217x Filetype PDF File size 0.10 MB Source: www.bahria.edu.pk
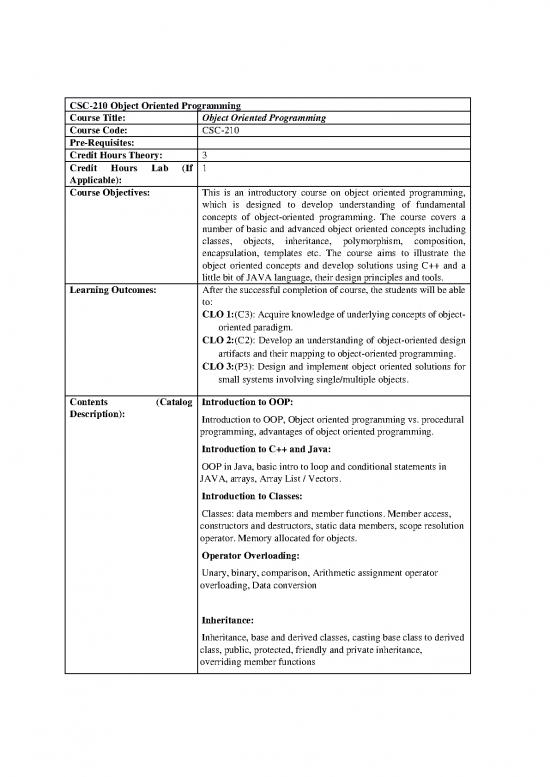
CSC-210 Object Oriented Programming
Course Title: Object Oriented Programming
Course Code: CSC-210
Pre-Requisites:
Credit Hours Theory: 3
1
Credit Hours Lab (If
Applicable):
Course Objectives: This is an introductory course on object oriented programming,
which is designed to develop understanding of fundamental
concepts of object-oriented programming. The course covers a
number of basic and advanced object oriented concepts including
classes, objects, inheritance, polymorphism, composition,
encapsulation, templates etc. The course aims to illustrate the
object oriented concepts and develop solutions using C++ and a
little bit of JAVA language, their design principles and tools.
Learning Outcomes: After the successful completion of course, the students will be able
to:
CLO 1: (C3): Acquire knowledge of underlying concepts of object-
oriented paradigm.
CLO 2: (C2): Develop an understanding of object-oriented design
artifacts and their mapping to object-oriented programming.
CLO 3: (P3): Design and implement object oriented solutions for
small systems involving single/multiple objects.
Contents (Catalog Introduction to OOP:
Description): Introduction to OOP, Object oriented programming vs. procedural
programming, advantages of object oriented programming.
Introduction to C++ and Java:
OOP in Java, basic intro to loop and conditional statements in
JAVA, arrays, Array List / Vectors.
Introduction to Classes:
Classes: data members and member functions. Member access,
constructors and destructors, static data members, scope resolution
operator. Memory allocated for objects.
Operator Overloading:
Unary, binary, comparison, Arithmetic assignment operator
overloading, Data conversion
Inheritance:
Inheritance, base and derived classes, casting base class to derived
class, public, protected, friendly and private inheritance,
overriding member functions
Composition:
Complex classes composed of objects of other classes
Polymorphism:
Overridden functions, abstract base class, and this pointer.
Object Oriented Design:
Class Diagram, Forward Engineering of class diagram to code,
Reverse Engineering of code to class diagram
Exception Handling:
Exception handling, Error handling, try/catch/finally blocks,
throwing an exception, re-throwing and exception
File Handling:
Streams, Stream objects, Character and binary I/O, Object I/O,
readers and writers, I/O with Multiple Objects, Position and offset
Templates
Simple Function templates, function templates with multiple
arguments, class templates.
Robert Lafore, Object-Oriented Programming in C++,
Recommended Text Books: Third Edition, The Waite’s Group.
th
Deitel and Deitel, Java How to Program, 9 Edition,
Prentice Hall, 2012.
Greg Perry and Marcus Johnson, Turbo C++ by Example,
Reference Books: Prentice Hall
nd
Stanley B. Lippman, C++ Primer, 2 edition.
Java Class Libraries Unleashed, SAMS Publishing.
Helping Web Sites:
Attendance is mandatory. Every class is important. All deadlines
are hard. Under normal circumstances late work will not be
accepted. Students are required to take all the tests. No make-up
tests will be given under normal circumstances. There is 0 tolerance
for plagiarism. Any form of cheating on
exams/assignments/quizzes is subject to serious penalty.
Attendance
General Instructions for
students: 75% attendance is mandatory. Latecomers will be marked as
absent.
Evaluation Criteria
Assignments/projects 20%
Quizzes 10%
Mid-Term 20%
Final 50%
CONTRIBUTION OF COURSE LEARNING OUTCOMES (CLOs) TO PROGRAMME
LEARNING OUTCOMES (PLOs)
BS Software Engineering Object Oriented Programming
No Program Learning Outcomes Course Learning Outcomes
12345
1 Engineering Knowledge
2 Problem analysis
3 Design/Development of solutions
4 Investigation
5 Modern tool usage
6 Engineer and society
7 Environment and sustainability
8 Ethics
9 Individual and Team work
10 Communication
11 Project Management
12 Lifelong learning
no reviews yet
Please Login to review.