139x Filetype PDF File size 0.64 MB Source: samples.jbpub.com
81644_CH12_179_190_QXP6.qxd 9/14/10 11:42 AM Page 179
© Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC © Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC
NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION
Chapter 12
Fluid and Electrolyte Disturbances Associated with
© Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC © Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC
Tube Feedings
NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION
© Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC © Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC
NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION
© Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC © Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC
Clinicians generally agree with the philosophy that “When FORMULA OSMOLALITY
NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION
the gut works, use it.” That is, if gastrointestinal function is
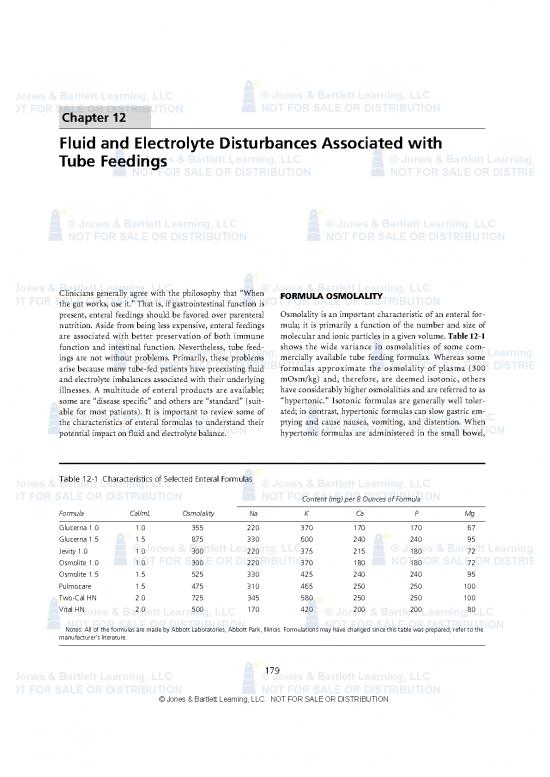
present, enteral feedings should be favored over parenteral Osmolality is an important characteristic of an enteral for-
nutrition. Aside from being less expensive, enteral feedings mula; it is primarily a function of the number and size of
are associated with better preservation of both immune molecular and ionic particles in a given volume. Table 12-1
function and intestinal function. Nevertheless, tube feed- shows the wide variance in osmolalities of some com-
© Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC © Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC
ings are not without problems. Primarily, these problems mercially available tube feeding formulas. Whereas some
NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION
arise because many tube-fed patients have preexisting fluid formulas approximate the osmolality of plasma (300
and electrolyte imbalances associated with their underlying mOsm/kg) and, therefore, are deemed isotonic, others
illnesses. A multitude of enteral products are available; have considerably higher osmolalities and are referred to as
some are “disease specific” and others are “standard” (suit- “hypertonic.” Isotonic formulas are generally well toler-
able for most patients). It is important to review some of ated; in contrast, hypertonic formulas can slow gastric em-
© Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC © Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC
the characteristics of enteral formulas to understand their ptying and cause nausea, vomiting, and distention. When
NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION
potential impact on fluid and electrolyte balance. hypertonic formulas are administered in the small bowel,
Table 12-1 Characteristics of Selected Enteral Formulas
© Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC © Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC
NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION
Content (mg) per 8 Ounces of Formula
Formula Cal/mL Osmolality Na K Ca P Mg
Glucerna 1.0 1.0 355 220 370 170 170 67
Glucerna 1.5 1.5 875 330 600 240 240 95
© Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC © Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC
Jevity 1.0 1.0 300 220 375 215 180 72
NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION
Osmolite 1.0 1.0 300 220 370 180 180 72
Osmolite 1.5 1.5 525 330 425 240 240 95
Pulmocare 1.5 475 310 465 250 250 100
Two-Cal HN 2.0 725 345 580 250 250 100
Vital HN 2.0 500 170 420 200 200 80
© Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC © Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC
NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION
Notes: All of the formulas are made by Abbott Laboratories, Abbott Park, Illinois. Formulations may have changed since this table was prepared; refer to the
manufacturer’s literature.
179
© Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC © Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC
NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION
© Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC. NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION.
