202x Filetype PDF File size 0.57 MB Source: uwm.edu
Benchmark
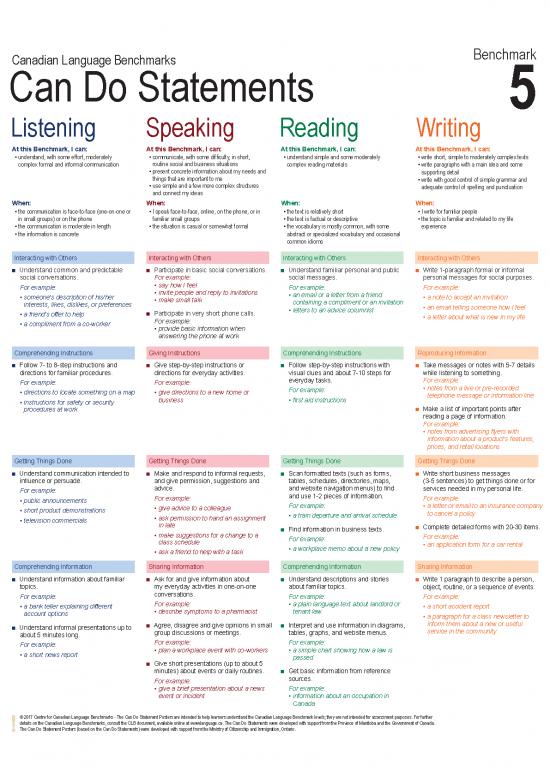
Canadian Language Benchmarks
Can Do Statements 5
Listening Speaking Reading Writing
At this Benchmark, I can: At this Benchmark, I can: At this Benchmark, I can: At this Benchmark, I can:
• understand, with some effort, moderately • communicate, with some difficulty, in short, • understand simple and some moderately • write short, simple to moderately complex texts
complex formal and informal communication routine social and business situations complex reading materials • write paragraphs with a main idea and some
• present concrete information about my needs and supporting detail
things that are important to me • write with good control of simple grammar and
• use simple and a few more complex structures adequate control of spelling and punctuation
and connect my ideas
When: When: When: When:
• the communication is face-to-face (one-on-one or • I speak face-to-face, online, on the phone, or in • the text is relatively short • I write for familiar people
in small groups) or on the phone familiar small groups • the text is factual or descriptive • the topic is familiar and related to my life
• the communication is moderate in length • the situation is casual or somewhat formal • the vocabulary is mostly common, with some experience
• the information is concrete abstract or specialized vocabulary and occasional
common idioms
Interacting with Others Interacting with Others Interacting with Others Interacting with Others
Interacting with Others Interacting with Others Interacting with Others Interacting with Others
■ Understand common and predictable ■ Participate in basic social conversations. ■ Understand familiar personal and public ■ Write 1-paragraph formal or informal
social conversations. For example: social messages. personal messages for social purposes.
For example: • say how I feel For example: For example:
• someone’s description of his/her • invite people and reply to invitations • an email or a letter from a friend • a note to accept an invitation
interests, likes, dislikes, or preferences • make small talk containing a compliment or an invitation
■ Participate in very short phone calls. • letters to an advice columnist • an email telling someone how I feel
• a friend’s offer to help • a letter about what is new in my life
• a compliment from a co-worker For example:
• provide basic information when
answering the phone at work
Comprehending Instructions Giving Instructions Comprehending Instructions Reproducing Information
■ Follow 7- to 8-step instructions and ■ Give step-by-step instructions or ■ Follow step-by-step instructions with ■ Take messages or notes with 5-7 details
directions for familiar procedures. directions for everyday activities. visual clues and about 7-10 steps for while listening to something.
For example: For example: everyday tasks. For example:
• directions to locate something on a map • give directions to a new home or For example: • notes from a live or pre-recorded
business • first aid instructions telephone message or information line
• instructions for safety or security ■ Make a list of important points after
procedures at work
reading a page of information.
For example:
• notes from advertising flyers with
information about a product’s features,
prices, and retail locations
Getting Things Done Getting Things Done Getting Things Done Getting Things Done
■ Understand communication intended to ■ Make and respond to informal requests, ■ Scan formatted texts (such as forms, ■ Write short business messages
influence or persuade. and give permission, suggestions and tables, schedules, directories, maps, (3-5 sentences) to get things done or for
For example: advice. and website navigation menus) to find services needed in my personal life.
