230x Filetype PDF File size 0.12 MB Source: www.kau.edu.sa
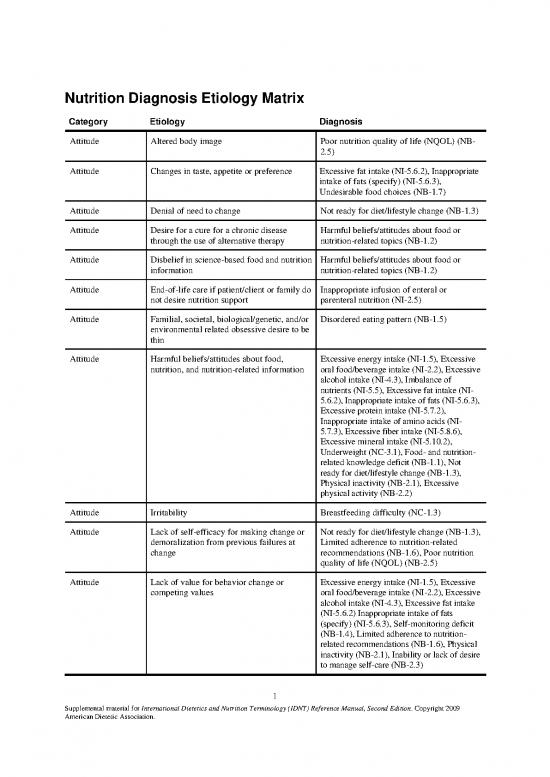
Nutrition Diagnosis Etiology Matrix
Category Etiology Diagnosis
Attitude Altered body image Poor nutrition quality of life (NQOL) (NB-
2.5)
Attitude Changes in taste, appetite or preference Excessive fat intake (NI-5.6.2), Inappropriate
intake of fats (specify) (NI-5.6.3),
Undesirable food choices (NB-1.7)
Attitude Denial of need to change Not ready for diet/lifestyle change (NB-1.3)
Attitude Desire for a cure for a chronic disease Harmful beliefs/attitudes about food or
through the use of alternative therapy nutrition-related topics (NB-1.2)
Attitude Disbelief in science-based food and nutrition Harmful beliefs/attitudes about food or
information nutrition-related topics (NB-1.2)
Attitude End-of-life care if patient/client or family do Inappropriate infusion of enteral or
not desire nutrition support parenteral nutrition (NI-2.5)
Attitude Familial, societal, biological/genetic, and/or Disordered eating pattern (NB-1.5)
environmental related obsessive desire to be
thin
Attitude Harmful beliefs/attitudes about food, Excessive energy intake (NI-1.5), Excessive
nutrition, and nutrition-related information oral food/beverage intake (NI-2.2), Excessive
alcohol intake (NI-4.3), Imbalance of
nutrients (NI-5.5), Excessive fat intake (NI-
5.6.2), Inappropriate intake of fats (NI-5.6.3),
Excessive protein intake (NI-5.7.2),
Inappropriate intake of amino acids (NI-
5.7.3), Excessive fiber intake (NI-5.8.6),
Excessive mineral intake (NI-5.10.2),
Underweight (NC-3.1), Food- and nutrition-
related knowledge deficit (NB-1.1), Not
ready for diet/lifestyle change (NB-1.3),
Physical inactivity (NB-2.1), Excessive
physical activity (NB-2.2)
Attitude Irritability Breastfeeding difficulty (NC-1.3)
Attitude Lack of self-efficacy for making change or Not ready for diet/lifestyle change (NB-1.3),
demoralization from previous failures at Limited adherence to nutrition-related
change recommendations (NB-1.6), Poor nutrition
quality of life (NQOL) (NB-2.5)
Attitude Lack of value for behavior change or Excessive energy intake (NI-1.5), Excessive
competing values oral food/beverage intake (NI-2.2), Excessive
alcohol intake (NI-4.3), Excessive fat intake
(NI-5.6.2) Inappropriate intake of fats
(specify) (NI-5.6.3), Self-monitoring deficit
(NB-1.4), Limited adherence to nutrition-
related recommendations (NB-1.6), Physical
inactivity (NB-2.1), Inability or lack of desire
to manage self-care (NB-2.3)
1
Supplemental material for International Dietetics and Nutrition Terminology (IDNT) Reference Manual, Second Edition. Copyright 2009
American Dietetic Association.
Nutrition Diagnosis Etiology Matrix
Category Etiology Diagnosis
Attitude Lacks motivation and or readiness to apply Undesirable food choices (NB-1.7)
or support systems change
Attitude Negative impact of current or previous Poor nutrition quality of life (NQOL) (NB-
medical nutrition therapy (MNT) 2.5)
Attitude Not ready for diet/lifestyle change Overweight/Obesity (NC-3.3), Self-monitor-
ing deficit (NB-1.4), Inability or lack of desire
to manage self-care (NB-2.3), Poor nutrition
quality of life (NQOL) (NB-2.5)
Attitude Perception of inadequate milk supply Breastfeeding difficulty (NC-1.3)
Attitude Perception that lack of resources (e.g., time,
financial, or interpersonal) prevent:
Selection/food choices consistent with Undesirable food choices (NB-1.7)
recommendations
Changes Not ready for diet/lifestyle change (NB-1.3),
Limited adherence to nutrition-related
recommendations (NB-1.6)
Sufficient level of activity Physical inactivity (NB-2.1)
Self-monitoring Self-monitoring deficit (NB-1.4), Inability or
ge self-care (NB-2.3)
lack of desire to mana
Attitude Unwilling or disinterested in:
Learning/applying information Food- and nutrition-related knowledge deficit
(NB-1.1), Not ready for diet/lifestyle change
(NB-1.3), Limited adherence to nutrition-
related recommendations (NB-1.6), Undesir-
able food choices (NB-1.7), Inability or lack
of desire to manage self-care (NB-2.3)
Reducing energy intake Excessive energy intake (NI-1.5)
Reducing intake Excessive oral food/beverage intake (NI-2.2)
Tracking progress Self-monitoring deficit (NB-1.4)
Attitude Unwillingness to consume fiber-containing Inadequate fiber intake (NI-5.8.5)
foods
Attitude Weight regulation/preoccupation significant- Disordered eating pattern (NB-1.5)
y influences self-esteem
l
Behavior Addictive behavior Excessive exercise (NB-2.2)
Behavior Consumption of high-dose nutrient supple- Imbalance of nutrients (NI-5.5)
ments
Behavior Eating behavior serves a purpose other than Harmful beliefs/attitudes about food or
(e.g., pica) pics (NB-1.2)
nourishment nutrition-related to
Behavior Excess energy intake Overweight/Obesity (NC-3.3)
Behavior Excessive physical activity Underweight (NC-3.1)
2
Supplemental material for International Dietetics and Nutrition Terminology (IDNT) Reference Manual, Second Edition. Copyright 2009
American Dietetic Association.
