203x Filetype PDF File size 1.65 MB Source: mingycomputersgh.files.wordpress.com
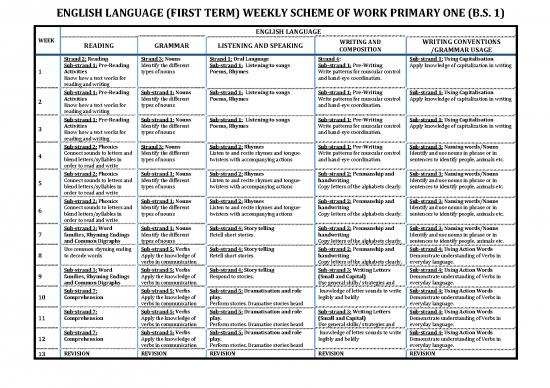
ENGLISH LANGUAGE (FIRST TERM) WEEKLY SCHEME OF WORK PRIMARY ONE (B.S. 1)
ENGLISH LANGUAGE
WEEK READING GRAMMAR LISTENING AND SPEAKING WRITING AND WRITING CONVENTIONS
COMPOSITION /GRAMMAR USAGE
Strand 2: Reading Strand 3: Nouns Strand 1: Oral Language Strand 4: Sub-strand 1: Using Capitalisation
Sub-strand 1: Pre-Reading Identify the different Sub-strand 1: Listening to songs Sub-strand 1: Pre-Writing Apply knowledge of capitalization in writing
1 Activities types of nouns Poems, Rhymes Write patterns for muscular control
Know how a text works for and hand-eye coordination.
reading and writing
Sub-strand 1: Pre-Reading Sub-strand 1: Nouns Sub-strand 1: Listening to songs Sub-strand 1: Pre-Writing Sub-strand 1: Using Capitalisation
2 Activities Identify the different Poems, Rhymes Write patterns for muscular control Apply knowledge of capitalization in writing
Know how a text works for types of nouns and hand-eye coordination.
reading and writing
Sub-strand 1: Pre-Reading Sub-strand 1: Nouns Sub-strand 1: Listening to songs Sub-strand 1: Pre-Writing Sub-strand 1: Using Capitalisation
3 Activities Identify the different Poems, Rhymes Write patterns for muscular control Apply knowledge of capitalization in writing
Know how a text works for types of nouns and hand-eye coordination.
reading and writing
Sub-strand 2: Phonics Strand 3: Nouns Sub-strand 2: Rhymes Sub-strand 1: Pre-Writing Sub-strand 3: Naming words/Nouns
4 Connect sounds to letters and Identify the different Listen to and recite rhymes and tongue- Write patterns for muscular control Identify and use nouns in phrase or in
blend letters/syllables in types of nouns twisters with accompanying actions and hand-eye coordination. sentences to identify people, animals etc.
order to read and write
Sub-strand 2: Phonics Sub-strand 1: Nouns Sub-strand 2: Rhymes Sub-strand 2: Penmanship and Sub-strand 3: Naming words/Nouns
5 Connect sounds to letters and Identify the different Listen to and recite rhymes and tongue- handwriting Identify and use nouns in phrase or in
blend letters/syllables in types of nouns twisters with accompanying actions Copy letters of the alphabets clearly. sentences to identify people, animals etc.
order to read and write
Sub-strand 2: Phonics Sub-strand 1: Nouns Sub-strand 2: Rhymes Sub-strand 2: Penmanship and Sub-strand 3: Naming words/Nouns
6 Connect sounds to letters and Identify the different Listen to and recite rhymes and tongue- handwriting Identify and use nouns in phrase or in
blend letters/syllables in types of nouns twisters with accompanying actions Copy letters of the alphabets clearly. sentences to identify people, animals etc.
order to read and write
Sub-strand 3: Word Sub-strand 1: Nouns Sub-strand 4: Story telling Sub-strand 2: Penmanship and Sub-strand 3: Naming words/Nouns
7 families, Rhyming Endings Identify the different Retell short stories. handwriting Identify and use nouns in phrase or in
and Common Digraphs types of nouns Copy letters of the alphabets clearly. sentences to identify people, animals etc.
Use common rhyming ending Sub-strand 5: Verbs Sub-strand 4: Story telling Sub-strand 2: Penmanship and Sub-strand 4: Using Action Words
8 to decode words Apply the knowledge of Retell short stories. handwriting Demonstrate understanding of Verbs in
verbs in communication Copy letters of the alphabets clearly. everyday language.