• public announcements For example: and use 1-2 pieces of information. For example:
• short product demonstrations • give advice to a colleague For example: • a letter or email to an insurance company
• ask permission to hand an assignment • a train departure and arrival schedule to cancel a policy
• television commercials in late ■ Complete detailed forms with 20-30 items.
• make suggestions for a change to a ■ Find information in business texts.
class schedule For example: For example:
• a workplace memo about a new policy • an application form for a car rental
• ask a friend to help with a task
Comprehending Information Sharing Information Comprehending Information Sharing Information
■ Understand information about familiar ■ Ask for and give information about ■ Understand descriptions and stories ■ Write 1 paragraph to describe a person,
topics. my everyday activities in one-on-one about familiar topics. object, routine, or a sequence of events.
For example: conversations. For example: For example:
• a bank teller explaining different For example: • a plain language text about landlord or • a short accident report
account options • describe symptoms to a pharmacist tenant law • a paragraph for a class newsletter to
■ Understand informal presentations up to ■ Agree, disagree and give opinions in small ■ Interpret and use information in diagrams, inform them about a new or useful
about 5 minutes long. group discussions or meetings. tables, graphs, and website menus. service in the community
For example: For example: For example:
• a short news report • plan a workplace event with co-workers • a simple chart showing how a law is
■ Give short presentations (up to about 5 passed
minutes) about events or daily routines. ■ Get basic information from reference
For example: sources.
• give a brief presentation about a news For example:
event or incident • information about an occupation in
Canada
© 2017 Centre for Canadian Language Benchmarks - The Can Do Statement Posters are intended to help learners understand the Canadian Language Benchmark levels; they are not intended for assessment purposes. For further
details on the Canadian Language Benchmarks, consult the CLB document, available online at www.language.ca. The Can Do Statements were developed with support from the Province of Manitoba and the Government of Canada.
!The Can Do Statement Posters (based on the Can Do Statements) were developed with support from the Ministry of Citizenship and Immigration, Ontario.
Benchmark
Canadian Language Benchmarks
Can Do Statements 6
Listening Speaking Reading Writing
At this Benchmark, I can: At this Benchmark, I can: At this Benchmark, I can: At this Benchmark, I can:
• understand most moderately complex, formal and • communicate with some confidence in everyday • understand a range of moderately complex • write short, moderately complex texts
informal communication related to life experience social situations reading materials • write paragraphs with clearly expressed main
• present concrete information in some detail about ideas and some supporting details
familiar topics that are important to me • write with good control of simple grammar and
• use simple and some complex structures and adequate control of spelling and punctuation
connect my ideas
When: When: When: When:
• the communication is face-to-face (one-on-one or • I speak face-to-face, online, on the phone, or in • the text is relatively short • I write for familiar people
in small groups) or on the phone mostly familiar small groups • the text is mostly factual or descriptive • the topic is familiar and related to my own
• the communication is moderate in length • the situation is casual or somewhat formal • the vocabulary is mostly common, with interests and experiences
• the information is concrete and sometimes some abstract or specialized vocabulary and
includes some abstract concepts occasional idioms
Interacting with Others Interacting with Others Interacting with Others Interacting with Others
■ Understand common social ■ Participate in routine social conversations. ■ Understand familiar personal and public ■ Write 1- to 2-paragraph formal or informal
conversations. For example: social messages. personal messages for social purposes.
For example: • make suggestions or arrangements for For example: For example:
• making and cancelling arrangements an event • a workplace announcement • a memo congratulating or thanking
• apologizing or making excuses • express opinions someone
• make excuses or apologies • a note to make an apology
■ Participate in short phone calls. • an e-mail offering to help someone
For example:
• make a call to the dentist to set up an
appointment
Comprehending Instructions Giving Instructions Comprehending Instructions Reproducing Information
■ Follow 9- to 10-step instructions and ■ Give step-by-step instructions or ■ Follow instructions with some visual ■ Take messages or notes with 7-8 details
directions for technical and non-technical directions for everyday activities. clues and about 10 steps for everyday while listening to something.
tasks. For example: tasks, even when the steps are not For example:
For example: • give instructions for using a bank always listed in order. • notes from a podcast or short
• instructions on how to write an essay machine For example: presentation
• instructional videos in a workplace • give instructions to a friend on how to • an application for post-secondary study ■ Make an outline or summary after reading
training session set up an account on a website
a page of information.
