214x Filetype PDF File size 0.40 MB Source: www.oakparkusd.org
UNIT 3 REVIEW SHEET KEY
MODERN PERIODIC TABLE AND TRENDS
1. What was the basis for Mendeleev’s arrangement of elements in his early periodic table?
- He first arranged the early periodic table by atomic mass.
2. Know the modern basis for the arrangement of the periodic table.
- The modern periodic table is arranged in order of increasing atomic number.
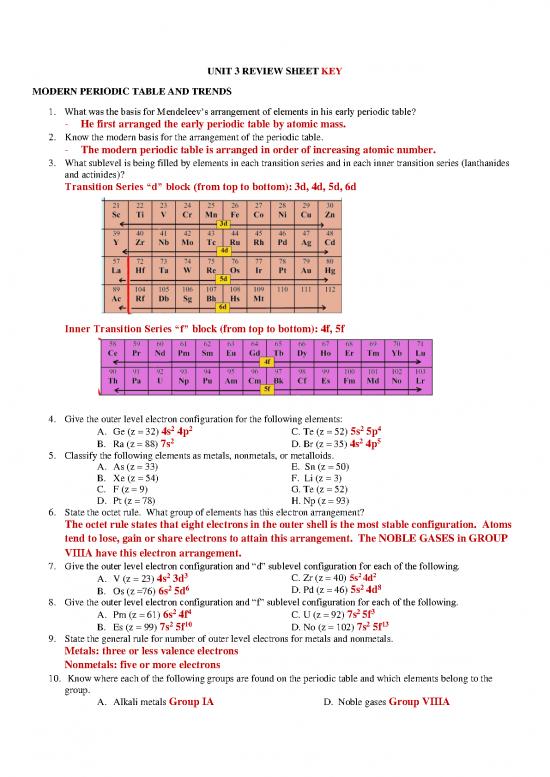
3. What sublevel is being filled by elements in each transition series and in each inner transition series (lanthanides
and actinides)?
Transition Series “d” block (from top to bottom): 3d, 4d, 5d, 6d
Inner Transition Series “f” block (from top to bottom): 4f, 5f
4. Give the outer level electron configuration for the following elements:
2 2 2 4
A. Ge (z = 32) 4s 4p C. Te (z = 52) 5s 5p
2 2 5
B. Ra (z = 88) 7s D. Br (z = 35) 4s 4p
5. Classify the following elements as metals, nonmetals, or metalloids.
A. As (z = 33) E. Sn (z = 50)
B. Xe (z = 54) F. Li (z = 3)
C. F (z = 9) G. Te (z = 52)
D. Pt (z = 78) H. Np (z = 93)
6. State the octet rule. What group of elements has this electron arrangement?
The octet rule states that eight electrons in the outer shell is the most stable configuration. Atoms
tend to lose, gain or share electrons to attain this arrangement. The NOBLE GASES in GROUP
VIIIA have this electron arrangement.
7. Give the outer level electron configuration and “d” sublevel configuration for each of the following.
2 3 C. Zr (z = 40) 5s2 4d2
A. V (z = 23) 4s 3d
2 6 2 8
B. Os (z =76) 6s 5d D. Pd (z = 46) 5s 4d
8. Give the outer level electron configuration and “f” sublevel configuration for each of the following.
2 4 2 3
A. Pm (z = 61) 6s 4f C. U (z = 92) 7s 5f
2 10 2 13
B. Es (z = 99) 7s 5f D. No (z = 102) 7s 5f
9. State the general rule for number of outer level electrons for metals and nonmetals.
Metals: three or less valence electrons
Nonmetals: five or more electrons
10. Know where each of the following groups are found on the periodic table and which elements belong to the
group.
A. Alkali metals Group IA D. Noble gases Group VIIIA
B. Alkaline earth metals Group IIA E. Lanthanides Atomic # 58-71
C. Halogens Group VIIA F. Actinides Atomic # 90-103
11. Give the symbol of each of the elements for each of the following outer level electron configurations and “d” or
“f” sublevel configurations.