Sub-strand 3: Word Sub-strand 5: Verbs Sub-strand 4: Story telling Sub-strand 3: Writing Letters Sub-strand 4: Using Action Words
9 families, Rhyming Endings Apply the knowledge of Respond to stories. (Small and Capital) Demonstrate understanding of Verbs in
and Common Digraphs verbs in communication Use general skills/ strategies and everyday language.
Sub-strand 7: Sub-strand 5: Verbs Sub-strand 5: Dramatisation and role knowledge of letter sounds to write Sub-strand 4: Using Action Words
10 Comprehension Apply the knowledge of play. legibly and boldly Demonstrate understanding of Verbs in
verbs in communication Perform stories. Dramatise stories heard everyday language.
Sub-strand 7: Sub-strand 5: Verbs Sub-strand 5: Dramatisation and role Sub-strand 3: Writing Letters Sub-strand 4: Using Action Words
11 Comprehension Apply the knowledge of play. (Small and Capital) Demonstrate understanding of Verbs in
verbs in communication Perform stories. Dramatise stories heard Use general skills/ strategies and everyday language.
Sub-strand 7: Sub-strand 5: Verbs Sub-strand 5: Dramatisation and role knowledge of letter sounds to write Sub-strand 4: Using Action Words
12 Comprehension Apply the knowledge of play. legibly and boldly Demonstrate understanding of Verbs in
verbs in communication Perform stories. Dramatise stories heard everyday language.
13 REVISION REVISION REVISION REVISION REVISION
GHANAIAN LANGUAGE WEEKLY SCHEME OF WORK PRIMARY ONE (B.S. 1)
WEEK
LISTENING AND SPEAKING GRAMMAR READING SKILLS WRITING SKILLS
UNIT 1: Listening, singing songs UNIT 1: Naming words UNIT 1 : Pre-Reading Activities Unit 1 : Manipulating objects
1 and Reciting rhymes and poems Common nouns Writing patterns for muscular
control and hand-eye cordination
UNIT 1: Listening, singing songs UNIT 1: Naming words UNIT 1 : Pre-Reading Activities items: Unit 1 : Manipulating objects
2 and Reciting rhymes and poems Common nouns Home and School Writing patterns for muscular
control and hand-eye cordination
UNIT 1: Listening, singing songs UNIT 2: Naming words UNIT 1 : Pre-Reading Activities Unit 1 : Manipulating objects
3 and Reciting rhymes and poems Common nouns Writing patterns for muscular
(Picture/Object/Colour description) control and hand-eye cordination
UNIT 1: Listening, singing songs UNIT 2: Naming words UNIT 1 : Pre-Reading Activities Unit 1 : Manipulating objects
4 and Reciting rhymes and poems Proper nouns Writing patterns for muscular
(Picture/Object/Colour description) control and hand-eye cordination
Unit 2: Story telling UNIT 3: Naming words UNIT 1 : Pre-Reading Activities Unit 1 : Manipulating objects
5 Proper nouns Writing patterns for muscular
(Picture/Object/Colour description) control and hand-eye cordination
Unit 2: Story telling UNIT 3: Naming words UNIT 1 : Pre-Reading Activities Unit 1 : Manipulating objects
6 Proper nouns Writing patterns for muscular
(Picture/Object/Colour description) control and hand-eye cordination
Unit 2: Story telling UNIT 4: Naming words UNIT 2: Introduction to formal Unit 1 : Manipulating objects
7 Singular and plural Reading Writing patterns for muscular
Picture and object match words control and hand-eye cordination
Unit 3: CONVERSATION UNIT 4: Naming words UNIT 2: Introduction to formal Unit 2: Copying letters and simple words
8 Singular and plural Reading
Picture and object match words
Unit 3: CONVERSATION UNIT 4: Naming words UNIT 2: Introduction to formal Unit 2: Copying letters and simple words
9 Making polite request Singular and plural Reading
Picture and object match words
Unit 3: CONVERSATION UNIT 5: Pronouns UNIT 2: Introduction to formal Unit 2: Copying letters and simple words
10 Making polite request Personal pronouns Reading
Picture and object match words
Unit 3: CONVERSATION UNIT 5: Pronouns UNIT 2: Introduction to formal Unit 2: Copying letters and simple words
11 Making polite request Personal pronouns Reading
Picture and object match words
12
13 REVISION REVISION REVISION REVISION
HISTORY OF GHANA WEEKLY SCHEME OF WORK FOR PRIMARY ONE (B.S. 1)
WEEK FIRST TERM SECOND TERM THIRD TERM
Strand 1: HISTORY AS A SUBJECT Strand 2: MY COUNTRY GHANA Sub-strand 1: Arrival of Europeans
