244x Filetype PDF File size 0.52 MB Source: msmonline.co.za
Life Sciences Grade 12 Annual Teaching Plan 2021 1
Term 1 – Grade 12
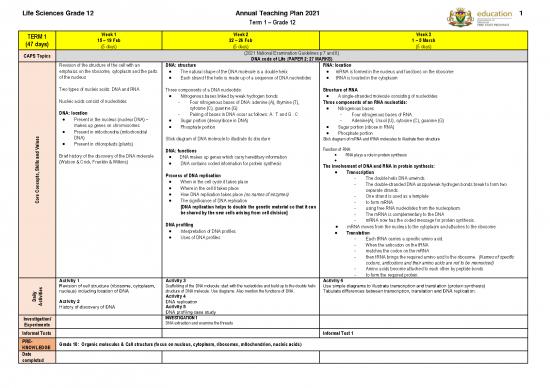
TERM 1 Week 1 Week 2 Week 3
(47 days) 15 – 19 Feb 22 – 26 Feb 1 – 5 March
(5 days) (5 days) (5 days)
CAPS Topics (2021 National Examination Guidelines p 7 and 8)
DNA code of Life (PAPER 2: 27 MARKS)
Revision of the structure of the cell with an DNA: structure RNA: location
emphasis on the ribosome, cytoplasm and the parts The natural shape of the DNA molecule is a double helix mRNA is formed in the nucleus and functions on the ribosome
of the nucleus Each strand f the helix is made up of a sequence of DNA nucleotides tRNA is located in the cytoplasm
Two types of nucleic acids: DNA and RNA Three components of a DNA nucleotide: Structure of RNA
Nitrogenous bases linked by weak hydrogen bonds: A single-stranded molecule consisting of nucleotides
Nucleic acids consist of nucleotides - Four nitrogenous bases of DNA: adenine (A), thymine (T), Three components of an RNA nucleotide:
cytosine (C), guanine (G) Nitrogenous bases
DNA: location - Pairing of bases in DNA occur as follows: A : T and G : C - Four nitrogenous bases of RNA:
Present in the nucleus (nuclear DNA) – Sugar portion (deoxyribose in DNA) - Adenine(A), Uracil (U), cytosine (C), guanine (G)
makes up genes on chromosomes Phosphate portion Sugar portion (ribose in RNA)
Present in mitochondria (mitochondrial Phosphate portion
s DNA) Stick diagram of DNA molecule to illustrate its structure Stick diagram of mRNA and tRNA molecules to illustrate their structure
e
u
l Present in chloroplasts (plants)
a
V Function of RNA:
DNA: functions
d
n Brief history of the discovery of the DNA molecule RNA plays a role in protein synthesis
a DNA makes up genes which carry hereditary information
s
l (Watson & Crick, Franklin & Wilkins)
l DNA contains coded information for protein synthesis
i The involvement of DNA and RNA in protein synthesis:
k
S
, Transcription
s Process of DNA replication
t
p - The double helix DNA unwinds.
e When in the cell cycle it takes place
c - The double-stranded DNA unzips/weak hydrogen bonds break to form two
n
o Where in the cell it takes place separate strands.
C
How DNA replication takes place (no names of enzymes)
e - One strand is used as a template
r
o The significance of DNA replication
C [DNA replication helps to double the genetic material so that it can - to form mRNA
be shared by the new cells arising from cell division] - using free RNA nucleotides from the nucleoplasm.
- The mRNA is complementary to the DNA
DNA profiling - mRNA now has the coded message for protein synthesis.
Interpretation of DNA profiles mRNA moves from the nucleus to the cytoplasm and attaches to the ribosome.
Uses of DNA profiles Translation
- Each tRNA carries a specific amino acid.
- When the anticodon on the tRNA
- matches the codon on the mRNA
- then tRNA brings the required amino acid to the ribosome. (Names of specific
codons, anticodons and their amino acids are not to be memorised)
- Amino acids become attached to each other by peptide bonds
- to form the required protein.
