180x Filetype PDF File size 0.87 MB Source: todaysveterinarypractice.com
ACVN NUTRITION NOTES Peer Reviewed
The Protein Paradigm:
ASSESSING DIETARY PROTEIN
IN HEALTH & DISEASE
Justin Shmalberg, DVM, Diplomate ACVN & ACVSMR
University of Florida The American College
of Veterinary Nutrition
Dietary protein is one of 3 primary metabolic Amino acids are absorbed in the gastrointestinal (acvn.org) and Today’s
fuels of the body that, together with fat and tract following disruption of peptide bonds by Veterinary Practice
are delighted to bring
carbohydrates, provides cellular energy. Amino pepsin, trypsin, chymotrypsin, and peptidases. you the Nutrition
acids extracted from dietary proteins are also used Cells use active transport to obtain amino acids Notes column, which
by animals to synthesize the functional proteins from the plasma and, subsequently, convert them provides the highest
quality, cutting edge
required for normal physiologic functions. to cell, tissue, or plasma proteins in target tissues. information on
Proteins, produced by combining amino acids, companion animal
are unique energy sources because they contain Amino Acid Structure nutrition, provided by
the ACVN’s foremost
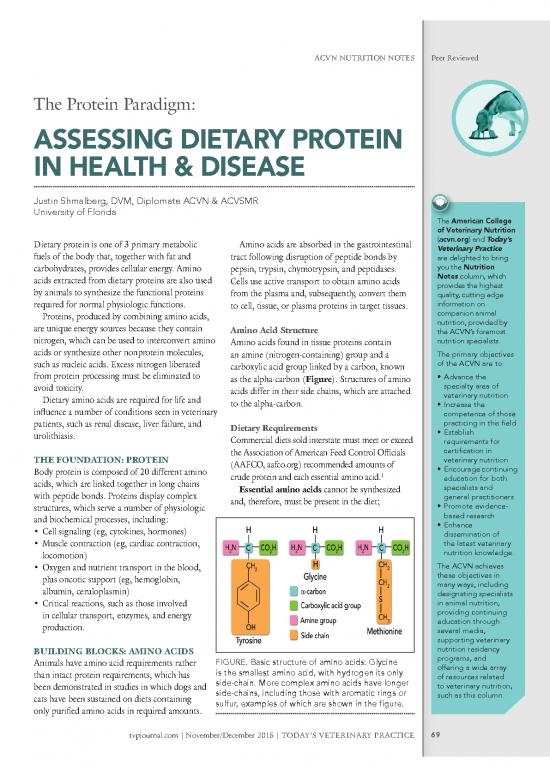
nitrogen, which can be used to interconvert amino Amino acids found in tissue proteins contain nutrition specialists.
acids or synthesize other nonprotein molecules, an amine (nitrogen-containing) group and a The primary objectives
such as nucleic acids. Excess nitrogen liberated carboxylic acid group linked by a carbon, known of the ACVN are to:
from protein processing must be eliminated to as the alpha-carbon (Figure). Structures of amino • Advance the
avoid toxicity. acids differ in their side chains, which are attached specialty area of
Dietary amino acids are required for life and to the alpha-carbon. veterinary nutrition
infl uence a number of conditions seen in veterinary • Increase the
competence of those
patients, such as renal disease, liver failure, and Dietary Requirements practicing in this field
urolithiasis. Commercial diets sold interstate must meet or exceed • Establish
requirements for
the Association of American Feed Control Offi cials certification in
THE FOUNDATION: PROTEIN (AAFCO, aafco.org) recommended amounts of veterinary nutrition
Body protein is composed of 20 different amino 1 • Encourage continuing
acids, which are linked together in long chains crude protein and each essential amino acid. education for both
with peptide bonds. Proteins display complex Essential amino acids cannot be synthesized specialists and
and, therefore, must be present in the diet; general practitioners
structures, which serve a number of physiologic • Promote evidence-
and biochemical processes, including: based research
• Cell signaling (eg, cytokines, hormones) • Enhance
dissemination of
• Muscle contraction (eg, cardiac contraction, the latest veterinary
locomotion) nutrition knowledge.