2 2 6
A. 2s Be C. 3s 3p Ar
2 8 2 10
B. 5s 4d Pd D. 6s 4f Ho
12. Give the following ending configurations for unknown elements A-D, answer each of the questions below.
2 4 1 1 2
A. 3s 3p B. 5s C. 7s D. 3s
(1) Which if any of these elements belong to the same period? Identify the period. A, D Period 3
(2) Which, if any belong to the same group? Identify the group. B, C Group IA
(3) Which, if any are nonmetals? A
(4) Which if any are metals? B, C, D
(5) Which if any are metalloids or semimetals? None
(6) Which if any belong to the alkali family? B, C
(7) Which if any belong to the alkaline family? D
13. Know what is the most important factor in determining the properties of an element? Valence Electrons
14. Know what happens to the size of atoms as you move across a period or down a group. Know which member of
the following pairs of particles is larger: Pd, Rb; Mg, Ba; Cs, Lu; Se, O
Atomic radii generally decrease as you move left to right across a period, and increase as you
move down a group.
15. Which of the following atoms would we expect to have the largest radius? Li, B, O, or F
16. Know which are larger, metal atoms or their ions. Also, know which are largest, non metal atoms or their ions.
- + - +3
Which member of the following pairs of particles is larger? Br, Br ; Na, Na ; F, F ; Al, Al
Positive ions of metals are smaller than their metal atoms. Negative ions of nonmetals are larger
than their nonmetal atoms.
17. Which of the following electron configurations would be the most stable chemically?
2 2 6 2 2
A. 1s 2s 2p C. 1s 2s
2 2 6 2 1 2 2 5
B. 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p D. 1s 2s 2p
18. Know the various properties of metal discussed in this chapter including malleability, ductility, luster and
electrical conductivity.
Metals are good conductors of heat and electricity, shiny, ductile (can be stretched into thin wires),
malleable (can be pounded into thin sheets), and are mostly solid at room temp
19. Know how electronegativity varies within a group and within a period on the periodic table (i.e., the trend).
Electronegativity generally increases as you move left-to-right across a period and decreases down
a group.
20. Know what element on the periodic table has the highest electronegativity and ionization energy. Know which
has the lowest electronegativity and ionization energy.
Highest electronegativity: Fluorine Lowest electronegativity: Francium
Highest ionization energy: Helium Lowest ionization energy: Francium
IONIC, COVALENT, METALLIC BONDING AND LEWIS STRUCTURES
1. Know the various properties of metals discussed in this chapter including malleability, ductility, luster, and
electrical conductivity.
Metals Nonmetals
♦ Malleable ♦ Not malleable
♦ Ductile ♦ Not ductile
♦ Shiny ♦ Dull luster
♦ Good conductors of electricity ♦ Poor conductors of electricity
2. Know the differences between ionic, covalent, and metallic bonds.
What kinds of bonds are found between (1) metal cations and delocalized electrons, Metallic Bonds (2)
between nonmetal atoms, Covalent Bonds (3) metal and nonmetal ions Ionic Bonds
a. What phases conduct electricity in ionic and covalent compounds and in metals?
IONIC: Liquid and gas phase only
COVALENT: None
METALLIC: Solids, liquids and gases
b. Which bond type is found in materials with extremely high boiling points? Metallic
c. What bond type forms molecules? Covalent
d. In which bond type is electrons shared Covalent
And in which are electrons transferred. Ionic
3. How are ions arranged in a crystal lattice structure?
Ions of opposite charges next to each other; Positive cations are surrounded by negative anions
and negative anions are surrounded by positive cations.
