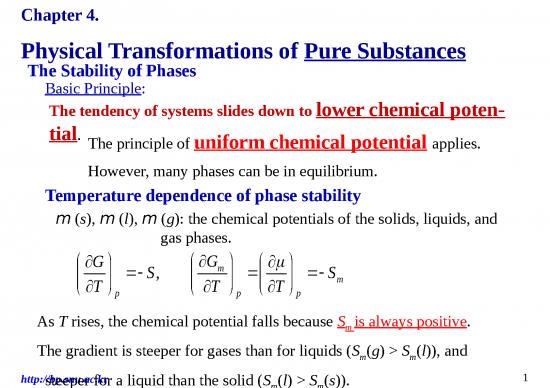
m The schematic temperature dependence of
curvature the chemical potential of the solid, liquid,
,
l
a and gas phases of a substance.
i
t Solid
n (In reality, the lines are curved).
e
t ×
o
p
l Liquid The phase with the lowest chemical poten-
a
c
i tial at the specified T and P is the most sta-
m
e Gas ble.
h
C
The transition temperatures, the melting
and boiling temperatures, are the tempera-
Solid Liquid Gas tures at which the chemical potentials of
stable stable stable two phases are equal.
T T
f b
Temperature, T
http://bp.snu.ac.kr 2
Figure 4.4
Critical The general regions of pressure and
Solid point temperature where solid, liquid, or gas
p
is stable (that has the lowest chemical
, Liquid
e
r potential).
u
s
s
e
r The solid phase is the most stable phase
P
Triple at low temperatures and high pressures.
point
Vapor
T T
3 c
Temperature, T
http://bp.snu.ac.kr 3
Uniform Chemical Potential
In Equilibrium
Figure 4.5
The vapor pressure of a liquid or
Vapor solid is the pressure exerted by the
vapor in equilibrium with the con-
V atom densed (L or S) phase.
↓ ↑
S atom T < T
sublimation
Solid (T < T )
boiling
http://bp.snu.ac.kr 4
T > Tc or
T < Tc or Figure 4.4
P > P
P < P c (a) A liquid in equilibrium with its vapor.
c
(b) When a liquid is heated in a sealed con-
tainer, the density of the vapor phase in-
creases and that of the liquid decreases
V V slightly.
V = L (c) There comes a stage at which the two
densities are equal, and the interface be-
tween the fluids disappears. This disap-
pearance occurs at the critical tempera-
L L ture.
The container needs to be strong: the
critical temperature of water is 374˚C
T + P going up and the vapor pressure is then 218 atm.
http://bp.snu.ac.kr 5
Figure 4.8
Phase diagram for carbon dioxide.
As the triple point lies at pressures well
above atmospheric, liquid carbon dioxide
does not exist under normal conditions
A pressure of at least 5.11 atm must be
applied.
Dry ice
http://bp.snu.ac.kr 6
no reviews yet
Please Login to review.