• Oxygen and nutrient transport in the blood, The ACVN achieves
plus oncotic support (eg, hemoglobin, these objectives in
albumin, ceruloplasmin) many ways, including
designating specialists
• Critical reactions, such as those involved in animal nutrition,
in cellular transport, enzymes, and energy providing continuing
production. education through
several media,
supporting veterinary
BUILDING BLOCKS: AMINO ACIDS nutrition residency
Animals have amino acid requirements rather FIGURE. Basic structure of amino acids: Glycine programs, and
than intact protein requirements, which has is the smallest amino acid, with hydrogen its only offering a wide array
side-chain. More complex amino acids have longer of resources related
been demonstrated in studies in which dogs and side-chains, including those with aromatic rings or to veterinary nutrition,
cats have been sustained on diets containing such as this column.
only purifi ed amino acids in required amounts. sulfur, examples of which are shown in the fi gure.
tvpjournal.com | November/December 2015 | TODAY’S VETERINARY PRACTICE 69
Peer Reviewed ACVN NUTRITION NOTES
humans, dogs, and cats need 9, 10, and 11 essential divided into glucogenic and ketogenic amino acids
2
amino acids in the diet, respectively (Table 1). depending on whether they can be used to produce
Nonessential amino acids in crude protein can glucose or acetyl coenzyme A, respectively.
provide nitrogen sources for biosynthetic pathways. In many pet foods, especially those with lower
Limiting amino acids are those amino acids protein content, taurine is added, but it is only
present in a food in the lowest amounts with essential in cats because, in dogs, enzymatic
regard to what the animal requires. These amino conversion of cysteine to taurine is more
acids can adversely affect effi ciency of protein active. Defi ciency most notably causes dilated
utilization and the amount of protein synthesis cardiomyopathy in dogs and cats and central
2 3
that occurs. In pet foods, methionine and lysine retinal degeneration in cats.
are often the limiting amino acids. While some species reduce food intake when
Excess amino acids can be used for fuel and are fed an amino-acid defi cient diet, cats are a notable
TABLE 1.
Essential & Selected Nonessential Amino Acids for Dogs & Cats
AMINO ACID SELECTED FUNCTIONS & REPORTED THERAPEUTIC BENEFITS
Essential Amino Acids
Branched Chain • Common constituents of proteins
Valine (Val) • Leucine supplementation may enhance lean body mass and prevent muscle
Leucine (Leu) catabolism
Isoleucine (Ile)
Arginine (Arg) • Stimulator and intermediate of urea cycle, preventing hyperammonemia
• Nitric oxide precursor
• Supplemented for immune function, cancer, and critical illness
Histidine (His) • High in hemoglobin
• Precursor to histamine
Lysine (Lys) • Precursor to carnitine
• Limiting in cooked cereal grains
• Lysine and carnitine may be helpful for weight loss
• Confl icting studies on benefi ts in cats with herpesvirus
Methionine (Met) • Limiting in many pet foods
• Hair and glutathione synthesis
• Methyl donor
• Translation (tRNA decodes mRNA sequences into proteins)
• Taurine precursor (dogs)
Phenylalanine • Thyroid hormones
(Phe) • Catecholamines
• Melanin
Tryptophan (Trp) • Serotonin and melatonin precursor
• Niacin (Vitamin B precursor, dogs)
3
Threonine (Thr) • Provides the site for phosphorylation of many enzymes
• Modulates neurotransmitter balance in the brain
Cats • Constituent of bile
Taurine (Tau) • Positive inotrope
• Supplemented in nutritional and nonnutritional dilated cardiomyopathy
Selected Nonessential Amino Acids
Glutamine (Gln) • Most abundant free amino acid
• Nitrogen store in muscle
• Primary fuel of enterocyte
• Supplemented to stabilize gastrointestinal barrier and combat cachexia
Asparagine (Asn) • Uncommonly supplemented
• Essential for some cancer cells
• Drug target of L-asparaginase, which converts to aspartic acid
70 TODAY’S VETERINARY PRACTICE | November/December 2015 | tvpjournal.com
ACVN NUTRITION NOTES Peer Reviewed
exception, presumably because their evolutionary Digestibility of animal products depends on the:
prey were never limiting in protein. • Animal from which it is derived
• Part(s) of the carcass used
PROTEIN SOURCES • Processing
Protein and essential amino acids can be derived • Cooking temperature and pressure.