4. Where are the hardest metals found? Farther into the d block
5. What type of bonds are found in the following compounds? NaCl, NaOH, BaSO , LiCl, CaS, CH , CO , C H O .
4 4 2 6 12 6
♦ NaCl – Ionic
+ -
♦ NaOH – Ionic betweem Na and OH
Covalent between O and H in OH-
+2 -2
♦ BaSO – Ionic between Ba and SO
4 4
-2
Covalent between the S and O in SO4
♦ LiCl - Ionic
♦ CaS – Ionic
♦ CH4 - Covalent
♦ CO2 - Covalent
♦ CH O - Covalent
6 12 6
6. When given the electronegativities of several elements, be able to predict what kind of bond would form between
them. As an example look up the electronegativities of the following elements and determine the type of bond
that would form between them: C-N, K-F, H-O, Ca-F, Na-Cl, Ba-Br. Electronegativity Chart
C – N = (3.04-2.55) = 0.49 Covalent Carbon 2.55
K – F = (3.98-0.82) = 3.16 Ionic Nitrogen 3.04
H – O = (3.44-2.20) = 1.24 Covalent Potassium 0.82
Ca – F = (3.98-1.00) = 2.98 Ionic Fluorine 3.98
N – Cl = (3.16-3.04) = .12 Covalent Hydrogen 2.20
Ba – Br = (2.96-0.89) = 2.07 Ionic Oxygen 3.44
Calcium 1.00
* Electronegativities will be provided for you on the test in a chart form similar to that Chlorine 3.98
shown to the left Barium 0.89
Bromine 2.96
-1
7. Give the Lewis Dot Structures for Cl , SiO , H O, and NO .
2 2 2 3
Cl : SiO : :O Si O:
2 2
HO: NO -1:
2 3
+2 -1
8. Give the correct formula for a compound composed of Ba and OH . Ba(OH)
2
9. In a properly written formula for a compound all the charges add up to what number? zero
10. Give the names of the following covalent compounds containing sulfur and oxygen
a. SO sulfur monoxide c. S O disulfur trioxide
2 3
b. SO sulfur dioxide d. S O disulfur pentoxide
2 2 5
11. Give the names of the compounds from the following formulas.
a. BaCl barium chloride d. Ba(ClO ) barium chlorate
2 3 2
b. Ba(ClO ) barium chlorite e. Ba(ClO ) bariumperchlorate
2 2 4 2
c. Ba(ClO)2 barium hypochlorite
12. Give the formulas for the following compounds.
a. Cobalt (III) Sulfate Co (SO )
2 4 3
b. Cobalt (II) Sulfate CoSO
4
c. Cobalt (III) Sulfite Co (SO )
2 3 3
d. Cobalt (II) Sulfite CoSO
3
e. Cobalt (III) Sulfide Co S
2 3
f. Cobalt (II) Sulfide CoS
13. Know the names of the five acids that were assigned and be able to recognize their formulas. SKIP
a. Acetic acid
b. Hydrochloric acid
c. Nitric acid
d. Sulfuric acid
e. Phosphoric acid
14. Be able to match the name to the formula for the hydrocarbons containing 1-10 carbon atoms. Be able also to
give the name of a hydrocarbon in a ring structure. As an example give the name of the following hydrocarbons.
a. CH SKIP
2 6
b. C H
5 12
c. CH
6 14
d. C H
3 8
15. Give the charges on the unknown ions below indicated as “X”. Use the charge on the given ion to determine the
answer.
a. XCl +1 e. XPO +3
4
b. X (SO ) +3 (typo on review sheet) f. X(NO ) +2
2 4 3 3 2
c. BaX -2 g. Cd2X -4 (assume Cadmium IV)
d. Al X -6 h. X S +3
2 2 3
16. Sodium is atomic number 11 and chlorine is atomic number 17?
a. What are their electron configurations?
2 2 6 1
Na: 1s 2s 2p 3s
2 2 6 2 5
Cl: 1s 2s 2p 3s 3s
b. When they react what are their resulting electron configurations?
2 2 6
Na: 1s 2s 2p
2 2 6 2 6
Cl: 1s 2s 2p 3s 3s
c. What is the advantage to each in the resulting electron configurations? Get 8 in outer energy level
d. What type of bond is formed between these two elements? Ionic Bond
e. What is the name of the resulting structure that forms? Describe its arrangement of particles. Crystal lattice
no reviews yet
Please Login to review.