For example:
• notes from a website about a procedure
Getting Things Done Getting Things Done Getting Things Done Getting Things Done
■ Understand communication intended to ■ Make and respond to somewhat formal ■ Scan formatted texts (such as maps, ■ Write short business messages (up to
influence or persuade. suggestions and indirect requests. course calendars, directories, and 1 paragraph) to get things done or for
For example: For example: website navigation menus) to find and services needed for everyday life.
• telemarketer offers • request a raise from an employer use 2-3 pieces of information. For example:
• public transit announcements For example: • a letter to ask a company for a refund for
• two courses of interest in a course a product that didn’t work
calendar ■ Complete detailed forms with 30-40 items.
■ Get information from moderately complex For example:
business texts. • a job application form
For example:
• product specifications for a home
appliance
• a cover letter for a job application
Comprehending Information Sharing Information Comprehending Information Sharing Information
■ Understand short group interactions and ■ Ask for and give information in some ■ Understand descriptions and stories ■ Write 1-2 connected paragraphs to
discussions on familiar topics. detail in one-on-one and in small group about familiar topics. describe a sequence of events, give
For example: discussions and meetings. For example: a detailed description or comparison
• group discussions about class projects For example: • a short current news item of people, things, routines or simple
■ Understand informal presentations up to • express feelings or opinions ■ Interpret and use information in charts, procedures.
about 10 minutes long. • express obligation, certainty or ability diagrams, tables, graphs, and website For example:
menus. • a description of daily routines at work
For example: ■ Give detailed presentations (up to For example: • a comparison of 2 job applicants
• short presentations by professionals about 7 minutes) about events, simple
such as public health nurses processes, or to describe or compare • crime rate data presented in a table
things. ■ Access, locate, and compare 2 or 3
For example: pieces of information online.
• an informal presentation to colleagues For example:
about immigrating to Canada • different online readings about a
familiar health problem
© 2017 Centre for Canadian Language Benchmarks - The Can Do Statement Posters are intended to help learners understand the Canadian Language Benchmark levels; they are not intended for assessment purposes. For further
details on the Canadian Language Benchmarks, consult the CLB document, available online at www.language.ca. The Can Do Statements were developed with support from the Province of Manitoba and the Government of Canada.
!The Can Do Statement Posters (based on the Can Do Statements) were developed with support from the Ministry of Citizenship and Immigration, Ontario.
Benchmark
Canadian Language Benchmarks
Can Do Statements 7
Listening Speaking Reading Writing
At this Benchmark, I can: At this Benchmark, I can: At this Benchmark, I can: At this Benchmark, I can:
• understand most moderately complex formal and • communicate with some confidence in many daily • understand a range of moderately complex • write clear, moderately complex texts
informal communication related to life experience routine, social, educational, and work situations reading materials • write well-organized paragraphs with clearly
and general knowledge • present concrete and some abstract information expressed main ideas and adequate supporting
on an expanding range of familiar topics details
• use simple and some complex structures, and • write with good control of simple grammar, spelling,
connect my ideas and punctuation
• write with adequate control of complex structures
When: When: When: When:
• the communication is face-to-face (one-on-one or • I speak face-to-face, online, on the phone, or in • the text is moderate in length • I write for familiar people or organizations
in small groups) or on the phone somewhat familiar groups • the text is factual, descriptive or argumentative • the topic is related to my own experience
• the communication is moderate in length • the situation is informal to formal with opinions and implied meanings
• the information includes some abstract concepts • the vocabulary includes a range of concrete,
and ideas abstract or specialized terms, and idiomatic
language
Interacting with Others Interacting with Others Interacting with Others Interacting with Others
■ Understand social conversations. ■ Participate in less routine social ■ Understand personal and public social ■ Write formal and informal messages
For example: conversations for many everyday messages for a variety of purposes. (about 2-3 paragraphs) for a range of
• a person expressing appreciation for a purposes. For example: social purposes.
favour For example: • a personal email expressing For example:
• a complaint from a friend or classmate • respond to appreciation or dissatisfaction appreciation, complaint, hopes, • an email to show or respond to
• a discussion among co-workers who ■ Participate in routine phone calls. satisfaction, or dissatisfaction appreciation
are not getting along • a letter from a friend relating some • a letter to make or respond to a complaint
For example: bad news • a note to express disappointment or
• leave a telephone message for a friend satisfaction
with details about an upcoming event
Comprehending Instructions Giving Instructions Comprehending Instructions Reproducing Information
■ Follow 10- to 12-step instructions ■ Give instructions and directions for ■ Follow instructions with up to about 13 ■ Reduce oral information (e.g., in a live
and directions for technical and technical and non-technical tasks, steps or 5-10 paragraphs for tasks that demonstration or from audio or video
non-technical tasks. procedures and processes. may be specialized or technical. material) into notes to write instructions.
