236x Filetype PDF File size 0.40 MB Source: pandas.pydata.org
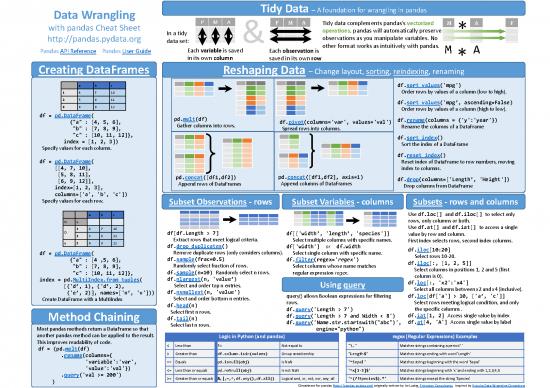
Data Wrangling Tidy Data –A foundation for wrangling in pandas
with pandas Cheat Sheet Tidy data complements pandas’s vectorized
In a tidy operations. pandas will automatically preserve *
http://pandas.pydata.org data set: & observations as you manipulate variables. No
PandasAPI Reference PandasUser Guide Each variable is saved Each observation is other format works as intuitively with pandas. M A
in its own column saved in its own row *
Creating DataFrames Reshaping Data –Change layout, sorting, reindexing, renaming
a b c df.sort_values('mpg')
1 4 7 10 Order rows by values of a column (low to high).
2 5 8 11 df.sort_values('mpg’, ascending=False)
3 6 9 12 Order rows by values of a column (high to low).
df = pd.DataFrame( pd.melt(df) df.rename(columns = {'y':'year'})
{"a" : [4, 5, 6], Gather columns into rows. df.pivot(columns='var', values='val') Rename the columns of a DataFrame
"b" : [7, 8, 9], Spread rows into columns.
"c" : [10, 11, 12]}, df.sort_index()
index = [1, 2, 3]) Sort the index of a DataFrame
Specify values for each column.
df.reset_index()
df = pd.DataFrame( Reset index of DataFrame to row numbers, moving
[[4, 7, 10], index to columns.
[5, 8, 11], pd.concat([df1,df2]) pd.concat([df1,df2], axis=1) df.drop(columns=['Length’, 'Height'])
[6, 9, 12]], Append rows of DataFrames Append columns of DataFrames Drop columns from DataFrame
index=[1, 2, 3],
columns=['a', 'b', 'c'])
Specify values for each row. Subset Observations - rows Subset Variables - columns Subsets - rows and columns
a b c Use df.loc[] and df.iloc[] to select only
N v rows, only columns or both.
1 4 7 10 Use df.at[] and df.iat[] to access a single
D 2 5 8 11 df[df.Length > 7] df[['width’, 'length’, 'species']] value by row and column.
e 2 6 9 12 Extract rows that meet logical criteria. Select multiple columns with specific names. First index selects rows, second index columns.
df.drop_duplicates() df['width'] or df.width df.iloc[10:20]
df = pd.DataFrame( Remove duplicate rows (only considers columns). Select single column with specific name. Select rows 10-20.
{"a" : [4 ,5, 6], df.sample(frac=0.5) df.filter(regex='regex') df.iloc[:, [1, 2, 5]]
"b" : [7, 8, 9], Randomly select fraction of rows. Select columns whose name matches Select columns in positions 1, 2 and 5 (first
"c" : [10, 11, 12]}, df.sample(n=10) Randomly select n rows. regular expression regex. column is 0).
index = pd.MultiIndex.from_tuples( df.nlargest(n, 'value’) df.loc[:, 'x2':'x4']
[('d’, 1), ('d’, 2), Select and order top n entries. Using query Select all columns between x2 and x4 (inclusive).
('e’, 2)], names=['n’, 'v'])) df.nsmallest(n, 'value') query() allows Boolean expressions for filtering df.loc[df['a'] > 10, ['a’, 'c']]
Create DataFramewith a MultiIndex Select and order bottom n entries. rows. Select rows meeting logical condition, and only
df.head(n) df.query('Length > 7') the specific columns .
Select first n rows. df.query('Length > 7 and Width < 8') df.iat[1, 2] Access single value by index
Method Chaining df.tail(n) df.query('Name.str.startswith("abc")', df.at[4, 'A'] Access single value by label
Most pandasmethods return a DataFrameso that Select last n rows. engine="python")
another pandas method can be applied to the result. Logic in Python (and pandas) regex (Regular Expressions) Examples
This improves readability of code. < Less than != Not equal to '\.' Matches strings containing a period '.'