Activity 1 Activity 3 Activity 6
s Revision of cell structure (ribosome, cytoplasm, Scaffolding of the DNA molecule: start with the nucleotides and build up to the double helix Use simple diagrams to illustrate transcription and translation (protein synthesis)
e nucleus) including location of DNA structure of DNA molecule. Use diagrams. Also mention the functions of DNA. Tabulate differences between transcription, translation and DNA replication.
y i
l t
i i
a v Activity 4
i
D t
c Activity 2 DNA replication
A History of discovery of DNA Activity 5
DNA profiling case study
Investigation/ INVESTIGATION 1
Experiments DNA extraction and examine the threads
Informal Tests Informal Test 1
PRE- Grade 10: Organic molecules & Cell structure (focus on nucleus, cytoplasm, ribosomes, mitochondrion, nucleic acids)
KNOWLEDGE
Date
completed
Life Sciences Grade 12 Annual Teaching Plan 2021 2
Term 1 – Grade 12
TERM 1 Week 4 Week 5 Week 6
(47 days) 8 – 12 March 15 – 19 March 23 – 26 March
(5 days) (5 days) (4 days)
CAPS Topics (2021 National Examination Guidelines p 9) (2021 National Examination Guidelines p 10)
Meiosis (PAPER 2: 21 MARKS) Reproduction in Vertebrates (PAPER 1: 8 MARKS)
Structure of chromosomes: Importance of meiosis: Diversity of reproductive strategies
Chromosomes consist of DNA (which makes up genes) and protein Production of haploid gametes
The number of chromosomes in a cell is a characteristic of an organism (e.g. humans have 46 The halving effect of meiosis overcomes the The role of the following reproductive strategies in animals in maximising
chromosomes) doubling effect of fertilisation, thus maintaining a reproductive success in different environments (using relevant examples):
Chromosomes which are single threads become double (two chromatids joined by a centromere) as a constant chromosome number from one generation
result of DNA replication to the next External fertilisation and internal fertilisation
Mechanism to introduce genetic variation through: Ovipary, ovovivipary and vivipary
Differentiate between: - Crossing over Amniotic egg
Haploid (n) and diploid (2n) cells in terms of chromosome number - The random arrangement of chromosomes Precocial and altricial development
Sex cells (gametes) and somatic cells (body cells) at the equator Parental care
Sex chromosomes (gonosomes) and autosomes
s
e
u
l Abnormal meiosis and consequences
a Meiosis – The process
V
Definition of meiosis and site of meiosis in plants and animals Non-disjunction and its consequences
d
n Non-disjunction of chromosomes at position 21
a
s
l during Anaphase in humans to form abnormal
l Events of interphase:
i
k gametes with an extra copy of chromosome 21
S DNA replication takes place
,
s The fusion between an abnormal gamete (24
t - Chromosomes which are single threads, become double
p
e - Each chromosome will now consist of two chromatids joined by a centromere chromosomes) and a normal gamete (23
c
n - DNA replication helps to double the genetic material so that it can be shared by chromosomes) may lead to Down syndrome
o
C
the new cells arising from cell division
e
r
o
C The events of the following phases of Meiosis I, using diagrams: Comparison
Prophase I (Including a description of crossing over) Similarities of mitosis and meiosis
Metaphase I (Including the random arrangement of the chromosomes)
Anaphase I Differences between mitosis and meiosis
Telophase I
The events of each phase of Meiosis II, using diagrams:
Prophase II
Metaphase II (Including the random arrangement of the chromosomes)
Anaphase II
Telophase II
Activity 7 Activity 11 Activity 13
Structure of chromosomes, differentiation of cells, revision of mitosis. Indicate the actions during interphase. Abnormal meiosis and importance of meiosis. Tabulate differences between internal and external fertilisation. Include examples as well
Revise the process of mitosis as advantages and disadvantages.
s Activity 12
e
i Activity 8 Comparison between mitosis and meiosis (similarities and Activity 14
t
i
v Tabulate the different phases of meiosis I including diagrams, micrographs and description of different phases. differences) Tabulate differences between ovipary, ovovivipary and vivipary with examples.
i
t
c
A
Activity 9 Activity 15
y
l
i Tabulate the different phases of meiosis II including diagrams, micrographs and description of different phases. Draw a diagram of an amniotic egg with labels and functions.
a
D
Activity 10 Activity 16
Compare each phase of meiosis I and II. Differentiate between precocial and altricial development with advantages and
disadvantages. Indicate the importance of parental care.