1 Sub-strand 1: Why and How We Study History Sub-strand 3: How Ghana Got Its Name Explore which Europeans came to Ghana.
Explore what history is about and how it is part of Why Ghana used to be called the Gold Coast
everyday life
Sub-strand 1: Why and How We Study History Strand 2: MY COUNTRY GHANA Sub-strand 1: Arrival of Europeans
2 Explore what history is about and how it is part of Sub-strand 3: How Ghana Got Its Name Explore which Europeans came to Ghana.
everyday life Why Ghana used to be called the Gold Coast
Sub-strand 1: Why and How We Study History Strand 2: MY COUNTRY GHANA Sub-strand 1: Arrival of Europeans
3 Explore what history is about and how it is part of Sub-strand 3: How Ghana Got Its Name Explore which Europeans came to Ghana.
everyday life Why Ghana used to be called the Gold Coast
Sub-strand 1: Why and How We Study History Sub-strand 5: Some Selected Individuals Strand 6: INDEPENDENT GHANA
4 Explore what history is about and how it is part of Important roles played by Ghanaians from different walks Sub-strand: The Republics
everyday life of life Identify the Presidents Ghana has had since 1960
Sub-strand 1: Why and How We Study History Sub-strand 5: Some Selected Individuals Strand 6: INDEPENDENT GHANA
5 Explore what history is about and how it is part of Important roles played by Ghanaians from different walks Sub-strand: The Republics
everyday life of life Identify the Presidents Ghana has had since 1960
Sub-strand 4: Community History Sub-strand 5: Some Selected Individuals Strand 6: INDEPENDENT GHANA
6 Similarities and differences between the commodities Important roles played by Ghanaians from different walks Sub-strand: The Republics
where learners live. of life Identify the Presidents Ghana has had since 1960
Sub-strand 4: Community History Sub-strand 5: Some Selected Individuals Strand 6: INDEPENDENT GHANA
7 Similarities and differences between the commodities Important roles played by Ghanaians from different walks Sub-strand: The Republics
where learners live. of life Identify the Presidents Ghana has had since 1960
Sub-strand 4: Community History Sub-strand 5: Some Selected Individuals Strand 6: INDEPENDENT GHANA
8 Similarities and differences between the commodities Important roles played by Ghanaians from different walks Sub-strand: The Republics
where learners live. of life Identify the Presidents Ghana has had since 1960
Strand 2: MY COUNTRY GHANA Strand 3: EUROPEANS IN GHANA Strand 6: INDEPENDENT GHANA
9 Sub-strand 3: How Ghana Got Its Name Sub-strand 1: Arrival of Europeans Sub-strand: The Republics
Why Ghana used to be called the Gold Coast Explore which Europeans came to Ghana. Identify the Presidents Ghana has had since 1960
Strand 2: MY COUNTRY GHANA Sub-strand 1: Arrival of Europeans
10 Sub-strand 3: How Ghana Got Its Name Explore which Europeans came to Ghana.
Why Ghana used to be called the Gold Coast
Strand 2: MY COUNTRY GHANA Sub-strand 1: Arrival of Europeans
11 Sub-strand 3: How Ghana Got Its Name Explore which Europeans came to Ghana.
Why Ghana used to be called the Gold Coast
Strand 2: MY COUNTRY GHANA Sub-strand 1: Arrival of Europeans
12 Sub-strand 3: How Ghana Got Its Name Explore which Europeans came to Ghana.
Why Ghana used to be called the Gold Coast
13 REVISION REVISION REVISION
SCIENCE WEEKLY SCHEME OF WORK FOR PRIMARY ONE (B.S. 1)
WEEK FIRST TERM SECOND TERM THIRD TERM
Strand 1: DIVERSITY OF MATTER Strand 3: SYSTEMS Strand 4: FORCES AND ENERGY
Sub-Strand 1: Living and Non-Living Things Sub-Strand 1: The Human Body Systems Sub-Strand 3: Forces and Movement
1 Physical features and life processes of living things and their Explore the different parts of the human body that work Explore forces as a pull or a push on an object.
classification. interdependently to perform specific function eg. Eyes, ears, Explain what simple machines are and cite
mouth, nose, legs, hands, shoulders, knees, fingers, toes and chest. examples.
