196x Filetype PDF File size 0.04 MB Source: www.leeward.hawaii.edu
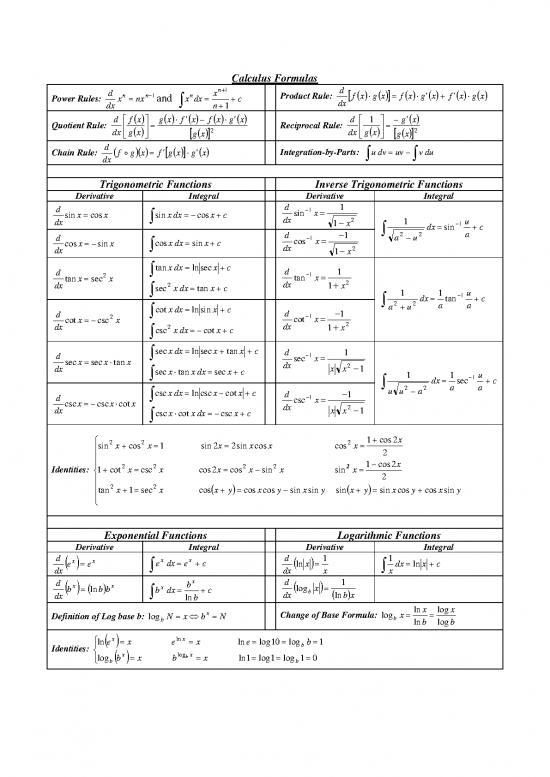
Calculus Formulas
d n n−1 n xn+1 Product Rule: d []() () () () () ()
Power Rules: x =nx and ∫x dx = +c dx f x ⋅ g x = f x ⋅ g' x + f ' x ⋅ g x
dx n+1
⎡ ⎤ ⎡ ⎤
() () () () ( ) ()
Quotient Rule: d ⎢ f x ⎥ = g x ⋅ f ' x − f x ⋅ g' x Reciprocal Rule: d ⎢ 1 ⎥ = − g' x
dx g()x 2 dx g()x 2
[]() []()
⎣ ⎦ g x ⎣ ⎦ g x
Chain Rule: d ( )() []() () Integration-by-Parts: u dv =uv − v du
dx f o g x = f ' g x ⋅ g' x ∫∫
Trigonometric Functions Inverse Trigonometric Functions
Derivative Integral Derivative Integral
d sinx = cosx ∫sinx dx = −cosx+c d sin−1 x = 1
dx dx 1−x2 ∫ 1 dx =sin−1 u + c
d d cos−1 x = −1 a2 −u2 a
dxcosx=−sinx ∫cosx dx =sinx+c dx 1−x2
d ∫tanx dx = lnsecx +c d 1
−
tan x = sec2 x tan 1 x =
dx ∫sec2 x dx = tan x + c dx 1+x2
1 dx = 1 tan−1 u + c
cot x dx = lnsin x + c ∫ a2 +u2 a a
d ∫ d − −1
cot x = −csc2 x cot 1 x =
dx ∫csc2 x dx = −cot x + c dx 1+x2
d ∫secx dx =lnsecx + tan x + c d sec−1 x = 1
dx secx =secx⋅tan x secx⋅tanx dx =secx+c dx x x2 −1
∫ ∫ 1 dx = 1 sec−1 u + c
cscx dx = lncscx−cotx +c d −1 u u2 −a2 a a
−
d cscx = −cscx⋅cotx ∫ csc 1 x =
dx ∫cscx⋅cotx dx=−cscx+c dx x x2 −1
⎧ 2 2 2 1+cos2x
sin x + cos x =1 sin 2x = 2sin xcos x cos x =
⎪ 2
⎪ 1−cos2x
⎪ 2 2 2 2 2
Identities: 1+ cot x = csc x cos2x = cos x −sin x sin x =
⎨ 2
⎪
⎪tan2 x +1=sec2 x cos()x + y = cos xcos y − sin xsin y sin()x + y = sin xcos y + cos xsin y
⎪
⎩
Exponential Functions Logarithmic Functions
Derivative Integral Derivative Integral
d x x ex dx = ex + c d ( ) 1 1
()
dx e =e ∫ dx ln x = x ∫ x dx = ln x + c
d x x x bx d ( ) 1
() log x =
b =()lnb b ∫b dx= +c b ()
dx lnb dx lnb x
Definition of Log base b: log N = x ⇔bx = N Change of Base Formula: log x = lnx = logx
b b lnb logb