Investigations INVESTIGATION 2
Experiments Observe and draw prepared microscope slides, micrographs or models of cells in different stages of meiosis
Informal Tests Informal Test 2
PRE- Grade 10: Mitosis & Cell structure (parts of the nucleus, centrosome/centrioles, cytoplasm)
KNOWLDGE
Date
completed
Life Sciences Grade 12 Annual Teaching Plan 2021 3
Term 1 – Grade 12
TERM 1 Week 7 Week 8 Week 9 Week 10
(47 days) 29 March – 1 April 6 – 9 April 12 – 16 April 19 – 23 April
(4 days) (4 days) (5 days) (5 days)
CAPS Topics (2021 National Examination Guideline p 10 & 11)
Human reproduction (PAPER 1: 41 MARKS)
Structure of male reproductive system, using a diagram The menstrual cycle includes the Fertilisation and development
Functions of the testis, epididymis, vas deference, seminal vesicle, prostate gland, Cowper’s gland, penis and the urethra uterine and the ovarian cycles of zygote to blastocyst CATCH-UP & REVISION
Structure of the female reproductive system, using a diagram Events in the ovarian cycle: - Definition of copulation and
Functions of the ovary, Fallopian tube, uterus lined by endometrium, cervix, vagina with its external opening and the vulva Development of the fertilisation
Structure of the ovary, using a diagram showing the primary follicles, the Graafian follicle and the corpus luteum Graafian follicle - Process of fertilisation
Ovulation - Development of zygote
Puberty Formation of the corpus embryo (morula and blastula/
Main changes that occur in male characteristics during puberty under the influence of testosterone. luteum
Main changes that occur in female characteristics during puberty under the influence of oestrogen. blastocyst) foetus
s Events in the uterine cycle:
e
u Gametogenesis
l Changes that take place in Gestation
a Formation of gametes (gametogenesis) by meiosis
V the thickness of the
d endometrium Definition of implantation
n
a
Male gametes formed by Spermatogenesis: Menstruation
s
l
l Under the influence of testosterone
i The role of oestrogen and
k diploid cells in the seminiferous tubules of the testes undergo meiosis
S Hormonal control of the menstrual progesterone in maintaining
,
s to form haploid sperm cells cycle (ovarian and uterine cycles) pregnancy
t
p
e with reference to the action of FSH,
c Structure of a sperm, using a diagram Structure of the developing foetus
n oestrogen, LH and progesterone
o Functions of the parts of the sperm cell (acrosome, head with haploid nucleus, middle portion/neck with mitochondria and a tail) in the uterus, using a diagram
C
e
r Negative-feedback mechanism
o Female gametes formed by Oogenesis: involving FSH and progesterone in Functions of the following parts:
C
Diploid cells in the ovary undergo mitosis controlling the production of ova Chorion and chorionic villi
to form numerous follicles (*See endocrine system for 2 more Amnion, amnion cavity and
At the onset of puberty neg. feedback examples) amniotic fluid
and under the influence of FSH, Umbilical cord (including
one cell inside a follicle enlarges and undergoes meiosis umbilical artery and
Of the four cells that are produced, only one survives to form a mature, haploid ovum in a Graafian follicle umbilical vein)
This occurs in a monthly cycle. Placenta
Structure of an ovum, using a diagram
Functions of the different parts of an ovum (layer of jelly, haploid nucleus, cytoplasm)
Activity 17 Activity 22 Activity 24 Activity 25
Flow diagram of the human life cycle. Emphasis on the role of meiosis, mitosis and fertilisation. Draw the ovary and explain the Diagram and table to indicate the Diagram with labels and functions as well as
events taking place during the fertilisation, development of description of gestation
s Activity 18 cycle. With emphasis on the fertilised ovum and implantation.
e
i Structure of male reproductive system with labels and functions. Use micro-scope slides to identify tissues and different structures of the testis hormonal control.
t
i
v and section through penis.
i
t
c Activity 23
A
Activity 19 Diagram/graph of the menstrual cycle
y
l
i Structure of female reproductive system with labels and functions. Use microscope slides to identify tissues and different structures of the ovaries. combining the ovarian and uterine
a
D Activity 20 cycle and influence of the different
Diagrams and description of spermatogenesis. Draw the sperm with labels and functions. hormones on these cycles.
Activity 21
Diagrams and description of oogenesis. Draw the ovum with labels and functions.
Investigations INVESTIGATION 3 INVESTIGATION 4 INVESTIGATION 5
Microscope slides of ovary, testes and section through penis. Identify tissues and different structures Prepared microscope slides or Stages of pregnancy by watching DVDs of the
Experiments micrographs or ultrasound pictures development of an embryo and the birth
of embryonic development. process.
Informal Tests
SBA (Formal PRACTICAL 1.1 FORMAL TEST 2.1
Assessment) Human Reproduction Week 1 – 9
Date: 1 April 2021 Date: 20 April 2021
Date
completed
Life Sciences Grade 12 Annual Teaching Plan 2021 4
Term 2 - Grade 12
TERM 2 Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4
(49 days) 3 – 7 May 10 – 14 May 17 – 21 May 24 – 28 May
(5 days) (5 days) (5 days) (5 days)
CAPS Topics (2021 National Examination Guidelines p 11, 12 & 13)
Genetics and Inheritance (PAPER 2: 48 MARKS)
Mention of Mendel as the father of genetics Sex determination Dihybrid crosses Genetic engineering
22 pairs of chromosomes in humans are Mendel's Principle of Independent Assortment – Biotechnology is the manipulation of biological
Concepts in inheritance
Chromatin and chromosomes autosomes and one pair of chromosomes are sex The various ‘factors’ controlling the different characteristics processes to satisfy human needs.