81644_CH12_179_190_QXP6.qxd 9/14/10 11:42 AM Page 180
© Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC © Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC
NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION
180 CHAPTER 12 FLUID AND ELECTROLYTE DISTURBANCES ASSOCIATED WITH TUBE FEEDINGS
they create an osmotic gradient that pulls water into the dence to the contrary, a standard formula is the product of
intestine. If the fluid is not adequately absorbed, cramping 2
choice for the majority of tube-fed patients.
© Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC © Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC
and diarrhea may result. For this reason, hypertonic for- Calorie-Dense Formulas
NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION
mulas are introduced slowly until the body has time to
adapt to them. A calorie-dense formula usually contains 2.0 kilocalories
A formula’s osmolality affects the renal solute load and per milliliter of fluid and is used in patients who require
thus the water requirements. Renal solute load can be fluid restriction—for example, patients with congestive
defined as the sum of substances that must be excreted by heart failure, syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hor-
© Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC © Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC
the kidneys (such as urea, potassium, sodium, and chlo- mone (SIADH), or renal failure. For instance, for a patient
NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION
ride). A high renal solute load (created by nutrient use) requiring 1800 kcal/day, the amount of water delivered in
requires a large water volume for excretion. If enough water the formula could be reduced by 900 mL merely by convert-
is not provided, the patient will become dehydrated. There- ing from a 1.0 calorie per milliliter formula to a 2.0 calories
fore, the renal solute load imposed by a formula should be per milliliter formula.3
considered in patients with impaired renal function and in
© Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC © Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC
those with increased losses of body fluids (such as from Fiber-Containing Formulas
NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION
fever or diarrhea). Fiber-containing formulas may be helpful in patients with
A number of liquid medications administered via feeding diarrhea or constipation. The fiber added to the formula
tubes are hyperosmolar and can cause osmotic diarrhea if increases stool bulk and helps to regulate bowel transit
given undiluted, especially into the small intestine. Among 4
time. Recall that the colon is the final site of water and elec-
these products are acetaminophen, potassium chloride, and trolyte absorption and ultimately determines fecal composi-
© Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC © Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC
phosphosoda. For example, the osmolality of an acetamino- tion. In patients who can tolerate high-residue formulas,
NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION
phen solution can range between 3000 and 6000 mOsm/kg. use of a high-fiber formula is thought to increase the
The delivery of hyperosmolar preparations should be lim- sodium and water absorptive ability of the colon, thereby
ited to the stomach; even then, the medications should be minimizing fecal fluid loss. For example, in a study of a
diluted before administration and water flushes given group of 20 critically ill patients randomized to either a sol-
through the tube before and after delivery. This action not uble fiber formula or a fiber-free formula, the number of
© Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC © Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC
only dilutes the medication, but also enhances its absorp- liquid stools was significantly lower in the fiber group.5 It
NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION
tion. Of course, it is important to keep any fluid restrictions has been recommended that this type of formula be consid-
in mind. At times, the parenteral route may be necessary for ered in patients for whom tube feedings will be the sole
electrolyte supplements when they are not tolerated by the source of nutrition for a long period of time, especially if
GI tract. intestinal disease is present.6
© Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC © Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC
TYPES OF FORMULAS Elemental Formulas
NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION
Commercial sources supply standardized as well as special- An elemental formula contains hydrolyzed protein and sim-
ized products targeted to patients with specific problems, ple sugars; further, it has a low fat content.7 This type of for-
such as renal, hepatic, and respiratory failure. Because mula is administered to patients with severe malabsorption,
numerous enteral formula products are available, it is such as may be seen with intestinal atrophy or loss of absorp-
© Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC © Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC
important to read the literature supplied by manufacturers. tive surface associated with profound malnutrition, critical
NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION
Enteral formulas are classified as standard, elemental, or spe- illness, and acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS).
cialized, with multiple formulas available in each category.1 Research reports focusing on the efficacy of elemental
diets provide mixed findings. For example, several studies
Standard Formulas have indicated that peptide-based formulas are helpful in
avoiding diarrhea in hypoalbuminemic, critically ill
© Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC patients.8,9 © Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC
A standard formula contains intact protein and is similar to In contrast, a larger prospective study did not
NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION
an average diet for healthy individuals; it can be adminis- demonstrate any advantage in a peptide-based formula over
10
tered to patients with normal digestion. These formulas are a standard, polymeric formula. Further, a meta-analysis of
available with and without added fiber. Unless there is evi- 10 trials involving a total of 334 patients found no significant
© Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC © Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC
NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION
© Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC. NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION.