from animal or plant sources. Digestibility of protein is both diffi cult to assess
from information found on food labels and to
Meat Sources measure because typical methods are not able to
Meats refer to striated muscle from mammals and separate digestibility by the animal versus that of
can contain other surrounding tissue, such as fat or intestinal bacteria.
skin. Muscle meat contains a large concentration of Atwater factors are used in human nutrition to
protein, but substantial amounts can also be found predict the amount of energy in a certain mass of
in other products, such as organ tissues. food. These factors assume a certain digestibility
Most pet foods rely on parts of the animal that and refl ect the anticipated amount of energy that is
are not destined for human consumption, and actually available after energetic losses in the urine
ingredients listed as a general descriptor, such and feces. The value used for many foods consumed
as chicken or beef, need not contain the whole by humans is 4 kilocalories (kcal) per gram of
2
animal but rather selected parts. For example, protein.
poultry or chicken, if listed on a label, refers to the AAFCO uses a modifi ed factor of 3.5 kcal per
clean combination of fl esh and skin with or without gram for commercial pet foods, as it is assumed
1
accompanying bone, derived from parts or whole that extruded pet foods have reduced digestibility.
carcasses of poultry.1 Fortunately, most foods contain excess amino acids
Some more expensive canned diets are marketed and crude protein due to the diffi culty of precisely
as containing prime cuts of meat (eg, chicken measuring protein digestibility.
breast, sirloin), but current labeling guidelines PROTEIN MODIFICATION FOR
make such claims diffi cult to evaluate. LIFE STAGES
A meat meal refers to a product that contains Requirements for dietary amino acids present in
similar inclusions as meats but is rendered and protein are well established for various life stages
dried to contain minimal moisture. Meals are and types of animals:
typically slightly higher in protein than meats, and • Growth, lactation, and late gestation increase
generally provide more calories by weight than protein and amino acid requirements, primarily
fresh meat; therefore, their appearance fi rst on an due to increased biosynthetic reactions (Table 2,
ingredient list suggests that they may provide the page 72).
primary source of calories in the food, which may • Cats (obligate carnivores) have higher protein
not be the case for meats. requirements than dogs (omnivores).
Plant Sources • Performance animals may require elevated
7
Plant proteins can provide digestible protein and dietary concentrations of protein.
amino acids. Many cereal grains are processed • Senior dogs have nearly double the protein
to produce starch, fat, and gluten. Gluten is the turnover of younger dogs and may require
protein containing fraction of grains. increased dietary protein due to decreased
Vegetable proteins may be benefi cial for muscle anabolism and, perhaps, decreased
8
reducing nitrogenous waste, with implications for protein digestibility or conversion.
4
hepatic encephalopathy and urate stones. Concerns with Glutens
Digestibility While gluten free is a common label in human foods, true gluten sensitivity
Animal proteins are generally more digestible appears to be rare in dogs and cats, but has been documented in certain
than plant proteins. However, this is not always lines of Irish setters. Adverse effects from long-term gluten exposure in
the case; for example, corn gluten can have better domestic animals have not been documented in scientifi c studies.