Genes and alleles chromosomes/gonosomes are separate entities, not influencing each other in any way, Genetic engineering is an aspect of
Dominant and recessive alleles and sorting themselves out independently during gamete biotechnology and includes:
Males have XY chromosomes and females have formation. Stem cell research – sources and
Phenotype and genotype XX chromosomes uses of stem cells
Homozygous and heterozygous Genetic lineages / Pedigrees Genetic modified organisms – brief
The Law of Dominance: A genetic lineage/pedigree traces the inheritance of outline of process (names of enzymes
When two homozygous organisms with contrasting Differentiate between sex chromosomes characteristics over many generations
characteristics are crossed, all the individuals of the F1 (gonosomes) and autosomes in the karyotypes of involved are not required) and benefits of
generation will display the dominant trait human males and females Mutations genetic modification
An individual that is heterozygous for a particular Definition of a mutation Cloning – brief outline of process and benefits
characteristic will have the dominant trait as the phenotype. Sex-linked inheritance Effects of mutations: harmful mutations, harmless mutations of cloning
Sex-linked alleles and sex-linked disorders and useful mutations
Monohybrid crosses Genetic problems involving the following sex-linked Mutations contribute to genetic variation Paternity testing
s Format for representing a genetic cross Definition of gene mutation and chromosomal mutation
e Mendel’s Principle of Segregation – An organism possesses two ‘factors’ which disorders: The use of each of the following in paternity
u
l
a separate or segregate so that each gamete contains only one of these ‘factors’ Haemophilia testing:
V
Two types of mutations that can alter characteristics leading
d Colour-blindness Blood grouping
n to genetic disorders:
a Types of dominance
Gene mutations: DNA profiles
s
l Complete dominance – one allele is dominant and the other is recessive, such that
l
i Blood grouping Haemophilia – absence of blood-clotting factors
k the effect of the recessive allele is masked by the dominant allele in the
S
Different blood groups are a result of multiple alleles Colour-blindness - due to absence of the proteins Genetic links
, heterozygous condition
s
t A B that comprise either red or green Mutations in mitochondrial DNA used in tracing
p The alleles I , I and i in different combinations result in
e cones/photoreceptors in the eye female ancestry
c Incomplete dominance – neither one of the two alleles of a gene is dominant over four blood groups
n Chromosomal mutation:
o the other, resulting in an intermediate phenotype in the heterozygous condition
C
Down syndrome – due to an extra copy of
e
r chromosome 21 as a result of non-disjunction during
o Co-dominance – both alleles of a gene are equally dominant whereby both alleles
C express themselves in the phenotype in the heterozygous condition meiosis
Activity 26 Activity 31 Activity 36 Activity 39
Concepts in inheritance by mentioning Mendel’s role and the 2 laws. Use a diagram to explain the karyotype of a human, showing the At least 2 different dihybrid crosses. Determination of the Genetic engineering such as stem cell research,
autosomes, the gonosomes, chromosomes XY and XX. proportion/ratio of genotypes and phenotypes GMO’s and cloning.
Activity 27
Draw and explain the format for representing a genetic cross. Indicate mark Activity 32 Activity 37
s allocation. Representation of a genetic cross to show the enheritance of sex At least 3 pedigree diagrams
e
i
t
i
v Activity 28 Activity 33 Activity 38
i
t
c At least 3 examples of monohybrid crosses. Sex-linked cross of haemophilia and colour-blindness. Mutation: effects and disorders
A
y
l
i Activity 29 Activity 34
a
D Tabulate the different types of dominance. Description of each, symbols to use with Solving genetic problems involving the inheritances of blood
examples. groups.
Activity 30 Activity 35
Solving genetic problems involving each of the three types of dominance. Proportion The role of blood grouping and DNA profiles in paternity testing.
and ratio of genotypes and phenotypes Mutations in mitochondrial DNA.
PRE- Grade 10: Differentiate between chromatin & chromosomes, genes and alleles; stem cells and cloning
KNOWLEDGE
Informal Tests Informal Test 3
SBA (Formal PRACTICAL 1.2
Assessment) Genetic lineages and mutations
Date: 25 May 2021
Date
completed
no reviews yet
Please Login to review.