193x Filetype PDF File size 2.44 MB Source: assets.press.princeton.edu
Copyrighted Material
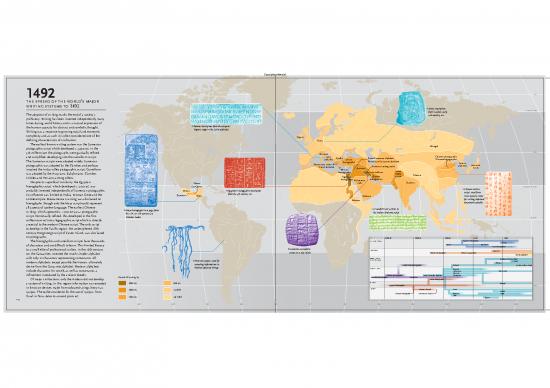
1492 75°
the spread of the world’s major
writing systems to 1492 Runic inscription
from Sweden, early Arctic Circle
The adoption of writing marks the end of a society’s 11th century ad.
prehistory. Writing has been invented independently many
times during world history and is a natural expression of
the human capacity for abstract and symbolic thought. Roman inscription from the emperor
Writing was a response to growing social and economic Trajan’s reign in the Latin alphabet.
complexity and as such it is often considered one of the Ogam
defining characteristics of civilization. Runic
The earliest known writing system was the Sumerian Mongol
pictographic script which developed c. 3400 bc. In the
3rd millennium the pictographs were gradually refined Etruscan 45°
and simplified, developing into the cuneiform script. Latin Cyrillic Proto-Canaanite alphabet Chinese pictographic
The Sumerian scripts were adopted widely. Sumerian alphabet Luvian Phoenician-Canaanite alphabet Chinese logographic
hieroglyphic Korean
pictographic was adopted by the Elamites and perhaps Mycenaean Linear B Sumerian pictographic alphabet Japanese
Greek alphabet Aramaic script
inspired the Indus valley pictographic script. Cuneiform Minoan Indus
was adopted by the Assyrians, Babylonians, Elamites hieroglyphic Cuneiform Valley
Egyptian Elamite script Tibetan
Hittites and Persians among others. hieroglyphic Nabataean pictographic
Despite its superficial similarity, the Egyptian Olmec Kufic Brahmic
hieroglyphic script, which developed c. 3100 bc, was Epi-Olmec Tropic of Cancer
probably invented independently of Sumerian pictographic. Mixtec Egyptian hieroglyphic inscription Chinese cursive
Its influence was limited to Nubia, Minoan Crete and the from the 4th century bc. script, used from
Zapotec Maya Sabaean Han dynasty times
Hittite empire. Mesoamerican writing was also based on Ethiopic for writing informal
hieroglyphs, though only the Maya script could represent documents quickly.
all aspects of spoken language. The earliest Chinese A Sanskrit text written in
writing, which appeared c. 1200 bc was a pictographic Maya hieroglyphs in a page from the Indian Brahmic script.
script. Continually refined, this developed in the first the 11th- or 12th-century ad
Dresden Codex. Equator
millennium bc into a logographic script which is directly
ancestral to the modern Chinese script. The only script
to develop in the Pacific region, the undeciphered 18th-
century Rongorongo script of Easter Island, was also based
on pictographs. 3000 Bc 2000 Bc 1000 Bc aD 1 1000
The hieroglyphic and cuneiform scripts have thousands THE AMERICAS Zapotec hieroglyphic
Mixtec
of characters and are difficult to learn. This limited literacy Olmec Epi-Olmec
Maya hieroglyphic
to a small elite of professional scribes. In the 16th century Sumerian cuneiform EAST ASIA Japanese
bc, the Canaanites invented the much simpler alphabet script on a clay tablet. Chinese pictographic Chinese logographic
Korean alphabet
with only 22 characters representing consonants. All SOUTH AND Southeast Asian scripts
Peruvian quipu, used for CENTRAL ASIA Mongol
modern alphabets, except possibly the Korean, ultimately encoding information in Tibetan
derive from the Canaanite alphabet. Western alphabets Indus Valley pictographic Brahmic Modern Indian scripts
knotted coloured strings. MIDDLE EAST Aramaic
include characters for vowels as well as consonants, a Nabataean Kufic Arabic
Sabaean
refinement introduced by the ancient Greeks. Elamite pictographic Proto-Canaanite alphabet Phoenician
Spread of writing by: Sumerian pictographic Cuneiform
Of major civilizations, only the Andean did not develop Luvian hieroglyphic
a system of writing. In this region information was encoded 3000 BC 500 BC AFRICA Ethiopic
in knots on devices made from coloured strings known as Egyptian hieroglyphic 45°
2000 EUROPE Minoan Linear A Greek
BC AD
quipus. The earliest evidence for the use of quipus, from 500 Cyrillic
Minoan hieroglyphic Mycenaean Linear B Etruscan Runic
Caral in Peru, dates to around 3000 bc. 1250 BC AD 1492 Latin
114 Ogam
150° 120° 90° 60° 30° 0° 30° 60° 90° 120°
150° 180°
no reviews yet
Please Login to review.