For example: For example: For example: For example:
• detailed directions on how to get • give instructions on how to use • how to remove a computer virus • notes from a detailed phone message at
somewhere specific functions on a spreadsheet • how to assemble a piece of furniture work
• instructions for procedures in the ■ Make an outline or summary after reading
workplace
up to about 2 pages of information.
For example:
• an outline of a sequence of events in a
historical text
Getting Things Done Getting Things Done Getting Things Done Getting Things Done
■ Understand communication intended to ■ Give extended warnings, suggestions, ■ Scan formatted texts (such as course ■ Write business messages (up to about 2
influence or persuade. recommendations or advice. calendars, directories, and website paragraphs long) for a range of routine
For example: For example: navigation menus) to find and use 3-4 and less routine purposes.
• reminders or requests from employers • give a detailed suggestion on how to pieces of information. For example:
• orders from law enforcement officials solve a problem For example: • a memo to pass on information or
• make recommendations on how to • course eligibility criteria, start date, and concerns
improve a friend’s class assignment pre-requisites • a report to make recommendations or
■ Get information from moderately complex warnings
business texts. ■ Complete detailed forms with about 40
For example: items and some written responses to
• a performance review questions.
• a public health advisory For example:
• an incident report form
Comprehending Information Sharing Information Comprehending Information Sharing Information
■ Understand short group interactions and ■ Give detailed information one-on-one and ■ Understand extended descriptions, ■ Write 2 or 3 connected paragraphs to
discussions on familiar topics. in small group discussions or meetings. reports, and stories about familiar topics. describe a sequence of events, make
For example: For example: For example: a comparison, or provide a detailed
• one-on-one meetings with supervisors • discuss a medical condition with a • a short research report description of a person, system, routine
at work doctor ■ Interpret and use information in charts, or procedure.
■ Understand informal presentations up to ■ Give detailed presentations (up to diagrams, tables, graphs, and flow charts. For example:
about 15 minutes long. about 10 minutes) about events, simple For example: • the procedure for becoming a Canadian
processes, or to describe or compare and citizen
For example: • a flow chart illustrating a company • a comparison of the education system of
• informal talks on general interest or contrast 2 events, jobs, or procedures. reporting system 2 countries for an academic preparation
occupation specific topics For example: ■ Use information from different online course
• compare and contrast the advantages reference sources.
and disadvantages of 2 workplace For example:
procedures
• reports of an event in 2 online
newspapers
© 2017 Centre for Canadian Language Benchmarks - The Can Do Statement Posters are intended to help learners understand the Canadian Language Benchmark levels; they are not intended for assessment purposes. For further
details on the Canadian Language Benchmarks, consult the CLB document, available online at www.language.ca. The Can Do Statements were developed with support from the Province of Manitoba and the Government of Canada.
!The Can Do Statement Posters (based on the Can Do Statements) were developed with support from the Ministry of Citizenship and Immigration, Ontario.
Benchmark
Canadian Language Benchmarks
Can Do Statements 8
Listening Speaking Reading Writing
At this Benchmark, I can: At this Benchmark, I can: At this Benchmark, I can: At this Benchmark, I can:
• understand moderately complex formal • communicate with confidence in most daily • understand most moderately complex reading • write clear, moderately complex texts
and informal communication related to life routine social, educational and work situations materials • write well-organized paragraphs with clearly
experience, general knowledge, and specialized • present concrete and some abstract information expressed main ideas and good supporting details
or work- related situations on a range of familiar topics • write with good control of complex structures,
• use an adequate range of grammatical structures spelling, and punctuation
in connected discourse
When: When: When: When:
• the communication is face-to-face (one-on-one • I speak face-to-face, online, on the phone, or in • the text is moderate in length • I write for a familiar or clearly defined audience
or in small groups) or on the phone familiar or unfamiliar groups • the text is factual, descriptive or argumentative • the topic is related to my own experiences or
• the communication is moderate in length • the situation is informal to formal with opinions and implied meanings ideas
• the information includes abstract concepts and • the vocabulary includes a range of concrete,
ideas abstract or specialized terms, and idiomatic
language
Interacting with Others Interacting with Others Interacting with Others Interacting with Others
■ Understand social conversations. ■ Participate in less routine social ■ Understand social messages for a ■ Write formal and informal messages
For example: conversations for most everyday variety of purposes. (about 3 paragraphs long) for a range of
• a co-worker discussing a colleague purposes. For example: social purposes.