Nutrition Diagnosis Etiology Matrix
Category Etiology Diagnosis
Behavior Food and nutrition compliance limitations Excessive carbohydrate intake (NI-5.8.2),
inappropriate intake of types of
carbohydrates (specify) (NI-5.8.3),
Inconsistent carbohydrate intake (NI-5.8.4)
Behavior Food or activity behavior-related difficulty Poor nutrition quality of life (NQOL) (NB-
2.5)
Behavior Food preparation or eating patterns that Excessive fiber intake (NI-5.8.6)
involve only high-fiber foods to the
exclusion of other nutrient-dense foods
Behavior Disordered eating pattern Excessive physical activity(NB-2.2),
Underweight (NC-3.1), Overweight/Obesity
(NC-3.3)
Behavior Frequent intake of foods containing Excessive bioactive substance intake (NI-
bioactive substances 4.2)
Behavior Inability to limit or refuse offered foods Excessive oral food/beverage intake (NI-2.2)
Behavior Inadequate energy intake Underweight (NC-3.1)
Behavior Lack of focus and attention to detail, Self-monitoring deficit (NB-1.4)
difficulty with time management and/or
organization
Behavior Over consumption of a limited variety of Excessive mineral intake (specify) (NI-
foods 5.10.2)
Behavior Poor or inappropriate food planning, Excessive oral food/beverage intake (NI-
purchasing and preparation practices 2.2), Inadequate fiber intake (NI-5.8.5),
Limited access to food (NB-3.2)
Behavior Reluctance or avoidance of self-feeding Self-feeding difficulty (NB-2.6)
Culture Cultural practices that affect ability to:
Access food variety Inadequate protein–energy intake (NI-5.3),
Inadequate fat intake (NI-5.6.1)
Breastfeed Breastfeeding difficulty (NC-1.3)
Learn/apply information Food- and nutrition-related knowledge
deficit (NB-1.1), Undesirable food choices
(NB-1.7)
Manage self-care Inability or lack of desire to manage self-
care (NB-2.3)
Reduce carbohydrate intake Excessive carbohydrate intake (NI-5.8.2)
Regulate timing of carbohydrate Inconsistent carbohydrate intake (NI-5.8.4)
consumption
Regulate types of carbohydrate Inappropriate intake of types of
consumed carbohydrates (specify) (NI-5.8.3)
Track personal progress Self-monitoring deficit (NB-1.4)
3
Supplemental material for International Dietetics and Nutrition Terminology (IDNT) Reference Manual, Second Edition. Copyright 2009
American Dietetic Association.
Nutrition Diagnosis Etiology Matrix
Category Etiology Diagnosis
Access Access to foods and supplements in excess Excessive vitamin intake (specify) (NI-5.9.2)
of needs
Access Caregiver intentionally or unintentionally not Limited access to food (NB-3.2)
providing access to food
Access Community and geographical constraints for Limited access to food (NB-3.2)
shopping and transportation
Access Environmental causes, e.g., inadequately Inadequate mineral intake (specify) (NI-
tested nutrient bioavailability of fortified 5.10.1)
foods, beverages, and supplements; inapp-
ropriate marketing of fortified foods,
beverages, supplements as a substitute for
natural food source of nutrient(s)
Access Exposure to contaminated water or food, Intake of unsafe food (NB-3.1)
e.g., community outbreak of illness
documented by surveillance and/or response
agency
Access Failure to participate in federal food Limited access to food (NB-3.2)
programs such as WIC, National School
Breakfast/Lunch Program, food stamps
Access Financial constraints that may prevent Physical inactivity (NB-2.1)
sufficient level of activity (e.g., to address
cost of equipment or shoes or club
membership to gain access)
Access Food insecurity Poor nutrition quality of life (NQOL) (NB-
2.5)
Access Lack of, or limited access to:
Adaptive eating devices conducive for Self-feeding difficulty (NB-2.6)
self-feeding
Available and safe exercise space and/or Physical inactivity (NB-2.1)
equipment
Fluid Inadequate fluid intake (NI-3.1), Inadequate
fiber intake (NI-5.8.5)
Fortified foods and beverages Inadequate mineral intake (specify) (NI-
5.10.1)
Specialized protein products Excessive protein intake (NI-5.7.2)
4
Supplemental material for International Dietetics and Nutrition Terminology (IDNT) Reference Manual, Second Edition. Copyright 2009
American Dietetic Association.
no reviews yet
Please Login to review.