81644_CH12_179_190_QXP6.qxd 9/14/10 11:42 AM Page 181
© Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC © Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC
NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION
Fluid and Electrolyte Disturbances Associated with Tube Feedings 181
difference in the efficacy of elemental versus non-elemental Formulas for Hepatic Disease
11
formulas. One group of investigators recommended that For patients with hepatic insufficiency who cannot tolerate
© Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC © Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC
the use of elemental formulas be limited to specific condi- the protein contained in standard enteral formulas, special-
NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION
tions in which absorption has been definitely shown to be ized products are available that are calorically dense and low
12
impaired. Another group of investigators indicated that in protein (to minimize ammonia production). Hepatic
enteral feeding with elemental diets can lessen diarrhea in formulas contain increased amounts of branched chain
patients infected with human immunodeficiency virus amino acids and reduced amounts of aromatic amino
13
(HIV). Elemental formulas are more expensive than stan- acids.16 Theoretically, hepatic enteral formulas should
© Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC © Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC
dard formulas and have an unpleasant taste and odor. reduce the neurological symptoms that occur with hepatic
NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION
encephalopathy.17 These products are expensive, however,
Specialized Formulas and their use is generally limited to patients with hepatic
Formulas for Renal Disease failure associated with encephalopathy.
Compared to standard enteral formulas, formulas designed Formulas for Diabetes
© Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC © Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC
specifically for renal patients are calorically dense, are lower The carbohydrate content in standard enteral formulas may
NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION
in protein, and have lower concentrations of potassium, not be tolerated by patients with diabetes or stress-induced
magnesium, and phosphorus. Such a formulation is used glucose intolerance. Thus use of a formula with complex
because patients with renal failure have difficulty excreting carbohydrates (such as fructose) and fiber improves blood
urea (the end product of protein metabolism), electrolytes sugar control by delaying gastric emptying and reducing
18
(especially potassium, phosphorus, and magnesium), and intestinal transit time. Trends toward better glycemic con-
© Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC © Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC
fluid. Thus an enteral formula for a renal failure patient not trol with the use of specialized diabetic formulas have been
NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION
19–21
receiving dialysis should be calorically dense and restricted reported in several small studies. However, it is unclear
in protein and minerals. The renal enteral formula contains if the difference in glycemic control between specialized
a high percentage of essential amino acids (allowing for pro- diabetic formulas and standard formulas is clinically signifi-
tein synthesis with minimal production of urea). Patients cant. Given the current emphasis on tight blood glucose
with renal failure who are being tube fed require frequent control via insulin drips in critically ill patients, special dia-
© Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC © Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC
monitoring of electrolyte values and fluid status. Standard betic formulas may be used less often.
NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION
enteral formulas are usually acceptable for patients with
mild renal impairment or those who are on dialysis.14
FLUID AND ELECTROLYTE DISTURBANCES
Formulas for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary ASSOCIATED WITH TUBE FEEDINGS
Disease Tube-fed patients tend to have the fluid and electrolyte dis-
© Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC © Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC
Compared to standard formulas, enteral formulas for pa- turbances associated with their underlying disease and
NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION
tients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) treatment conditions. Theoretically, then, it should be pos-
are lower in carbohydrate and higher in fat—a formulation sible to observe all types of electrolyte disturbances in tube-
intended to lower carbon dioxide production and, there- fed patients. In addition, factors related to the enteral
fore, improve pulmonary status. Recall that metabolism of formula itself can produce disturbances if these products
are used incorrectly. A combination of electrolyte imbal-
© Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC © Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC
carbohydrate yields more carbon dioxide than does metab-
olism of fat. Lessening the formation of carbon dioxide ances is associated with refeeding syndrome, a potentially
NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION
reduces the workload on the lungs, which are responsible deadly complication.
for eliminating carbon dioxide.
It has been pointed out that the amount of carbon dioxide Refeeding Syndrome
generated is more a function of the number of calories deliv-
© Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC 15 Definition © Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC
ered than of the formula’s fat-to-carbohydrate ratio. For
NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION
this reason, it is important to not overfeed pulmonary Refeeding syndrome (RFS) comprises a constellation of
patients. Moreover, it is more difficult to wean a patient from metabolic derangements that can occur when either par-
a mechanical ventilator when excessive calories are delivered. enteral or enteral nutrients are administered to a patient
© Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC © Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC
NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION
© Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC. NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION.