who suddenly left the company For example: • general opinions in a blog For example:
• a formal farewell at a retirement party • comfort someone in distress • responses to complaints or sympathy • a memo clarifying a conflict
• formal and informal condolences from • introduce guest speakers formally to a • an email giving reassurance
friends after a funeral group
■ Make short professional phone calls.
For example:
• reassure a customer that his/her order
will arrive on time
Comprehending Instructions Giving Instructions Comprehending Instructions Reproducing Information
■ Follow long, detailed instructions and ■ Give instructions and directions for ■ Follow extended instructions with up to ■ Listen and take notes to prepare for writing
directions (over 12 steps) for technical a broad range of technical and non- about 13 steps or 8-15 paragraphs for instructions about established procedures.
and non-technical tasks. technical tasks, procedures, and specialized tasks. For example:
For example: processes. For example: • detailed notes of a recipe presented
• instructions from a technical assistant For example: • how to program a small electronic item during a cooking show
to resolve a simple computer software • give detailed, multistep instructions • how to perform cardiopulmonary ■ Make an outline or summary of a text that
issue to a student on how to conduct a resuscitation (CPR) is up to 2 pages long.
• detailed instructions from a supervisor science experiment For example:
about a familiar but complex process • a summary of the main ideas in a text
Getting Things Done Getting Things Done Getting Things Done Getting Things Done
■ Understand communication intended to ■ Propose or recommend solutions to ■ Locate, integrate, and use 3 or 4 pieces ■ Write for many purposes to communicate
influence or persuade. problems in familiar areas. of information from formatted texts. at work, with businesses, or with places
For example: For example: For example: providing a service.
• warnings about door-to-door • respond to a customer complaint, • an online financial table which indicates For example:
salespeople and suggestions for the providing various suggestions to the amount that a person is eligible to • a report documenting work done
best ways to deal with them resolve it receive, or needs to pay • a memo indicating a problem
• public announcements containing ■ Get information from business • a letter requesting a change
extended warnings and service texts containing proposals, ■ Complete and provide written responses
recommendations recommendations and statements of
rules, regulations, and policies. in a range of detailed forms with over 40
For example: items.
• an organization’s declaration of rights For example:
and responsibilities • lengthy paper-based or online job
application forms
Comprehending Information Sharing Information Comprehending Information Sharing Information
■ Understand group interactions about ■ Give detailed information one-on-one ■ Understand extended descriptions, ■ Write 3-4 connected paragraphs to discuss
abstract and complex ideas on familiar and in small group discussions or feature articles, reports, and narrations. a historical event, provide a detailed
topics. meetings. For example: description of a phenonemon, explain
For example: For example: • letters to the editor expressing opinions a procedure, or express and analyze
• discussion about controversial social • participate in a performance review with about a controversial issue opinions on a familiar abstract topic.
issues in a class debate an employer ■ Interpret and use information in charts, For example:
■ Understand informal or semi-formal ■ Give presentations (up to about 20 diagrams, tables, graphs, and flow charts. • an essay for an entrance exam to a
presentations up to about 20 minutes minutes long) on familiar, concrete, or For example: post-secondary institution
long. abstract topics based on research. • a patient health status chart for nurses ■ Write 1 paragraph to explain information
For example: For example: ■ Access and use several pieces of presented in a table, graph, flow chart or
• presentations in workplace or • research and present on a political information from different online reference diagram.
community meetings process for a course sources. For example:
For example: • a paragraph describing information in a
• information on the Statistics Canada statistical table listing average incomes
website of Canadians by family type
© 2017 Centre for Canadian Language Benchmarks - The Can Do Statement Posters are intended to help learners understand the Canadian Language Benchmark levels; they are not intended for assessment purposes. For further
details on the Canadian Language Benchmarks, consult the CLB document, available online at www.language.ca. The Can Do Statements were developed with support from the Province of Manitoba and the Government of Canada.
!The Can Do Statement Posters (based on the Can Do Statements) were developed with support from the Ministry of Citizenship and Immigration, Ontario.
no reviews yet
Please Login to review.