⎧ x ln x
()
ln e =x e =x ln e = log10 = log b=1
Identities: ⎪ b
⎨ x log x
⎪ () b
logb b =x b =x ln1= log1= logb 1= 0
⎩
Infinite Series: Definitions & Tests
⎧ ∞ ()
⎪ an =a +a +a +... Infinite Series
∑ 1 2 3
⎪n=
⎪ 1
⎪ n ()
1. Series: ⎨s = a =a +a +...+a nth Partial Sum
⎪ n ∑ i 1 2 n
⎪ i=1
⎪ ∞ ()
if lim sn = s where s∈ℜ then an = s Infinite Sum
⎪ n→∞ ∑
⎩ n=1
∞ ⎧ a , if r <1
n 2 3 ⎪
2. Geometric Series: ar =a+ar+ar +ar +... = 1−r
∑ ⎨
n=0 ⎪diverges, if r ≥1
⎩
∞ converges, if p >1
3. P-Series: 1 ⎧
⇒
∑np ⎨diverges, if p≤1 if p =1, the series is called the harmonic series.
n=1 ⎩
⎧ ∞
∞ if lim a ≠0, then a diverges
⎪ n ∑ n
4. Quick Divergence Test: Given ⎪ n→∞
a ⇒
∑ n ⎨ n=1
n=1 ⎪
if lim an = 0, then No Conclusion! Do another test!
⎪ n→∞
⎩
⎧ ∞ ∞
⎪if an dn converges then an converges
∞ ⎪ ∫ ∑
5. Integral Test: Given a , a >0, a decreasing ⇒ ⎪ c n=c
∑ n n n ⎨ ∞ ∞
n=c ⎪if a dn diverges then a diverges
⎪ ∫ n ∑ n
⎪ c n=c
⎩
⎧ ∞
⎪ an converges, when p <1,
∑
⎪n=c
∞ a ⎪ ∞
n+1 ⎪
6. Ratio Test: Given a , a >0 ⇒ if lim = p then a diverges, when p >1,
n n ⎨ n
∑ n→∞ a ∑
n=c n ⎪n=c
⎪No Conclusion, when p =1
⎪
⎪
⎩
⎧ ∞
⎪ an converges, when p <1,
∑
⎪n=c
∞ 1 ⎪ ∞
n () ⎪
7. Root Test: Given a , a >0 ⇒ if lim a = lim a n = p then a diverges, when p >1,
n n n n ⎨ n
∑ n→∞ n→∞ ∑
n=c ⎪n=c
⎪No Conclusion, when p =1
⎪
⎪
⎩
∞ ∞ ⎧ if lim an = p, p > 0, p finite
⎪ n→∞ b
8. Limit Comparison Test: a and b , a >0, b >0 ⇒
∑ n ∑n n n ⎨ n
n=c n=c ⎪then both series converge or both diverge
⎩
∞ ∞ ⎧ if b converges then a converges,
9. Comparison Test: a and b , a ≥0, b ≥0, a ≤b ⇒ n n
∑ n ∑n n n n n ⎨
if an diverges then bn diverges
n=c n=c ⎩
∞ ∞
n n
10. Alternating Series Test: Given () ()
−1 an , if an >0, an+1 < an, lim an = 0, then −1 an converges
∑ n→∞ ∑
n=c n=c
no reviews yet
Please Login to review.