Sub-Strand 1: Living and Non-Living Things Sub-Strand 1: The Human Body Systems Sub-Strand 3: Forces and Movement
2 Physical features and life processes of living things and their Explore the different parts of the human body that work Explore forces as a pull or a push on an object.
classification. interdependently to perform specific function eg. Eyes, ears, Explain what simple machines are and cite
mouth, nose, legs, hands, shoulders, knees, fingers, toes and chest. examples.
Sub-Strand 1: Living and Non-Living Things Sub-Strand 1: The Human Body Systems Strand 5: HUMANS AND THE ENVIRONMENT
3 Differences between living things, non-living things and Explore the different parts of the human body that work Sub-Strand 1: Personal Hygiene and Sanitation
things which have never been alive interdependently to perform specific function eg. Eyes, ears, Importance of personal hygiene
mouth, nose, legs, hands, shoulders, knees, fingers, toes and chest.
Sub-Strand 1: Living and Non-Living Things Sub-Strand 2: Ecosystem Sub-Strand 1: Personal Hygiene and Sanitation
4 Differences between living things, non-living things and Interactions and interdependencies of organisms in an ecosystem. Importance of personal hygiene
things which have never been alive
Sub-Strand 2: Materials Sub-Strand 2: Ecosystem Sub-Strand 2: Diseases
5 Recognise materials as important resources for providing Interactions and interdependencies of organisms in an ecosystem. Common diseases of humans, causes, symptoms,
human needs. effects and prevention.
Sub-Strand 2: Materials Sub-Strand 2: Ecosystem Sub-Strand 2: Diseases
6 Recognise materials as important resources for providing Interactions and interdependencies of organisms in an ecosystem. Common diseases of humans, causes, symptoms,
human needs. effects and prevention.
Sub-Strand 2: Materials Strand 4: FORCES AND ENERGY Sub-Strand 3: Science and Industry
7 Identify and classify materials as solid, liquid and gas. Explore Sub-Strand 1: Sources and Forms of Energy The impact of science and technology on society.
mixtures, the types, their formation, uses and ways of Concepts of energy, its various forms and sources and the ways in Food processing and preservation.
separating them into their components. which it can be transformed and conserved.
Sub-Strand 2: Materials Sub-Strand 1: Sources and Forms of Energy Sub-Strand 3: Science and Industry
8 Identify and classify materials as solid, liquid and gas. Explore Concepts of energy, its various forms and sources and the ways in The impact of science and technology on society.
mixtures, the types, their formation, uses and ways of which it can be transformed and conserved. Food processing and preservation.
separating them into their components.
Strand 2: CYCLES Sub-Strand 1: Sources and Forms of Energy Sub-Strand 4: Climate Change
Sub-Strand 1: Earth Science Concepts of heat energy in terms of its importance, effects, sources Climate change as an important environmental
9 Explore natural phenomena, such as day and night, occur and transfer from one medium to another. issue facing the world today
repeatedly. Explain condensation, evaporation, transpiration
and precipitation in the hydrological cycle.
Sub-Strand 1: Earth Science Sub-Strand 2: Electricity and Electronics
10 Explore natural phenomena, such as day and night, occur Generation of electricity, its transmission and transformation into
repeatedly. Explain condensation, evaporation, transpiration other forms of energy.
and precipitation in the hydrological cycle.
Sub-strand 2: Life Cycle of Organisms Sub-Strand 2: Electricity and Electronics
11 Examine the structure of plants. Observe different kinds of Generation of electricity, its transmission and transformation into
seeds. other forms of energy.
Sub-strand 2: Life Cycle of Organisms Sub-Strand 2: Electricity and Electronics
12 Examine the structure of plants. Observe different kinds of Generation of electricity, its transmission and transformation into
13 seeds. REVISION other forms of energy. REVISION REVISION
no reviews yet
Please Login to review.