5 Fish, casein (a dairy In addition, owners may express concern about plant proteins due to
availability than lamb meal. recalls in response to melamine contamination of wheat gluten-containing
protein), and egg are animal proteins that often 6
foods.
display the highest digestibility.
tvpjournal.com | November/December 2015 | TODAY’S VETERINARY PRACTICE 71
Peer Reviewed ACVN NUTRITION NOTES
Protein modifi cation TABLE 2.
has been suggested for 2
weight loss, renal disease, Species-Specifi c Protein Recommendations by Life Stage
urolithiasis, liver failure, LIFE STAGES RECOMMENDED ALLOWANCE OF PROTEIN
food allergy, and other (g/1000 kcal)
conditions. However, no Canine Feline
evidence exists that protein Growth(4–14 weeks) 56
restriction in healthy, older 56
8 Growth(> 14 weeks) 44
dogs prevents disease.
CLINICAL Adult maintenance 25 50
IMPLICATIONS OF Senior 75 > 50
DIETARY PROTEIN Late gestation & 50 53
Performance lactation
The nutritional needs for See Clinical Resources at tvpjournal.com to read:
exercise and performance in • AAFCO Defi nitions for Common Pet Food Ingredients
• Beyond the Guaranteed Analysis: Comparing Pet Foods
dogs are well established.
Less is known about cats as they infrequently • Dietary thermogenesis: Cats had higher energy
perform vigorous exercise in competitive situations. expenditure when a greater number of calories
12
Dogs utilize adenosine triphosphate and carbohydrate came from protein and, in a separate study,
reserves for initial bursts of energy; then rely on fat were able to consume 10% more food during a
2 13
for endurance. Excess protein is used for energy weight loss protocol.
and does not increase body stores. Protein catabolism
acts as a reserve of substrates for gluconeogenesis and Feline Health
ketogenesis. Leucine administration, however, may help Cats display metabolic adaptations consistent with
prevent muscle catabolism.9 an obligate carnivore:
Considerations for performance dogs include: • Higher protein requirements
• Sprinting dogs and most agility dogs do not • Increased insulin response to amino acids
require more protein than that found in most • Lack of sweet taste receptors
moderate protein diets (60–90 g/1000 kcal) • Limited downregulation of gluconeogenesis
• Endurance dogs likely require around 75 g/1000 • Requirement for preformed taurine.2
7 Cats prefer a high dietary protein content (130
kcal protein, based on limited studies
• High protein, low carbohydrate diets may g/1000 kcal), which is consistent with diets of feral
7 10,14,15
impair performance in some cases. cats and the composition of rodents. Cats
do, however, effi ciently absorb and utilize dietary
Weight Loss carbohydrates in amounts commonly found in
16
Diets with elevated amounts of protein are pet foods. Long-term comparisons of cats fed
recommended for both overweight cats and diets with different concentrations of protein and
dogs. Many veterinary diets for weight loss carbohydrates are not available.
are formulated with increased protein (> 90 While high protein diets may improve diabetic
17
g/1000 kcal). Diets for weight management or control or remission, there is no association
maintenance without increased protein are not between high carbohydrate diets and obesity, the
18
appropriate for weight loss protocols. main risk factor for feline diabetes.
High protein diets are associated with:
• Increased palatability: Cats show a preference Lower Urinary Tract Disease
for high protein diets, while dogs prefer protein Many therapeutic diets for lower urinary tract
10 diseases are restricted in dietary protein. The
over carbohydrates when fat is reduced
• Preservation of lean body mass (during weight evidence for such an approach varies by condition.
loss)11 Canine struvite uroliths are almost always a
• Prevention of defi ciencies associated with product of infection; protein restriction has been
limiting amino acids (when calories are used in canine struvite dissolution diets to reduce
19
signifi cantly restricted) urea, a substrate for urease-positive bacteria.
72 TODAY’S VETERINARY PRACTICE | November/December 2015 | tvpjournal.com
no reviews yet
Please Login to review.