df = (pd.melt(df)
.rename(columns={ > Greater than df.column.isin(values) Group membership 'Length$' Matches strings ending with word 'Length'
'variable':'var', == Equals pd.isnull(obj) Is NaN '^Sepal' Matches strings beginning with the word 'Sepal'
'value':'val'}) <= Less than or equals pd.notnull(obj) Is not NaN '^x[1-5]$' Matches strings beginning with 'x' and ending with 1,2,3,4,5
.query('val >= 200') >= Greater than or equals &,|,~,^,df.any(),df.all() Logical and, or, not, xor, any, all '^(?!Species$).*' Matches strings except the string 'Species'
) Cheatsheet for pandas (http://pandas.pydata.org/ originally written by Irv Lustig, Princeton Consultants, inspired by Rstudio Data Wrangling Cheatsheet
Summarize Data Handling Missing Data Combine Data Sets
df['w'].value_counts() df.dropna() adf bdf
Count number of rows with each unique value of variable Drop rows with any column having NA/null data. x1 x2 x1 x3
len(df) df.fillna(value) A 1 A T
# of rows in DataFrame. Replace all NA/null data with value. B 2 B F
df.shape C 3 D T
Tuple of # of rows, # of columns in DataFrame. Make New Columns Standard Joins
df['w'].nunique() x1 x2 x3
# of distinct values in a column. pd.merge(adf, bdf,
df.describe() A 1 T how='left', on='x1')
Basic descriptive and statistics for each column (or GroupBy). B 2 F Join matching rows from bdf to adf.
C 3 NaN
df.assign(Area=lambda df: df.Length*df.Height) x1 x2 x3
Compute and append one or more new columns. A 1.0 T pd.merge(adf, bdf,
pandas provides a large set of summary functions that operate on df['Volume'] = df.Length*df.Height*df.Depth B 2.0 F how='right', on='x1')
different kinds of pandas objects (DataFrame columns, Series, Add single column. D NaN T Join matching rows from adf to bdf.
GroupBy, Expanding and Rolling (see below)) and produce single pd.qcut(df.col, n, labels=False)
values for each of the groups. When applied to a DataFrame, the Bin column into n buckets. x1 x2 x3
result is returned as a pandas Series for each column. Examples: A 1 T pd.merge(adf, bdf,
how='inner', on='x1')
sum() min() Vector Vector B 2 F Join data. Retain only rows in both sets.
Sum values of each object. Minimum value in each object. function function
count() max() x1 x2 x3 pd.merge(adf, bdf,
Count non-NA/null values of Maximum value in each object. pandas provides a large set of vector functions that operate on all A 1 T how='outer', on='x1')
each object. mean() columns of a DataFrameor a single selected column (a pandas B 2 F Join data. Retain all values, all rows.
median() Mean value of each object. Series). These functions produce vectors of values for each of the C 3 NaN
Median value of each object. var() columns, or a single Series for the individual Series. Examples: D NaN T
quantile([0.25,0.75]) Variance of each object. max(axis=1) min(axis=1) Filtering Joins
Quantiles of each object. std() Element-wise max. Element-wise min. x1 x2 adf[adf.x1.isin(bdf.x1)]
apply(function) Standard deviation of each clip(lower=-10,upper=10) abs() A 1 All rows in adf that have a match in bdf.
Apply function to each object. object. Trim values at input thresholds Absolute value. B 2
Group Data x1 x2 adf[~adf.x1.isin(bdf.x1)]
df.groupby(by="col") The examples below can also be applied to groups. In this case, the C 3 All rows in adf that do not have a match in bdf.
Return a GroupByobject, grouped function is applied on a per-group basis, and the returned vectors
by values in column named "col". are of the length of the original DataFrame. ydf zdf
shift(1) shift(-1) x1 x2 x1 x2
df.groupby(level="ind") Copy with values shifted by 1. Copy with values lagged by 1. A 1 B 2
Return a GroupByobject, grouped rank(method='dense') cumsum() B 2 C 3
by values in index level named Ranks with no gaps. Cumulative sum. C 3 D 4
"ind". rank(method='min') cummax() Set-like Operations
Ranks. Ties get min rank. Cumulative max. x1 x2 pd.merge(ydf, zdf)
All of the summary functions listed above can be applied to a group. rank(pct=True) cummin() B 2 Rows that appear in both ydf and zdf
Additional GroupByfunctions: Ranks rescaled to interval [0, 1]. Cumulative min. C 3 (Intersection).
size() agg(function) rank(method='first') cumprod()
Size of each group. Aggregate group using function. Ranks. Ties go to first value. Cumulative product. x1 x2 pd.merge(ydf, zdf, how='outer')
A 1 Rows that appear in either or both ydf and zdf
Windows Plotting B 2 (Union).
C 3
df.expanding() df.plot.hist() df.plot.scatter(x='w',y='h') D 4 pd.merge(ydf, zdf, how='outer',
Return an Expanding object allowing summary functions to be Histogram for each column Scatter chart using pairs of points x1 x2 indicator=True)
applied cumulatively. A 1 .query('_merge == "left_only"')
df.rolling(n) .drop(columns=['_merge'])
Return a Rolling object allowing summary functions to be Rows that appear in ydf but not zdf (Setdiff).
applied to windows of length n. Cheatsheet for pandas (http://pandas.pydata.org/) originally written by Irv Lustig, Princeton Consultants, inspired by Rstudio Data Wrangling Cheatsheet
no reviews yet
Please Login to review.