81644_CH12_179_190_QXP6.qxd 9/14/10 11:42 AM Page 182
© Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC © Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC
NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION
182 CHAPTER 12 FLUID AND ELECTROLYTE DISTURBANCES ASSOCIATED WITH TUBE FEEDINGS
remains a serious problem during aggressive enteral feeding
who has been malnourished for a period ranging from days
to weeks.22 Although parenteral nutrition has received more of starving patients. Despite the phosphate content in
© Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC © Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC
attention as a precipitator of RFS, enteral feedings are not enteral formulas, patients with protein-energy malnutrition
NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION
without risk. For example, the sudden deaths of four mal- can develop severe hypophosphatemia during enteral feed-
nourished children within 6 to 9 days of starting high- ings; additive risk factors include chronic alcoholism and
23 26
caloric enteral feedings have been reported. intestinal malabsorptive conditions. For this reason, it is
The major electrolyte imbalances in RFS are hypophos- important to monitor serum phosphate levels daily for at
phatemia, hypokalemia, and hypomagnesemia (discussed least 1 week after commencement of feedings in malnour-
© Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC © Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC
separately later in this chapter). These imbalances are asso- ished patients.
NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION
ciated with many of the symptoms of RFS (Table 12-2).
Other problems associated with this syndrome include fluid Hypokalemia. Hypokalemia is a component of the refeed-
and sodium retention, hyperglycemia, thiamine deficiency, ing syndrome. Adding to the problem are other causes of
and neurologic and hematolic complications, occurring hypokalemia, including the use of potassium-losing diuret-
within the first few days of feeding a starving patient.24 ics and diarrhea. As shown in Table 12-1, the potassium
© Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC © Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC
While the pathophysiology of RFS is complex, it is primarily content of tube feeding formulas varies. Hypokalemia can
NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION
the result of an acute intracellular shift of electrolytes result if the potassium intake is chronically less than body
(phosphate, potassium, and magnesium), increased requirements.
demand for phosphate during tissue anabolism, and forma-
tion of high-energy intracellular bonds.25 Hypomagnesemia. Hypomagnesemia is another compo-
Potentially life-threatening complications of RFS include nent of RFS. As with the other primary cellular electrolytes
© Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC © Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC
cardiac arrhythmias, heart failure, respiratory failure, and (potassium and phosphorus), extracellular magnesium
NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION
hematologic derangements. (See Case Study 11-3.) Table deficiency may result if inadequate amounts are present in
12-3 summarizes selected risk factors associated with this the formula or added as supplements (either enterally or
syndrome. parenterally).
Major Electrolyte Problems Sodium and Water Retention. For an unknown reason, the
© Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC © Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC
Hypophosphatemia. As indicated previously, refeeding body retains fluid during RFS, causing the extracellular
NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION
causes phosphates to shift into the cells during tissue syn- space to expand. This fluid retention increases cardiac
thesis; when this happens, the plasma phosphate level may workload, to the point that it may precipitate heart failure
drop precipitously. Hypophosphatemia tends to occur less in patients with cardiovascular disease. The increased fluid
often in enterally fed patients than in those who receive retention, coupled with the adverse cardiac effects of
total parenteral nutrition (TPN), because enteral nutrition hypophosphatemia, hypokalemia, and hypomagnesemia,
© Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC © Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC
solutions usually contain adequate phosphate for patients places all patients with this syndrome at risk for adverse car-
NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION
with normal phosphate stores. However, this imbalance diac events.
Table 12-2 Selected Clinical Features of Refeeding Syndrome and Associated Imbalances
© Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC © Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC
Clinical Feature Probable Associated Imbalances
NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION
Paresthesias and muscle weakness Hypokalemia, hypophosphatemia
Cardiac dysrhythmias Hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia
Decreased cardiac muscle strength Hypophosphatemia
Respiratory failure Hypophosphatemia, hypokalemia
© Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC © Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC
Congestive heart failure Hypophosphatemia, salt and water retention
Rhabdomyolysis, muscle pain Hypophosphatemia
NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION
Dysfunction of erythrocytes, leukocytes, and platelets Hypophosphatemia
Slowed gastrointestinal motility Hypokalemia
© Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC © Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC
NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION
© Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC. NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION.
no reviews yet
Please Login to review.