167x Filetype PDF File size 0.08 MB Source: www.sausd.us
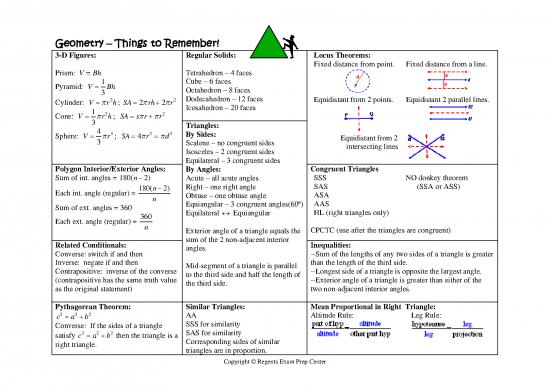
Geometry – Things to Remember!
3-D Figures: Regular Solids: Locus Theorems:
Fixed distance from point. Fixed distance from a line.
Prism: V = Bh Tetrahedron – 4 faces
1 Cube – 6 faces
Pyramid: VB= h Octahedron – 8 faces
3
2 2 Dodecahedron – 12 faces Equidistant from 2 points. Equidistant 2 parallel lines.
Cylinder: Vr=π h; SA=+22πrh πr Icosahedron – 20 faces
Cone: 1 2 2
Vr= π h; SA=+sπr πr
3 Triangles:
4 3 22
Sphere: Vr= π ; SA==4πr πd By Sides: Equidistant from 2
3 Scalene – no congruent sides intersecting lines
Isosceles – 2 congruent sides
Equilateral – 3 congruent sides
Polygon Interior/Exterior Angles: By Angles: Congruent Triangles
Sum of int. angles = 180(n−2) Acute – all acute angles SSS NO donkey theorem
Each int. angle (regular) = 180(n−2) Right – one right angle SAS (SSA or ASS)
n Obtuse – one obtuse angle ASA
Sum of ext. angles = 360 Equiangular – 3 congruent angles(60º) AAS
360 Equilateral ↔ Equiangular HL (right triangles only)
Each ext. angle (regular) = n
Exterior angle of a triangle equals the CPCTC (use after the triangles are congruent)
Related Conditionals: sum of the 2 non-adjacent interior Inequalities:
Converse: switch if and then angles. --Sum of the lengths of any two sides of a triangle is greater
Inverse: negate if and then than the length of the third side.
Contrapositive: inverse of the converse Mid-segment of a triangle is parallel --Longest side of a triangle is opposite the largest angle.
(contrapositive has the same truth value to the third side and half the length of --Exterior angle of a triangle is greater than either of the
as the original statement) the third side. two non-adjacent interior angles.
Pythagorean Theorem: Similar Triangles: Mean Proportional in Right Triangle:
222 AA Altitude Rule: Leg Rule:
ca=+b SSS for similarity
Converse: If the sides of a triangle
222 SAS for similarity
satisfy ca=+b then the triangle is a Corresponding sides of similar
right triangle. triangles are in proportion.
Copyright © Regents Exam Prep Center
Parallels: If lines are parallel … Quadrilaterals: Transformations:
Parallelogram: opp Trapezoid: Glide
sides parallel Only one set reflection is
opp sides = parallel sides. composition
opp angles = of a reflection
consec. angles supp Median of trap is and a
Corresponding angles are equal. diag bis each other parallel to both translation.
m<1=m<5, m<2=m<6, m<3=m<7, m<4=m<8 Rectangle: add 4 rt bases and = ½
sum bases. Isometry –
Alternate Interior angles are equal. angles, diag. = :
m<3=m<6, m<4=m<5 Rhombus: add 4 = Isosceles Trap: keeps length.
Alternate Exterior angles are equal. sides, diag. perp, diag legs =
m<1=m<8, m<2=m<7 bisect angles. base angles = Orientation –
Same side interior angles are supp. Square: All from diagonals = label order
m<3+m<5=180, m<4+m<6=180 above. opp angles supp
Circle Segments Circle Angles:
In a circle, a radius perpendicular to a chord Central angle = arc Inscribed angle = half arc Angle by tangent/chord = half arc
bisects the chord.
Intersecting Chords Rule:
(segment part)(segment part) =
(segment part)(segment part)
Secant-Secant Rule: Angle formed by 2 chords Angle formed by 2 tangents, or 2 secants, or a tangent/secant
(whole secant)(external part) = = half the sum of arcs = half the difference of arcs
(whole secant)(external part)
Secant-Tangent Rule:
2
(whole secant)(external part) = (tangent)
Hat Rule: Two tangents are equal.
Slopes and Equations: Coordinate Geometry Formulas: Circles:
vertical change y − y Distance Formula: Equation of circle center at origin:
21
m= =. 22 222
horizontal change x −x dx=−()x+(y−y) x + yr= where r is the radius.
21 21 21 Equation of circle not at origin:
ym=+xb slope-intercept Midpoint Formula:
222
yy−=m(x−x) point-slope x ++xyy ()x − hy+−(k)=r where (h,k) is the
11 ⎛⎞
1212
(,xy)= ,
⎜⎟center and r is the radius.
22
⎝⎠
Copyright © Regents Exam Prep Center
no reviews yet
Please Login to review.